ASTM E3340-22
(Guide)Standard Guide for Development of Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analysis Methods for Powder Materials
Standard Guide for Development of Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analysis Methods for Powder Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The technique of laser diffraction for particle size distribution analysis is extensively used in industry and academia both for on-line control and laboratory needs. Guidance is obviously useful in this regard.
5.2 This guide can be used to develop methods of particle size analysis where well-established analysis procedures do not already exist. See Guide B821 for similar guidance and useful procedures for wet dispersion of metal powders and related compounds.
SCOPE
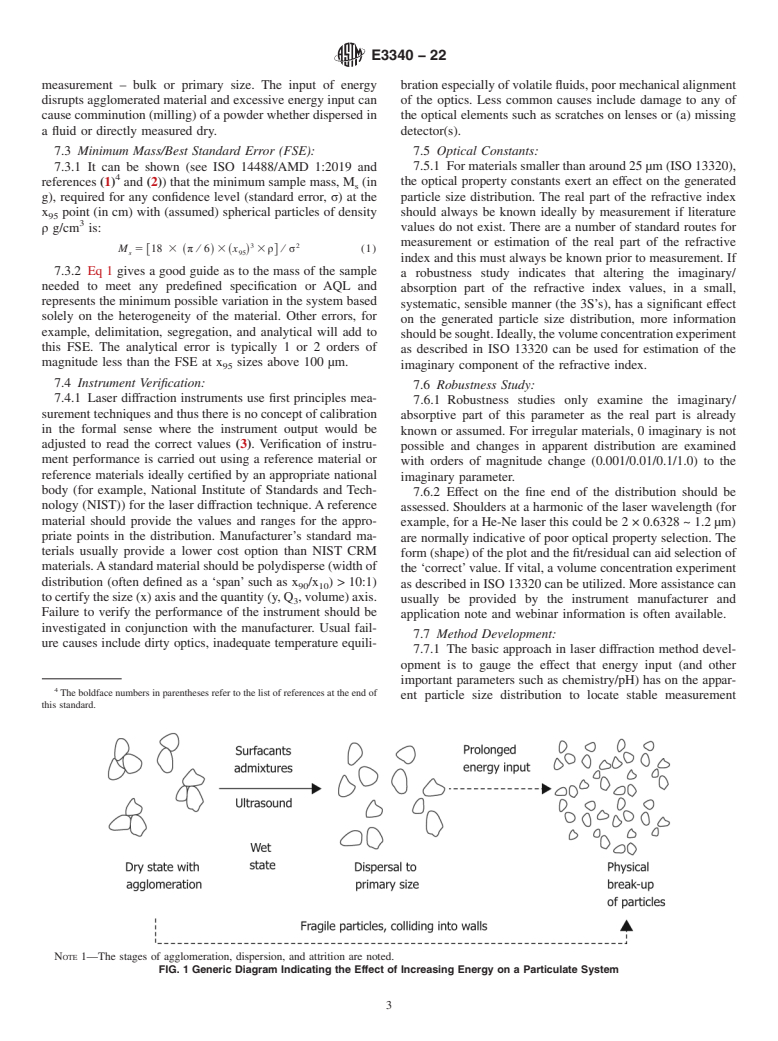
1.1 This guide sets out the general approach to the particle size distribution measurement of powders, suspensions, or slurries using an appropriate wet or dry methodology by the laser diffraction technique. It is recommended for use in measurements of broad particle size distributions.
1.2 The guide provides guidelines to the parameters that should be specified and a generalized guideline to reasonable and acceptable tolerances for points in the volume-based distribution curve such as x10 (Dv10), x50 (Dv50), x90 (Dv90), and D[4, 3] (volume moment mean). It is noted that ISO prefers the term x for particle size as opposed to other usage of d or D (implying diameter).
1.3 This guide provides guidance on the verification of instrument performance in conjunction with the internal quality control (QC) audit functions of the instrument owner. Results should be reported in the format indicated by Practice E1617 and ISO 13320.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E3340 − 22
Standard Guide for
Development of Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analysis
1
Methods for Powder Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E3340; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This guide sets out the general approach to the particle 2.1 ASTM Standards:
size distribution measurement of powders, suspensions, or B821Guide for Liquid Dispersion of Metal Powders and
slurries using an appropriate wet or dry methodology by the Related Compounds for Particle Size Analysis
laser diffraction technique. It is recommended for use in E1617Practice for Reporting Particle Size Characterization
measurements of broad particle size distributions. Data
E2490Guide for Measurement of Particle Size Distribution
1.2 The guide provides guidelines to the parameters that
of Nanomaterials in Suspension by Photon Correlation
should be specified and a generalized guideline to reasonable
Spectroscopy (PCS)
and acceptable tolerances for points in the volume-based
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
distribution curve such as x (D 10), x (D 50), x (D 90),
10 v 50 v 90 v
ISO 13320Particle size analysis — Laser diffraction meth-
and D[4, 3] (volume moment mean). It is noted that ISO
ods
prefersthetermxforparticlesizeasopposedtootherusageof
ISO14887Samplepreparation—Dispersingproceduresfor
d or D (implying diameter).
powders in liquids
1.3 This guide provides guidance on the verification of
ISO 14488/AMD 1:2019Particulate materials — Sampling
instrumentperformanceinconjunctionwiththeinternalquality
and sample splitting for the determination of particulate
control (QC) audit functions of the instrument owner. Results
properties
should be reported in the format indicated by Practice E1617
and ISO 13320. 3. Terminology
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
3.1 Definitions:
asstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthis 3.1.1 Some of the definitions in 3.2 will differ slightly from
standard.
those used within other (non-particle sizing) standards. For
further details, see the Terminology section of Guide E2490.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.1 differential pressure (∆P), n—the pressure difference
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
acrossaventurithatcausesacceleration(andthusshearforces)
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
leading to dispersion (and possibly attrition) in a dry laser
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
diffraction measurement.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2.2 laser diffraction, n—light scattering technique primar-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
ily used for particle size distribution analysis, applicable to the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
approximate range 0.1 – 3000 µm, where multiple angles are
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E29 on Particle and Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Spray Characterization and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E29.02 on the ASTM website.
3
Non-Sieving Methods. Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
Current edition approved March 1, 2022. Published April 2022. DOI: 10.1520/ Central Secretariat, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier, Geneva,
E3340-22. Switzerland, https://www.iso.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E3340 − 22
usedtoanalyzethe(laserlight)scatteringfromanensembleof already exist. See Guide B821 for similar guidance and useful
particles in liquid or dry suspension. See ISO 13320. procedures for wet dispersion of metal powders and related
compounds.
3.2.3 method development, n—in laser diffraction, this re-
fers to the actions involved in understanding how e
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.