ASTM E2736-17
(Guide)Standard Guide for Digital Detector Array Radiography
Standard Guide for Digital Detector Array Radiography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
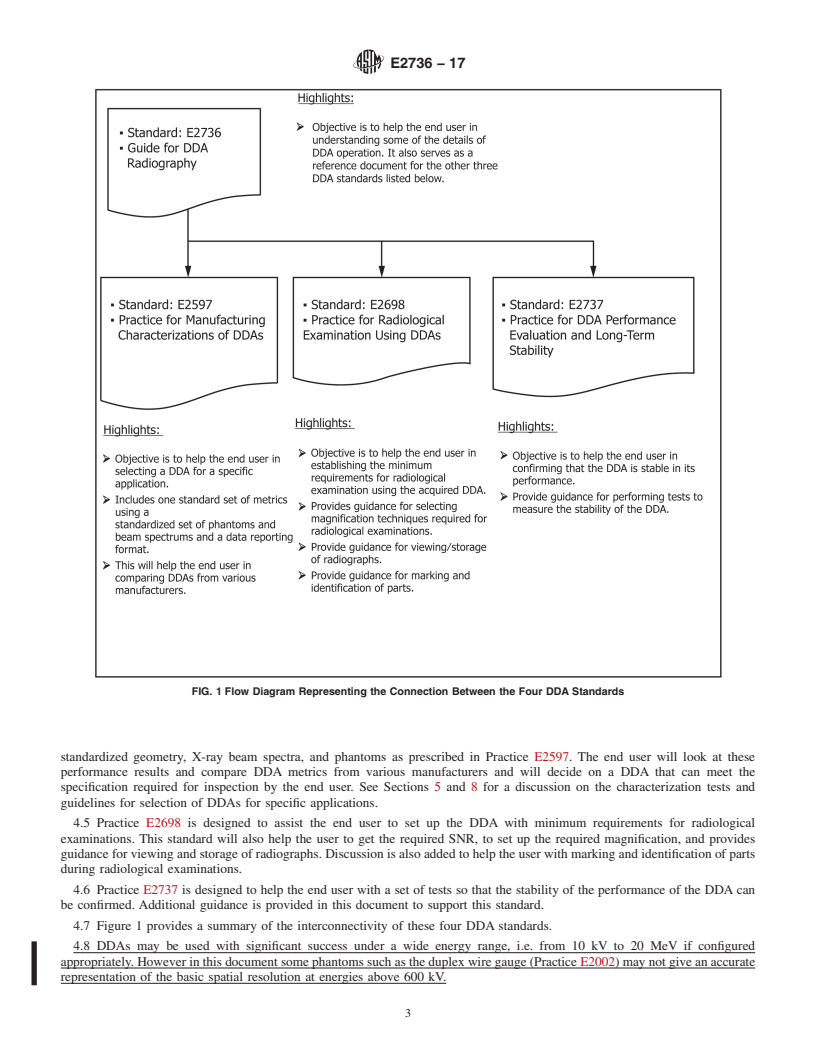
4.1 This standard provides a guide for the other DDA standards (see Practices E2597, E2698, and E2737). It is not intended for use with computed radiography apparatus. Figure 1 describes how this standard is interrelated with the aforementioned standards.
FIG. 1 Flow Diagram Representing the Connection Between the Four DDA Standards
4.2 This guide is intended to assist the user to understand the definitions and corresponding performance parameters used in related standards as stated in 4.1 in order to make an informed decision on how a given DDA can be used in the target application.
4.3 This guide is also intended to assist cognizant engineering officers, prime manufacturers, and the general service and manufacturing customer base that may rely on DDAs to provide advanced radiological results so that these parties may set their own acceptance criteria for use of these DDAs by suppliers and shops to verify that their parts and structures are of sound integrity to enter into service.
4.4 The manufacturer characterization standard for DDA (see Practice E2597) serves as a starting point for the end user to select a DDA for the specific application at hand. DDA manufacturers and system integrators will provide DDA performance data using standardized geometry, X-ray beam spectra, and phantoms as prescribed in Practice E2597. The end user will look at these performance results and compare DDA metrics from various manufacturers and will decide on a DDA that can meet the specification required for inspection by the end user. See Sections 5 and 8 for a discussion on the characterization tests and guidelines for selection of DDAs for specific applications.
4.5 Practice E2698 is designed to assist the end user to set up the DDA with minimum requirements for radiological examinations. This standard will also help the user to get the required SNR, to set up the required magnification, and provides guidance for viewing and storage of radiographs. Discussion is also...
SCOPE
1.1 This standard is a user guide, which is intended to serve as a tutorial for selection and use of various digital detector array systems nominally composed of the detector array and an imaging system to perform digital radiography. This guide also serves as an in-detail reference for the following standards: Practices E2597, E2698, and E2737.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E2736 − 17
Standard Guide for
1
Digital Detector Array Radiography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2736; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope amination by Using Representative Quality Indicators
(RQIs)
1.1 This standard is a user guide, which is intended to serve
E2002Practice for Determining Total Image Unsharpness
as a tutorial for selection and use of various digital detector
and Basic Spatial Resolution in Radiography and Radios-
arraysystemsnominallycomposedofthedetectorarrayandan
copy
imagingsystemtoperformdigitalradiography.Thisguidealso
E2422Digital Reference Images for Inspection of Alumi-
serves as an in-detail reference for the following standards:
num Castings
Practices E2597, E2698, and E2737.
E2445Practice for Performance Evaluation and Long-Term
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Stability of Computed Radiography Systems
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
E2446Practice for Manufacturing Characterization of Com-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
puted Radiography Systems
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
E2597Practice for Manufacturing Characterization of Digi-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tal Detector Arrays
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
E2660Digital Reference Images for Investment Steel Cast-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ings for Aerospace Applications
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
E2669Digital Reference Images for Titanium Castings
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
E2698Practice for Radiological Examination Using Digital
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Detector Arrays
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
E2737Practice for Digital Detector Array Performance
Evaluation and Long-Term Stability
2. Referenced Documents 3
2.2 ISO Document:
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: ISO 17636-2 Non-Destructive Testing of Welds—
E94Guide for Radiographic Examination Using Industrial Radiographic Testing - Part 2: X- and Gamma-Ray Tech-
Radiographic Film niques with Digital Detector
E155Reference Radiographs for Inspection of Aluminum
3. Terminology
and Magnesium Castings
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
E192Reference Radiographs of Investment Steel Castings
3.1.1 achievable contrast sensitivity (CSa)—best contrast
for Aerospace Applications
sensitivity (see Terminology E1316 for a definition of contrast
E1000Guide for Radioscopy
E1316Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations sensitivity)obtainableusingastandardphantomwithanX-ray
technique that has little contribution from scatter.
E1320Reference Radiographs for Titanium Castings
E1815Test Method for Classification of Film Systems for
3.1.2 bad pixel—a bad pixel is a pixel identified with a
Industrial Radiography
performance outside of the specification for a pixel of a DDA
E1817Practice for Controlling Quality of Radiological Ex-
as defined in Practice E2597.
3.1.3 burn-in—change in gain of the scintillator or photo-
conductor that persists well beyond the exposure.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nondestruc-
3.1.4 effıciency—SNR (see 3.1.6 of Practice E2597) di-
n
tive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.01 on Radiology
vided by the square root of the dose (in mGy) and is used to
(X and Gamma) Method.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017. Published February 2018. Originally
measuretheresponseofthedetectoratdifferentbeamenergies
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as E2736–10. DOI:
and qualities.
10.1520/E2736-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier,
the ASTM website. Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2736 − 17
3.1.5 grooved wedge—awedgewithonegroove,thatis5% 3.1.10 specific material thickness range (SMTR)—material
of the base material thickness and that is used for achievable thickness range within which a given image quality is
con
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2736 − 10 E2736 − 17
Standard Guide for
1
Digital Detector Array RadiologyRadiography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2736; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This standard is a user guide, which is intended to serve as a tutorial for selection and use of various digital detector array
systems nominally composed of the detector array and an imaging system to perform digital radiography. This guide also serves
as an in-detail reference for the following standards: Practices E2597, E2698, and E2737.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E94 Guide for Radiographic Examination Using Industrial Radiographic Film
E155 Reference Radiographs for Inspection of Aluminum and Magnesium Castings
E192 Reference Radiographs of Investment Steel Castings for Aerospace Applications
E747 Practice for Design, Manufacture and Material Grouping Classification of Wire Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used for
Radiology
E1000 Guide for Radioscopy
E1025 Practice for Design, Manufacture, and Material Grouping Classification of Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI)
Used for Radiology
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
E1320 Reference Radiographs for Titanium Castings
E1742 Practice for Radiographic Examination
E1815 Test Method for Classification of Film Systems for Industrial Radiography
E1817 Practice for Controlling Quality of Radiological Examination by Using Representative Quality Indicators (RQIs)
E2002 Practice for Determining Total Image Unsharpness and Basic Spatial Resolution in Radiography and Radioscopy
E2422 Digital Reference Images for Inspection of Aluminum Castings
E2445 Practice for Performance Evaluation and Long-Term Stability of Computed Radiography Systems
E2446 Practice for Manufacturing Characterization of Computed Radiography Systems
E2597 Practice for Manufacturing Characterization of Digital Detector Arrays
E2660 Digital Reference Images for Investment Steel Castings for Aerospace Applications
E2669 Digital Reference Images for Titanium Castings
E2698 Practice for Radiological Examination Using Digital Detector Arrays
E2737 Practice for Digital Detector Array Performance Evaluation and Long-Term Stability
3
2.2 ISO Document:
ISO 17636-2 Non-Destructive Testing of Welds—Radiographic Testing - Part 2: X- and Gamma-Ray Techniques with Digital
Detector
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.01 on Radiology (X and
Gamma) Method.
Current edition approved April 15, 2010Dec. 1, 2017. Published July 2010February 2018. Originally approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as
E2736 – 10. DOI: 10.1520/E2736-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier, Geneva,
Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2736 − 17
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 digital detector array (DDA) system—an electronic device that converts ionizing or penetrating radiation into a discrete
array of analog signals which are subsequently digitized and transferred to a computer for display as a digi
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.