ASTM B599-92(2003)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Nickel-Iron-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Stabilized Alloy (UNS N08700) Plate, Sheet, and Strip
Standard Specification for Nickel-Iron-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Stabilized Alloy (UNS N08700) Plate, Sheet, and Strip
ABSTRACT
This specification covers nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-columbium stabilized alloy (UNS N08700) plate, sheet, and strip in the solution-annealed condition. Minor cold working such as flattening or temper rolling may be performed after the final solution annealing treatment. The material shall conform to the chemical requirements for nickel, iron, chromium, molybdenum, columbium, carbon, silicon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, and copper. The material shall conform to the mechanical property requirements for tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and Rockwell hardness. The material shall be free of injurious imperfections and shall correspond to the designated finish for sheet, strip, and plate. Test methods (chemical analysis, tension test, corrosion test) for chemical composition and mechanical properties determination shall be performed in accordance to referenced ASTM documents itemized herein.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers nickel-iron-chromiummolydenum-columbium stabilized alloy (UNS N08700)* plate, sheet, and strip in the solution-annealed condition.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: B 599 – 92 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Specification for
Nickel-Iron-Chromium-Molybdenum-Columbium Stabilized
Alloy (UNS N08700) Plate, Sheet, and Strip
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 599; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—Keywords were added editorially in November 2003.
1. Scope E55 PracticeforSamplingWroughtNonferrousMetalsand
Alloys for Determination of Chemical Composition
1.1 This specification covers nickel-iron-
E 140 HardnessConversionTablesforMetals(Relationship
chromiummolydenum-columbium stabilized alloy (UNS
Between Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
N08700)* plate, sheet, and strip in the solution-annealed
Hardness, Rockwell Superficial Hardness, and Knoop
condition.
Hardness)
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
E 350 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Carbon
as the standard.
Steel, Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron,
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and Wrought Iron
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
E 353 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Stainless,
responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar
Heat-Resisting, Maraging, and Other Similar Chromium-
with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate
Nickel-Iron Alloys
Material Safety Data Sheet for this product/material as pro-
vided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and
3. Terminology
health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
limitations prior to use.
3.1.1 The terms plate, sheet, and strip as used in this
2. Referenced Documents specification are described as follows:
3.1.1.1 plate—material 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) and over in
2.1 ASTM Standards:
thickness and over 10 in. (254 mm) in width.
A 262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranu-
3.1.1.2 sheet—material under 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) in
lar Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
thickness and over 24 in. (610 mm) in width.
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
3.1.1.3 strip—material under 0.1875 in. (4.76 mm) in thick-
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materi-
ness and under 24 in. (610 mm) in width.
als
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
4. Ordering Information
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials
4.1 Orders for material under this specification should
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
include the following information:
Determine Conformance with Specifications
4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces).
4.1.2 Name of material or UNS N08700.
4.1.3 Form (plate, sheet, or strip).
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on
4.1.4 Dimensions.
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
4.1.5 Type of edge required (for strip only, see 9.4).
Current edition approved November 1, 2003. Published November 2003.
4.1.6 Finish (Section 10)—For sheet ordered with No. 4
Originally approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 1992 as
finish, specify whether one or both sides are to be polished.
B 599 – 92 (1997).
4.1.7 ASTM designation and year of issue.
* New designation established in accordance withASTM E 527 and SAE J1086,
Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS).
4.1.8 Corrosion Test— State if intergranular corrosion test
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
is required (Section 8).
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.1.9 Marking—State if metal die identification is required
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. on plate ⁄4 in. (6.35 mm) or thicker (Section 17).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
´1
B 599 – 92 (2003)
TABLE 2 Product (Check) Analysis
4.1.10 Certification or Test Reports—Stateifcertificationor
test reports are required (Section 16). Tolerances Over the Maximum
Element Limit or Under the Minimum
Limit, %
5. Materials and Manufacture
Nickel 0.20
5.1 Heat Treatment— The final heat treatment shall be a
Chromium 0.20
solution anneal. Minor cold working such as flattening or Molybdenum 0.10
Columbium 0.05
temper rolling may be performed after the final solution
Carbon 0.01
annealing treatment.
Silicon 0.05
Manganese 0.04
NOTE 1—This recommended solution anneal consists of heating to a
Phosphorus 0.005
minimum temperature of 2000°F (1090°C) and cooling rapidly to room
Sulfur 0.005
temperature.
Copper 0.03
6. Chemical Composition
9.4.1 The various types of edges procurable shall be as
6.1 The material sampled, in accordance with 11.2, shall
follows:
conform to the composition limits prescribed in Table 1.
9.4.1.1 No. 1 Edge—Rolled edge, contour as specified.
6.2 If a product analysis is subsequently made, the material
9.4.1.2 No. 3 Edge—An edge produced by slitting.
shall conform to the composition limits with the product
9.4.1.3 No. 5 Edge—Approximately square edge produced
analysis variation prescribed in Table 2.
by rolling or filing, or both, after slitting.
7. Mechanical Requirements Mechanical Requirements
10. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
7.1 The material shall conform to the requirements as to the
10.1 The material shall be free of injurious imperfections
mechanical property prescribed in Table 3.
and shall correspond to the designated finish as described as
follows:
8. Intergranular Corrosion Test
10.1.1 Sheet—The various types of finish procurable on
8.1 All material supplied to this specification shall be
sheet products shall be as follows:
capable of passing the intergranular corrosion test, but the test
10.1.1.1 No. 1 Finish— Hot rolled, annealed, and descaled;
need not be performed on any given lot unless it is specified on
produced by hot rolling to specified thicknesses followed by
the purchase order. If the test is specified, it shall be performed
annealing and descaling (see 10.2).
by the manufacturer on specimens taken in the as-shipped
10.1.1.2 No. 2D Finish— Dull, cold-rolled finish; produced
condition. Specimens shall be tested in the sensitized condition
by cold rolling to the specified thickness, annealing, and
(1hat1250°F(677°C)),andtestedinaccordancewithPractice
descaling. The dull finish results from the descaling and
C of Practices A 262. The corrosion rate shall not exceed 2.5
pickling operations.
mils/month (165 mg/dm ·day).
10.1.1.3 No. 2B Finish— Bright, cold-rolled finish; pro-
duced by giving a final light cold-rolled pass with polished
9. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
rolls, to a sheet that has been annealed and descaled.
9.1 Sheet—The material referred to as sheet shall conform
10.1.1.4 No. 4 Finish— General-purpose polished finish.
to the variations in dimensions prescribed in Tables 4-9,
Following initial grinding with coarser abrasives, sheets are
inclusive.
generallyfinishedlastwithabrasivesapproximately120to150
9.2 Cold-Rolled Strip—The material referred to as cold-
mesh. Sheets can be produced with one or two sides polished.
rolled strip shall conform to the permissible variations in
When polished on one side only, the other side may be rough
dimensions prescribed in Tables 10-13, inclusive.
ground in order to obtain the necessary flatness.
9.3 Plate—Thematerialreferredtoasplateshallconformto
10.1.1.5 Bright Annealed— Bright finish produced by cold
the permissible variations in dimensions prescribed in Tables
rolling to thickness, then annealing in a protective atmosphere.
14-19, inclusive.
10.1.2 Strip—The type of finish procurable on cold-rolled
9.4 Edges for Cold-Rolled Strip:
strip shall be as follows:
10.1.2.1 No. 1 Finish— Cold rolled to specified thickness,
annealed, and pickled (see 10.2).Appearance of this finish is a
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
dull gray.
Element Composition, %
10.1.2.2 No. 2 Finish— Same as No. 1 finish, followed by
Nickel 24.0–26.0
A afinallightcold-rolledpass,generallyonhighlypolishedrolls.
Iron remainder
Chromium 19.0–23.0
10.1.2.3 Bright Annealed— Bright finish produced by cold
Molybdenum 4.3–5.0
rolling to thickness, then annealing in a protective atmosphere.
Columbium 8 3 carbon to 0.40
10.1.3 Plate—The types of finish procurable on plates shall
Carbon, max 0.04
Silicon, max 1.00
be as follows:
Manganese, max 2.00
10.1.3.1 Hot- or Cold-Rolled, Annealed—Scale not re-
Phosphorus, max 0.040
moved (see 10.2).
Sulfur, max 0.030
Copper, max 0.50
10.1.3.2 Hot- or Cold-Rolled, Annealed, Descaled—Scale
A
Determined arithmetically by difference. removed by a blast cleaning or pickling operation (see 10.2).
´1
B 599 – 92 (2003)
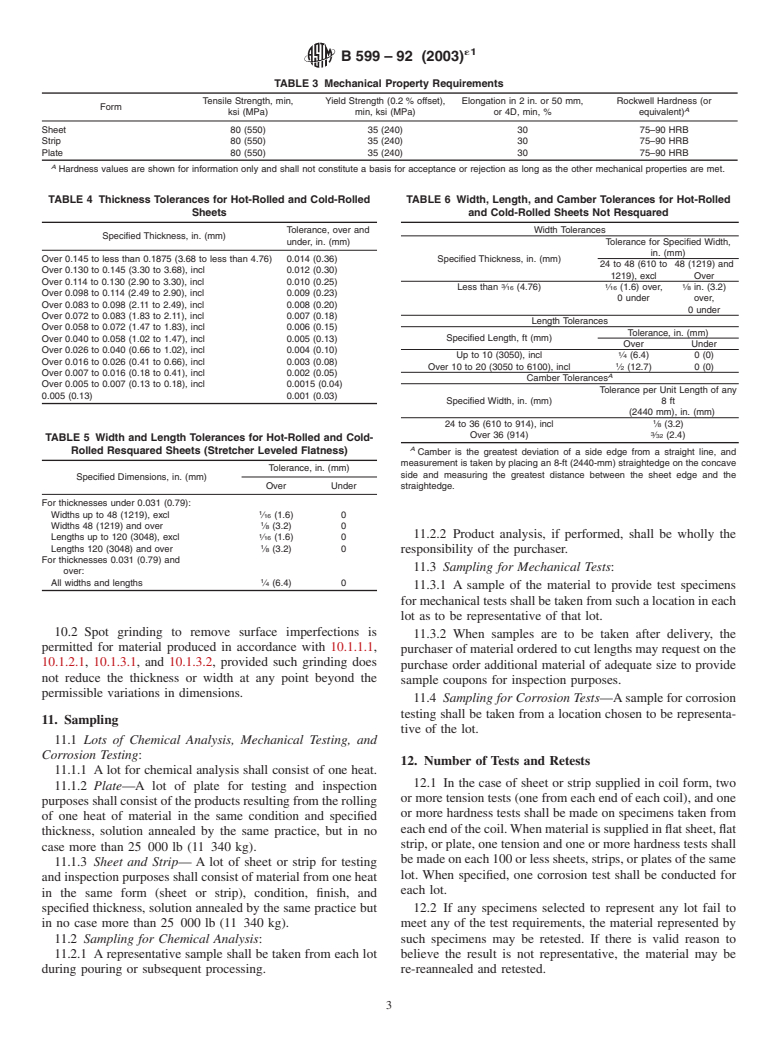
TABLE 3 Mechanical Property Requirements
Tensile Strength, min, Yield Strength (0.2 % offset), Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, Rockwell Hardness (or
Form
A
ksi (MPa) min, ksi (MPa) or 4D, min, % equivalent)
Sheet 80 (550) 35 (240) 30 75–90 HRB
Strip 80 (550) 35 (240) 30 75–90 HRB
Plate 80 (550) 35 (240) 30 75–90 HRB
A
Hardness values are shown for information only and shall not constitute a basis for acceptance or rejection as long as the other mechanical properties are met.
TABLE 4 Thickness Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled TABLE 6 Width, Length, and Camber Tolerances for Hot-Rolled
Sheets and Cold-Rolled Sheets Not Resquared
Tolerance, over and Width Tolerances
Specified Thickness, in. (mm)
under, in. (mm) Tolerance for Specified Width,
in. (mm)
Over 0.145 to less than 0.1875 (3.68 to less than 4.76) 0.014 (0.36) Specified Thickness, in. (mm)
24 to 48 (610 to 48 (1219) and
Over 0.130 to 0.145 (3.30 to 3.68), incl 0.012 (0.30)
1219), excl Over
Over 0.114 to 0.130 (2.90 to 3.30), incl 0.010 (0.25)
3 1 1
Less than ⁄16 (4.76) ⁄16 (1.6) over, ⁄8 in. (3.2)
Over 0.098 to 0.114 (2.49 to 2.90), incl 0.009 (0.23)
0 under over,
Over 0.083 to 0.098 (2.11 to 2.49), incl 0.008 (0.20)
0 under
Over 0.072 to 0.083 (1.83 to 2.11), incl 0.007 (0.18)
Length Tolerances
Over 0.058 to 0.072 (1.47 to 1.83), incl 0.006 (0.15)
Tolerance, in. (mm)
Over 0.040 to 0.058 (1.02 to 1.47), incl 0.005 (0.13) Specified Length, ft (mm)
Over Under
Over 0.026 to 0.040 (0.66 to 1.02), incl 0.004 (0.10)
Up to 10 (3050), incl ⁄4 (6.4) 0 (0)
Over 0.016 to 0.026 (0.41 to 0.66), incl 0.003 (0.08)
Over 10 to 20 (3050 to 6100), incl ⁄2 (12.7) 0 (0)
Over 0.007 to 0.016 (0.18 to 0.41), incl 0.002 (0.05)
A
Camber Tolerances
Over 0.005 to 0.007 (0.13 to 0.18), incl 0.0015 (0.04)
Tolerance per Unit Length of any
0.005 (0.13) 0.001 (0.03)
Specified Width, in. (mm) 8ft
(2440 mm), in. (mm)
24 to 36 (610 to 914), incl ⁄8 (3.2)
Over 36 (914) ⁄32 (2.4)
TABLE 5 Width and Length Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-
A
Rolled Resquared Sheets (Stretcher Leveled Flatness) Camber is the greatest deviation of a side edge from a straight line, and
measurement is taken by placing an 8-ft (2440-mm) straightedge on the concave
Tolerance, in. (mm)
side and measuring the greatest distance between the sheet edge and the
Specified Dimensions, in. (mm)
Over Under straightedge.
For thicknesses under 0.031 (0.79):
Widths up to 48 (1219), excl ⁄16 (1.6) 0
Widths 48 (1219) and over ⁄8 (3.2) 0
1 11.2.2 Product analysis, if performed, shall be wholly the
Lengths up to 120 (3048), excl ⁄16 (1.6) 0
Lengths 120 (3048) and over ⁄8 (3.2) 0
responsibility of the purchaser.
For thicknesses 0.031 (0.79) and
11.3 Sampling for Mechanical Tests:
over:
All widths and lengths ⁄4 (6.4) 0
11.3.1 A sample of the material to provide test specimens
for mechanical tests shall be taken from such a location in each
lot as to be representative of that lot.
10.2 Spot grinding to remove surface imperfections is
11.3.2 When samples are to be taken after delivery, the
permitted for material produced in accordance with 10.1.1.1,
purchaser of material ordered to cut lengths may request on the
10.1.2.1, 10.1.3.1, and 10.1.3.2, provided such grinding does
purchase order additional material of adequate size to provide
not reduce the thickness or width at any point beyond the
sample coupons for inspection purposes.
permissible variations in dimensions.
11.4 Sampling for Corrosion Tests—Asample for corrosion
testing shall be taken from a location chosen to be representa-
11. Sampling
tive of the lot.
11.1 Lots of Chemical Analysis, Mechanical Testing, and
Corrosion Testing:
12. Number of Tests and Retests
11.1.1 A lot for chemical analysis shall consist of one heat.
12.1 In the case of sheet or strip supplied in coil form, two
11.1.2 Plate—A lot of plate for testing and inspection
or more tension tests (one from each end of each coil), and one
purposes shall consist of the products resulting from the rolling
or more hardness tests shall be made on specimens taken from
of one heat of material in the same condition and specified
eachendofthecoil.Whenmaterialissuppliedinflatsheet,flat
thickness, solution annealed by the same practice, but in no
strip, or plate, one tension and one or more hardness tests shall
case more than 25 000 lb (11 340 kg).
bemadeoneach100orlesssheets,strips,orplatesofthesame
11.1.3 Sheet and Strip— A lot of sheet or strip for testing
lot. When specified, one corrosion test shall be conducted for
and inspection purposes shall consist of material from one heat
each lot.
in the same form (sheet or strip), condition, finish, and
specified thickness, solution annealed by the same practice but 12.2 If any specimens selected to represent any lot fail to
in no case more than 25 000 lb (11 340 kg). meet any of the test requirements, the material represented by
11.2 Sampling for Chemical Analysis: such specimens may be retested. If there is valid reason to
11.2.1 A representative sample shall be taken from each lot believe the result is not representative, the material may be
during pouring or subsequent processing. re-reannealed and retested.
´1
B 599 – 92 (2003)
TABLE 7 Flatness Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Sheets
Sheets not Specified to Stretcher Leveled Standard of Flatness
Flatness Tolerance (max Deviation from a
Specified Thickness, in. (mm) Width, in. (mm)
Horizontal Flat Surface), in. (mm)
0.062 (1.57) and over to 60 (1524), incl ⁄2 (12.7)
over 60 to 72 (1524 to ⁄4 (19.1)
1829), incl
over 72 (1829) 1 (25.4)
Under 0.062 (1.57) to 36 (914), incl ⁄2 (12.7)
over 36 to 60 (914 to ⁄4 (19.1)
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.