ASTM D4554-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for In Situ Determination of Direct Shear Strength of Rock Discontinuities
Standard Test Method for In Situ Determination of Direct Shear Strength of Rock Discontinuities
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of peak and residual direct shear strength of in situ rock discontinuities as a function of stress normal to the sheared plane. This sheared plane is usually a significant discontinuity which may or may not be filled with gouge or soil-like material.
1.2 The measured shear properties are affected by scale factors. The severity of the effect of these factors must be assessed and applied to the specific problems on an individual basis.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4554–02
Standard Test Method for
In Situ Determination of Direct Shear Strength of Rock
1
Discontinuities
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4554; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope * 3.2.2 peak shear strength—the maximum shear stress in the
complete curve of stress versus displacement obtained for a
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of peak and
specified constant normal stress.
residual direct shear strength of in situ rock discontinuities as
3.2.3 residual shear strength—the shear stress at which
a function of stress normal to the sheared plane. This sheared
nominally no further rise or fall in shear strength is observed
plane is usually a significant discontinuity which may or may
with increasing shear displacement and constant normal stress
not be filled with gouge or soil-like material.
(Fig. 1). A true residual strength may only be reached after
1.2 The measured shear properties are affected by scale
considerably greater shear displacement than can be achieved
factors. The severity of the effect of these factors must be
in testing. The test value should be regarded as approximate
assessed and applied to the specific problems on an individual
and should be assessed in relation to the complete shear stress
basis.
- displacement curve.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
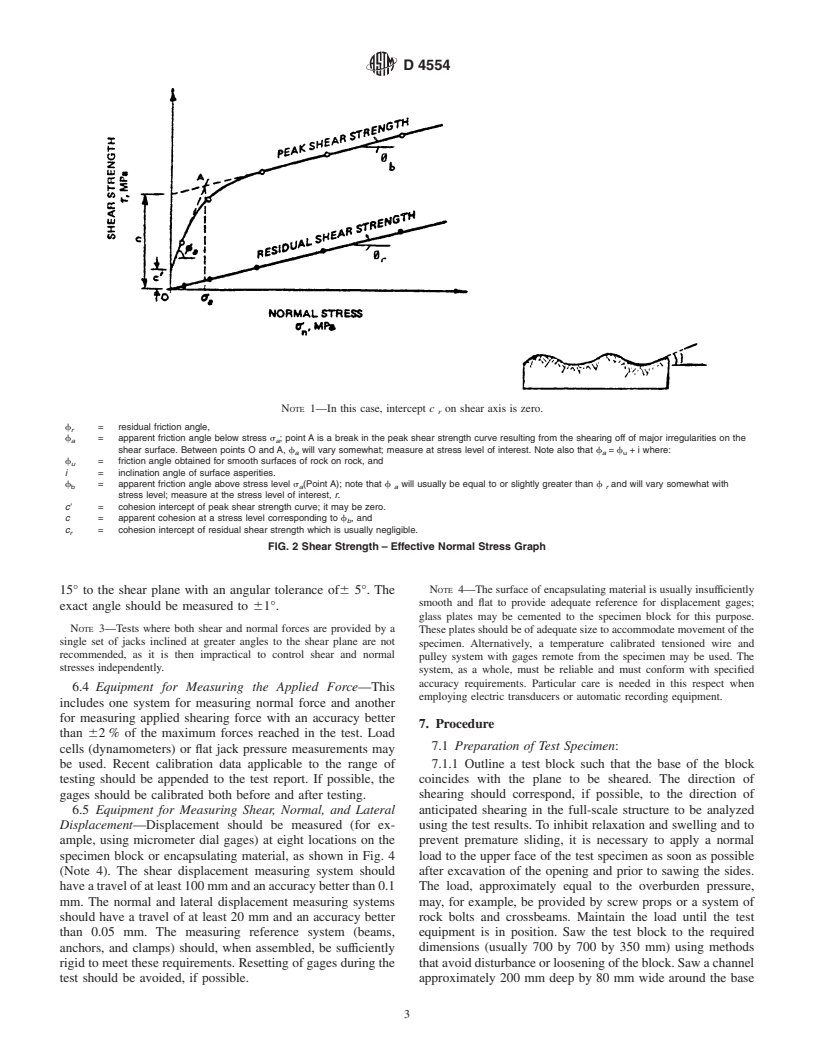
3.2.4 shear strength parameter, c(seeFig.2)—theprojected
standard.
intercept on the shear stress axis of the plot of shear stress
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
versus normal stress (see Note).
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.5 shear strength parameter, f (see Fig. 2)—the angle of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the tangent to the failure curve at a normal stress that is
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
relevant to design.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.2.5.1 Discussion—Different values of c and f relate to
2. Referenced Documents
different stages of a test (for example, c8, c 8, f , and f,of
r a b
Fig. 2).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
4. Summary of Test Method
2
Fluids
4.1 This test method is performed on rectangular-shaped
D 3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
blocks of rock that are isolated on all surfaces, except for the
Engaged in the Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock
2
shear plane surface.
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
4.2 The blocks are not to be disturbed during preparation
3. Terminology
operations.Thebaseoftheblockcoincideswiththeplanetobe
sheared.
3.1 Definitions: See Terminology D 653 for general defini-
4.3 A normal load is applied perpendicular to the shear
tions.
plane and then a side load is applied to induce shear along the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
plane and discontinuity (see Fig. 3).
3.2.1 discontinuities—this includes joints, schistosity,
faults, bedding planes, cleavage, and zones of weakness, along
5. Significance and Use
with any filling material.
5.1 Because of scale effects, there is no simple method of
predicting the in situ shear strength of a rock discontinuity
from the results of laboratory tests on small specimens; in situ
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D18 on Soil and
tests on large specimens are the most reliable means.
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.12 on Rock Mechanics.
5.2 Results can be employed in stability analysis of rock
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 2002. Published April 2002. Originally
engineering problems, for example, in studies of slopes,
published as D 4554 – 85. Last previous edition D 4554 – 90.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.08. underground openings, and dam foundations. In applying the
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4554
FIG. 1 Shear Stress–Displacement Graphs
operating characteristics are identically matched and they are in exact
test results, the pore water pressure conditions and the possi-
parallel alignment.
bility of progressive failure must be assessed for the design
case, as they may differ from the test conditions.
6.2.1 Each ram should be provided with a spherical seat.
5.3 Tests on intact rock (free from planes of weakness) are
The travel of rams, and particularly o
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.