ASTM F1378-17
(Specification)Standard Specification for Shoulder Prostheses
Standard Specification for Shoulder Prostheses
ABSTRACT
This specification covers shoulder prostheses for total or hemiarthroplasty used to provide functioning articulation by employing glenoid and humeral components. The prostheses may be constrained, partially constrained, or unconstrained. Modular prostheses are included in this specification, but devices for custom applications are not covered. The prostheses are required to meet the prescribed mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, wear of alternative, and range of motion.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers shoulder prostheses for total or hemiarthroplasty used to provide functioning articulation by employing glenoid and humeral components.
1.2 Devices for custom applications are not covered by this specification. Modular prostheses are included in this specification.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
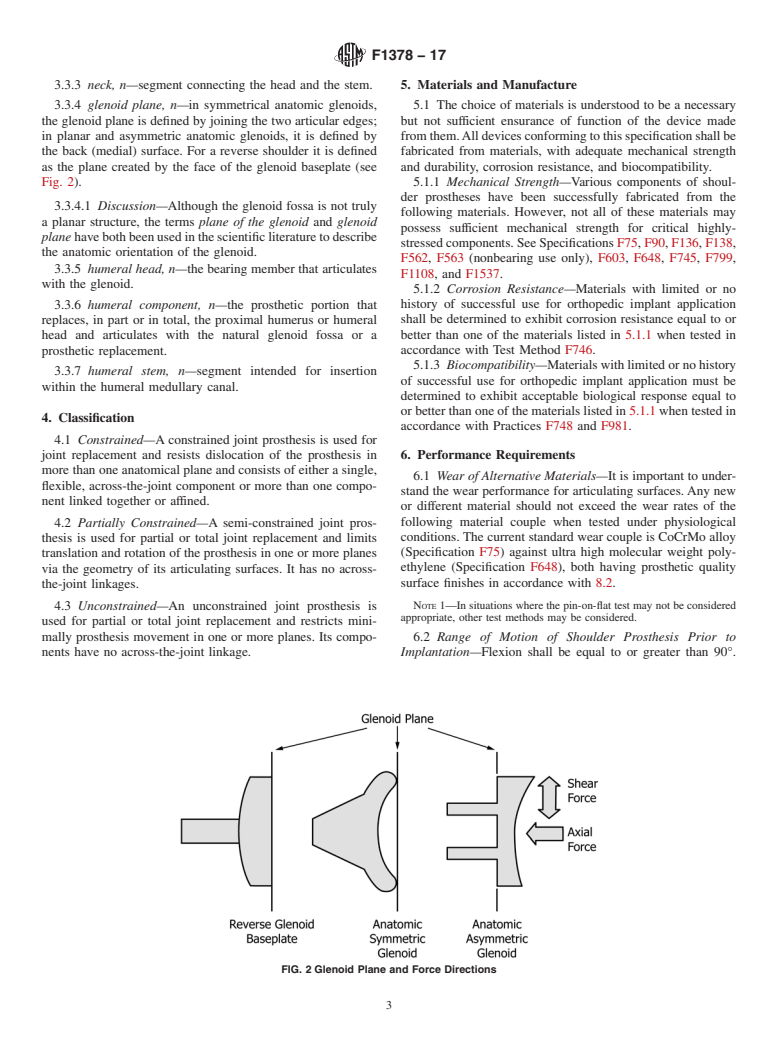
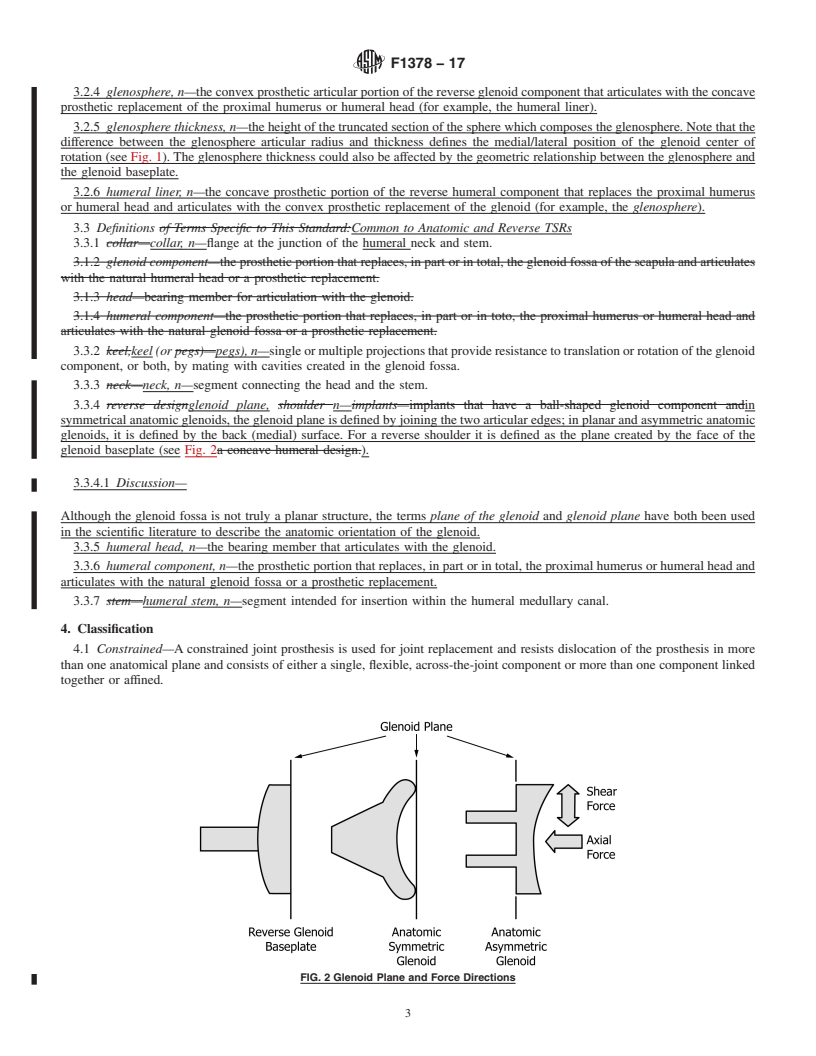
FIG. 1 Glenosphere Thickness
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1378 −17
Standard Specification for
1
Shoulder Prostheses
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1378; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F562 Specification for Wrought 35Cobalt-35Nickel-
20Chromium-10Molybdenum Alloy for Surgical Implant
1.1 This specification covers shoulder prostheses for total or
Applications (UNS R30035)
hemiarthroplasty used to provide functioning articulation by
F563 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-20Nickel-
employing glenoid and humeral components.
20Chromium-3.5Molybdenum-3.5Tungsten-5Iron Alloy
1.2 Devices for custom applications are not covered by this
for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R30563) (With-
specification. Modular prostheses are included in this specifi- 3
drawn 2005)
cation.
F603 Specification for High-Purity Dense Aluminum Oxide
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as for Medical Application
F648 Specification for Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Poly-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard. ethylene Powder and Fabricated Form for Surgical Im-
plants
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
F745 Specification for 18Chromium-12.5Nickel-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel for Cast and Solution-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Annealed Surgical Implant Applications (Withdrawn
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3
2012)
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
F746 Test Method for Pitting or Crevice Corrosion of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Metallic Surgical Implant Materials
F748 PracticeforSelectingGenericBiologicalTestMethods
2. Referenced Documents
for Materials and Devices
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F799 Specification for Cobalt-28Chromium-6Molybdenum
F75 Specification for Cobalt-28 Chromium-6 Molybdenum
Alloy Forgings for Surgical Implants (UNS R31537,
Alloy Castings and Casting Alloy for Surgical Implants
R31538, R31539)
(UNS R30075)
F981 Practice for Assessment of Compatibility of Biomate-
F86 Practice for Surface Preparation and Marking of Metal-
rials for Surgical Implants with Respect to Effect of
lic Surgical Implants
Materials on Muscle and Insertion into Bone
F90 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-20Chromium-
F983 Practice for Permanent Marking of Orthopaedic Im-
15Tungsten-10NickelAlloy for Surgical ImplantApplica-
plant Components
tions (UNS R30605)
F1044 Test Method for Shear Testing of Calcium Phosphate
F136 Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-
Coatings and Metallic Coatings
4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial)Alloy for Surgical
F1108 Specification for Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium
Implant Applications (UNS R56401)
Alloy Castings for Surgical Implants (UNS R56406)
F138 Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-
F1147 Test Method for Tension Testing of Calcium Phos-
2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical
phate and Metallic Coatings
Implants (UNS S31673)
F1537 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-28Chromium-
6Molybdenum Alloys for Surgical Implants (UNS
R31537, UNS R31538, and UNS R31539)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of F1829 Test Method for Static Evaluation of Anatomic Gle-
Subcommittee F04.22 on Arthroplasty.
noid Locking Mechanism in Shear
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017. Published January 2018. Originally
F2028 Test Methods for Dynamic Evaluation of Glenoid
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F1378 – 12. DOI:
Loosening or Disassociation
10.1520/F1378-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1378−17
FIG. 1Glenosphere Thickness
4
2.2 ANSI Standard: from one or more materials; most commonly, the reverse
ASME B46.1–1995 glenoid is composed of a metal glenosphere that is modularly
connected to a metal glenoid baseplate which is fixed to the
3. Terminology
glenoid fossa.
3.1 Anatomic Total Shoulder Replacement (TSR) Definitions
3.2.3 glenoid baseplate, n—the nonarticular portion of the
3.1.1 anatomic
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1378 − 12 F1378 − 17
Standard Specification for
1
Shoulder Prostheses
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1378; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers shoulder prostheses for total or hemiarthroplasty used to provide functioning articulation by
employing glenoid and humeral components.
1.2 Devices for custom applications are not covered by this specification. Modular prostheses are included in this specification.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F75 Specification for Cobalt-28 Chromium-6 Molybdenum Alloy Castings and Casting Alloy for Surgical Implants (UNS
R30075)
F86 Practice for Surface Preparation and Marking of Metallic Surgical Implants
F90 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-20Chromium-15Tungsten-10Nickel Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS
R30605)
F136 Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy for Surgical Implant
Applications (UNS R56401)
F138 Specification for Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical Implants
(UNS S31673)
F562 Specification for Wrought 35Cobalt-35Nickel-20Chromium-10Molybdenum Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications
(UNS R30035)
F563 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-20Nickel-20Chromium-3.5Molybdenum-3.5Tungsten-5Iron Alloy for Surgical Implant
3
Applications (UNS R30563) (Withdrawn 2005)
F603 Specification for High-Purity Dense Aluminum Oxide for Medical Application
F648 Specification for Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene Powder and Fabricated Form for Surgical Implants
F745 Specification for 18Chromium-12.5Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel for Cast and Solution-Annealed Surgical
3
Implant Applications (Withdrawn 2012)
F746 Test Method for Pitting or Crevice Corrosion of Metallic Surgical Implant Materials
F748 Practice for Selecting Generic Biological Test Methods for Materials and Devices
F799 Specification for Cobalt-28Chromium-6Molybdenum Alloy Forgings for Surgical Implants (UNS R31537, R31538,
R31539)
F981 Practice for Assessment of Compatibility of Biomaterials for Surgical Implants with Respect to Effect of Materials on
Muscle and Insertion into Bone
F983 Practice for Permanent Marking of Orthopaedic Implant Components
F1044 Test Method for Shear Testing of Calcium Phosphate Coatings and Metallic Coatings
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.22 on Arthroplasty.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2012Dec. 1, 2017. Published January 2012January 2018. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20102012 as
F1378 – 05 (2010).F1378 – 12. DOI: 10.1520/F1378-12.10.1520/F1378-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1378 − 17
FIG. 1 Glenosphere Thickness
F1108 Specification for Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium Alloy Castings for Surgical Implants (UNS R56406)
F1147 Test Method for Tension Testing of Calcium Phosphate and Metallic Coatings
F1537 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-28Chromium-6Molybdenum Alloys for Surgical Implants (UNS R31537, UNS
R31538, and UNS R31539)
F1829 Test Method for Static Evaluation of Anatomic Glenoid Locking Mechanism in Shear
F2028 Test Methods for Dynamic Evaluation of Glenoid Loosening or Disassociation
4
2.2 ANSI Standard:
ASME B46.1–1995
3. T
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.