ASTM D6599-00(2014)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Construction of Live Fascines on Slopes
Standard Practice for Construction of Live Fascines on Slopes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Live fascines are used to provide erosion and sedimentation control by increasing infiltration, slowing or redirecting runoff, and trapping seed and sediments. The method provides shallow mechanical surface slope stabilization, and provides enhanced values through vegetative growth and additional shallow soil reinforcement through the development of the roots. The ability of live fascines to function properly depends on the quality and choice of the materials used to construct the live fascine, the means and methods of fabrication and installation, and proper consideration of site characteristics and time of year. For the live fascine to function completely, it is important that the live fascine develops suitable growth.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the material, fabrication and installation work to construct live fascines.
1.2 The values in this standard are in SI units and are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing one or more specific operations. This document cannot replace education or experience and should be used in conjunction with professional judgement. Not all aspects of this practice may be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to represent or replace standard of care by which the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without considerations of a project's many unique aspects. The word “Standard” in the title of this document means only that the document has been approved through the ASTM consensus process.
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6599 − 00(Reapproved 2014)
Standard Practice for
1
Construction of Live Fascines on Slopes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6599; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.1.4 live stake, n—a woody stem or branch of vegetatively
self-propagating woody plant species. Live stakes are approxi-
1.1 This practice covers the material, fabrication and instal-
mately 2.5 to 4 cm (.5" to 1.5") in diameter and 60 to 75 cm
lation work to construct live fascines.
(24"–30") in length with the terminal end sharpened to a point
1.2 The values in this standard are in SI units and are to be
orasteepangularcut.Uselivestakesasadditionalanchorsand
regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in
propagating material on the downslope side of live fascine
parentheses are for information only.
bundles.
1.3 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing
one or more specific operations.This document cannot replace
3. Summary of Practice
educationorexperienceandshouldbeusedinconjunctionwith
3.1 A live fascine is comprised of live cut plant stems and
professional judgement. Not all aspects of this practice may be
branches, typically of woody plant species (for example,
applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not
willow, dogwood, poplar, etc.) that are formed into linear
intended to represent or replace standard of care by which the
bundles. These bundles are installed in shallow trenches,
adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor
secured in the trench with wood stakes, then backfilled with
should this document be applied without considerations of a
enoughsoiltoleaveasmallportionontopofthebranchbundle
project’smanyuniqueaspects.Theword“Standard”inthetitle
exposed. Live fascines assist to control erosion, encourage
of this document means only that the document has been
vegetative top growth establishment and rooting for shallow
approved through the ASTM consensus process.
soil stabilization.
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials,
operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
4. Significance and Use
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
4.1 Live fascines are used to provide erosion and sedimen-
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
tation control by increasing infiltration, slowing or redirecting
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
runoff, and trapping seed and sediments. The method provides
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
shallow mechanical surface slope stabilization, and provides
2. Terminology
enhanced values through vegetative growth and additional
shallow soil reinforcement through the development of the
2.1 Definitions:
roots. The ability of live fascines to function properly depends
2.1.1 live fascine, n—a linear bundle of live cut branches of
on the quality and choice of the materials used to construct the
woody plant material that propagates easily from cuttings.The
live fascine, the means and methods of fabrication and
bundle is anchored in a shallow trench and partially covered
installation,andproperconsiderationofsitecharacteristicsand
with soil.
time of year. For the live fascine to function completely, it is
2.1.2 rolled erosion control product, n— a material manu-
important that the live fascine develops suitable growth.
factured into rolls designed to reduce erosion and assist in the
germination, establishment and/or anchorage of vegetation.
5. Materials
2.1.3 dead stout stake, n—a wood stake approximately .75
5.1 Live Woody Plant Material are woody stems and branch
to 1 m (2.5 to 3 ft) in length. Construct dead stout stakes from
cuttings of vegetatively self-propagating woody plant species.
3.8×8.9cm(2"×4")dimensionallumbercutdiagonallyalong
When constructing a live fascine, use only fresh or well-
the 8.9 cm face.
preserved viable cuttings. Do not use dead plant material in
1
live fascines. The stems or branches should be long, straight
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.25 on Erosion and
and flexible to allow easy assembly into bundles. Typically,
Sediment Control Technology.
plants are harvested near the project site within the same
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2014. Published September 2014. Originally
climatic zone. Cut the plant material in lengths ranging from 2
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D6599–00(2008).
DOI: 10.1520/D6599-00R14. to 4 m (6' to 13')
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6599 − 00 (Reapproved 2008) D6599 − 00 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Practice for
1
Construction of Live Fascines on Slopes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6599; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers the material, fabrication and installation work to construct live fascines.
1.2 The values in this standard are in SI units and are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses
are for information only.
1.3 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing one or more specific operations. This document cannot replace
education or experience and should be used in conjunction with professional judgement. Not all aspects of this practice may be
applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to represent or replace standard of care by which the adequacy
of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without considerations of a project’s many
unique aspects. The word “Standard” in the title of this document means only that the document has been approved through the
ASTM consensus process.
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Terminology
2.1 Definitions:
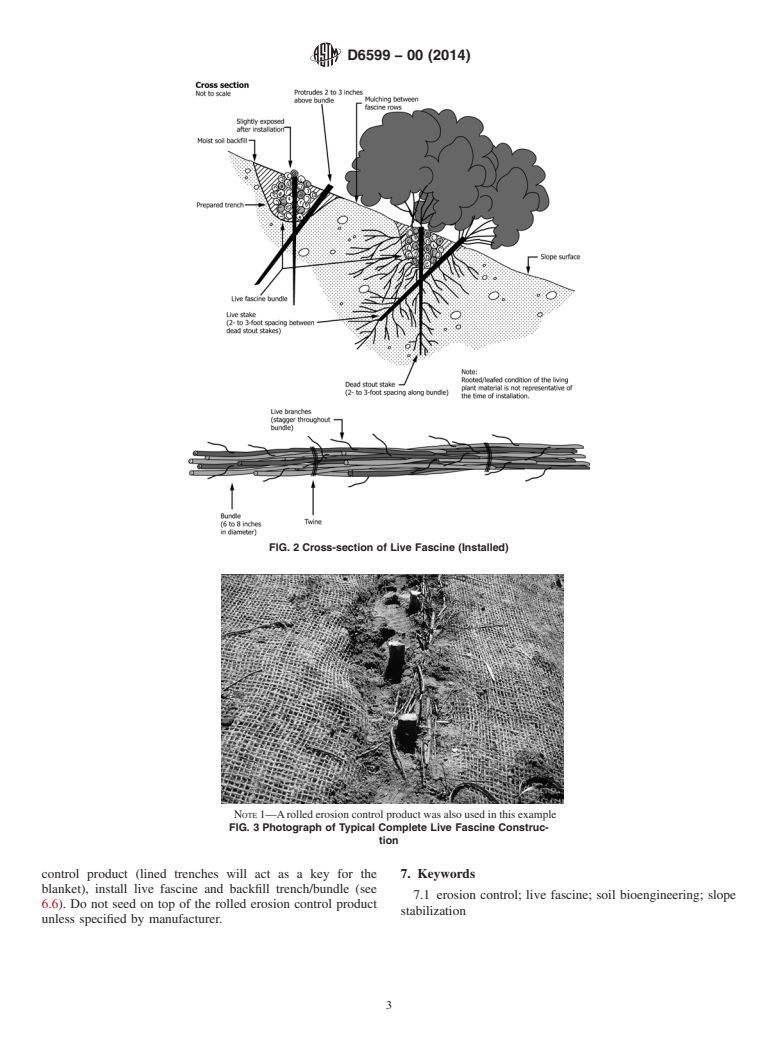
2.1.1 live fascine, n—a linear bundle of live cut branches of woody plant material that propagates easily from cuttings. The
bundle is anchored in a shallow trench and partially covered with soil.
2.1.2 rolled erosion control product, n— a material manufactured into rolls designed to reduce erosion and assist in the
germination, establishment and/or anchorage of vegetation.
2.1.3 dead stout stake, n—a wood stake approximately .75 to 1 m (2.5 to 3 ft) in length. Construct dead stout stakes from 3.8
× 8.9 cm (2" × 4") dimensional lumber cut diagonally along the 8.9 cm face.
2.1.4 live stake, n—a woody stem or branch of vegetatively self-propagating woody plant species. Live stakes are approximately
2.5 to 4 cm (.5" to 1.5") in diameter and 60 to 75 cm (24"–30") in length with the terminal end sharpened to a point or a steep
angular cut. Use live stakes as additional anchors and propagating material on the downslope side of live fascine bundles.
3. Summary of Practice
3.1 A live fascine is comprised of live cut plant stems and branches, typically of woody plant species (e.g., (for example, willow,
dogwood, poplar, etc.) that are formed into linear bundles. These bundles are installed in shallow trenches, secured in the trench
with wood stakes, then backfilled with enough soil to leave a small portion on top of the branch bundle exposed. Live fascines
assist to control erosion, encourage vegetative top growth establishment and rooting for shallow soil stabilization.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Live fascines are used to provide erosion and sedimentation control by increasing infiltration, slowing or redirecting runoff,
and trapping seed and sediments. The method provides shallow mechanical surface slope stabilization, and provides enhanced
values through vegetative growth and additional shallow soil reinforcement through the development of the roots. The ability of
live fascines to function properly depends on the quality and choice of the materials used to construct the live fascine, the means
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.25 on Erosion and Sediment
Control Technology.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2008Aug. 15, 2014. Published February 2008September 2014. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20002008
as D6599 – 00.D6599 – 00(2008). DOI: 10.1520/D6599-00R08.10.1520/D6599-00R14.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6599 − 00 (2014)
and methods of fabrication and installation, and proper consideration of site characteristics and time of year
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.