ASTM E477-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurements of Acoustical and Airflow Performance of Duct Liner Materials and Prefabricated Silencers
Standard Test Method for Laboratory Measurements of Acoustical and Airflow Performance of Duct Liner Materials and Prefabricated Silencers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Specimens tested using this standard, for example, duct silencers, are used to control sound propagation through ventilation ducts. The results gathered from testing specimens to this standard can be used to estimate the reduction in fan sound levels in ducted airflow systems caused by including a sound attenuating device in the system. The device can be a component in a source-path-receiver analysis where calculations are performed to determine the resultant sound level in an occupied space. Correct selection of a sound attenuating device can enable a designer to achieve in-space background noise criteria.
5.2 The insertion loss of a silencer varies with frequency and with the direction and speed of airflow. Because silencers partially obstruct the air path and provide resistance to airflow, two other effects must be quantified: pressure drop and airflow-generated noise. Both increase with increasing air speeds; thus data are required for several airflows to correctly characterize performance.
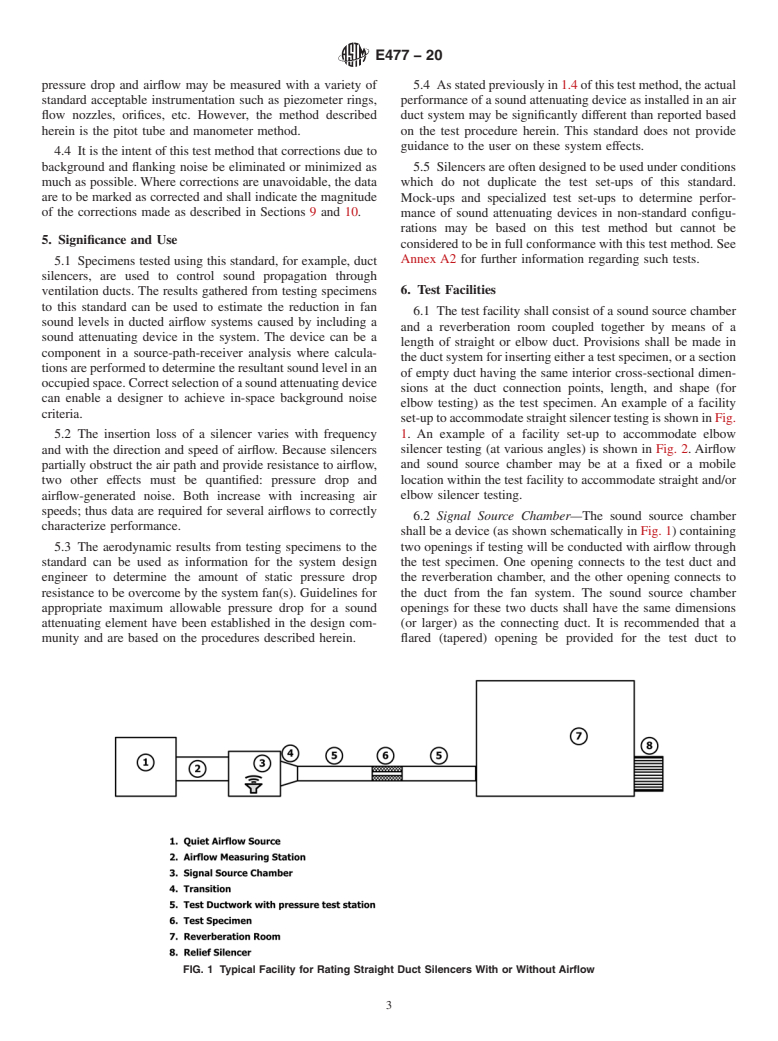
5.3 The aerodynamic results from testing specimens to the standard can be used as information for the system design engineer to determine the amount of static pressure drop resistance to be overcome by the system fan(s). Guidelines for appropriate maximum allowable pressure drop for a sound attenuating element have been established in the design community and are based on the procedures described herein.
5.4 As stated previously in 1.4 of this test method, the actual performance of a sound attenuating device as installed in an air duct system may be significantly different than reported based on the test procedure herein. This standard does not provide guidance to the user on these system effects.
5.5 Silencers are often designed to be used under conditions which do not duplicate the test set-ups of this standard. Mock-ups and specialized test set-ups to determine performance of sound attenuating devices in non-standard configurations may be based on this test...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory testing of some of the acoustical properties of sound attenuating devices including duct liner materials, integral ducts, and in-duct absorptive straight and elbow silencers used in the ventilation systems of buildings. Procedures are described for the measurement of acoustical insertion loss, airflow generated noise, and pressure drop as a function of airflow.
1.2 Excluded from the scope are reactive mufflers and those designed for uses other than in ventilation systems, such as automobile mufflers.
1.3 This test method includes a provision for a simulated semi-reflective plenum to fit around thin-walled duct and silencer test specimens, since the acoustical environments around such thin-walled specimens can affect the measured insertion loss.
1.4 This method tests the performance of the specimen in well-defined and controlled conditions. If the specimen is installed in the field in any different manner, the results may be different. This standard does not provide estimating procedures for determining the actual installed performance of the specimen under field conditions.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E477 −20
Standard Test Method for
Laboratory Measurements of Acoustical and Airflow
Performance of Duct Liner Materials and Prefabricated
1
Silencers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E477; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory testing of some
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
of the acoustical properties of sound attenuating devices
including duct liner materials, integral ducts, and in-duct
2. Referenced Documents
absorptive straight and elbow silencers used in the ventilation
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
systems of buildings. Procedures are described for the mea-
C634 Terminology Relating to Building and Environmental
surement of acoustical insertion loss, airflow generated noise,
Acoustics
and pressure drop as a function of airflow.
3
2.2 ANSI Standards:
1.2 Excluded from the scope are reactive mufflers and those
S1.1-2013 Acoustical Terminology
designed for uses other than in ventilation systems, such as
S1.11-2014/Part 1/IEC 61260:1-2014 Electroacoustics –
automobile mufflers.
Octave-Band and Fractional-Octave-Band Filters – Part 1:
1.3 This test method includes a provision for a simulated
Specifications
semi-reflective plenum to fit around thin-walled duct and
S12.5-2016/ISO 6926-2016 Requirements for the Perfor-
silencer test specimens, since the acoustical environments
mance and Calibration of Reference Sound Sources Used
around such thin-walled specimens can affect the measured
for the Determination of Sound Power Levels
insertion loss.
S12.51-2012/ISO 3741:2010 (R2017) Acoustics-Determina-
tion of Sound Power Levels of Noise Sources Using
1.4 This method tests the performance of the specimen in
Sound Pressure-Precision Method for Reverberation
well-defined and controlled conditions. If the specimen is
Rooms
installed in the field in any different manner, the results may be
4
2.3 ASHRAE Documents and Standards:
different.This standard does not provide estimating procedures
2017 ASHRAE Handbook Fundamentals, Chapter 37, Mea-
for determining the actual installed performance of the speci-
surement and Instruments
men under field conditions.
ANSI/ASHRAE 41.2-2018 Standard Methods forAirVeloc-
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
ity and Airflow Measurement
standard. The values in parentheses are provided for informa-
ANSI/ASHRAE 41.3-2014 Standard Method for Pressure
tion only.
Measurement
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the 5
2.4 IEC Standards:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
61672-1:2013 Electroacoustics – Sound Level Meters – Part
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1: Specifications
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
1 4
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE33onBuilding Available from American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-
and Environmental Acoustics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (ASHRAE), 1791 Tullie Circle, NE, Atlanta, GA
E33.08 on Mechanical and Electrical System Noise. 30329, http://www.ashrae.org.
5
Current edition approved July 1, 2020. Published October 2020. Originally Available from International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 3, rue de
ε1
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as E477 – 13 . DOI: Varembé, 1st floor, P.O. Box 131, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, https://
10.1520/E0477-20. www.iec.ch.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E477 − 20
6
2.5 NAIMA Documents and Stan
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: E477 − 13 E477 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Laboratory Measurements of Acoustical and Airflow
Performance of Duct Liner Materials and Prefabricated
1
Silencers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E477; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Equations 9 and 10 were editorially corrected in September 2015.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory testing of some of the acoustical properties of sound attenuating devices including duct
liner materials, integral ducts, and in-duct absorptive straight and elbow silencers used in the ventilation systems of buildings.
Procedures are described for the measurement of acoustical insertion loss, airflow generated noise, and pressure drop as a function
of airflow.
1.2 Excluded from the scope are reactive mufflers and those designed for uses other than in ventilation systems, such as
automobile mufflers.
1.3 This test method includes a provision for a simulated semi-reflective plenum to fit around thin-walled duct and silencer test
specimens, since the acoustical environments around such thin-walled specimens can affect the measured insertion loss.
1.4 This method tests the performance of the specimen in well-defined and controlled conditions. If the specimen is installed in
the field in any different manner, the results may be different. This standard does not provide estimating procedures for determining
the actual installed performance of the specimen under field conditions.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E33 on Building and Environmental Acoustics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E33.08
on Mechanical and Electrical System Noise.
Current edition approved June 1, 2013July 1, 2020. Published August 2013October 2020. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20062013 as
ε1
E477 – 06a.E477 – 13 . DOI: 10.1520/E0477-13E0110.1520/E0477-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E477 − 20
C634 Terminology Relating to Building and Environmental Acoustics
3
2.2 ANSI Standards:
S1.1–1994(R2004)S1.1-2013 Acoustical Terminology
S1.11–2004(R2009)S1.11-2014/Part 1/IEC 61260:1-2014 Specification Octave, Half-Octave and Third-Octave Band Filter
SetsElectroacoustics – Octave-Band and Fractional-Octave-Band Filters – Part 1: Specifications
S1.43-1997(R2007) Specifications for Integrating-Averaging Sound Level Meters
S12.5-2006/ISO 6926:1999(R2011)S12.5-2016/ISO 6926-2016 Requirements for the Performance and Calibration of Reference
Sound Sources Used for the Determination of Sound Power Levels
S12.51–2012/ISOS12.51-2012/ISO 3741:2010 (R2017) Acoustics-Determination of Sound Power Levels of Noise Sources
Using Sound Pressure-Precision Method for Reverberation Rooms
4
2.3 ASHRAE Documents and Standards:
20092017 ASHRAE Handbook,Handbook Fundamentals,Chapter 36, Fundamentals, Chapter 37, Measurement and Instruments
ANSI/ASHRAE 41.2-2018 Standard Methods for Air Velocity and Airflow Measurement
ANSI/ASHRAE 41.3-198941.3-2014 Standard Method for Pressure Measurement (plus errata dated 5 January 1998)
5
2.4 IEC Standards:
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.