ASTM E2068-00(2016)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Operating Force of Sliding Windows and Doors
Standard Test Method for Determination of Operating Force of Sliding Windows and Doors
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method determines the operational forces of sliding windows and doors by simulating force applied by hand directly to movable sash or panels. Breakaway and in-motion operating forces are measures of the ease of operation of fenestration products. Product specifications, building codes, and building specifications establish operating force limits as measures of product performance or limits for handicapped accessibility, or both.
5.2 Window and door performance standards for air infiltration and water penetration in some cases require operating force measurements to be made and reported as an indication of the operability of the test specimen.
5.3 Operating forces can vary significantly from unit to unit due to factors such as installation parameters, wearing of sliding or rolling parts, lubrication, stiffening or softening of weather-strip, and environmental factors (for example, humidity, temperature, accumulation of dirt, and so forth). Therefore, when applied to new product designs, this test method requires that units be tested in a laboratory under controlled conditions including accurate mounting (plumb, square, and level) following the manufacturer's instructions. Use of this test method in the field does not necessarily indicate the operating forces that are inherent in the particular window design, but rather, provides a measurement of the forces required for operation of the particular unit at the particular time. The user is cautioned that installation defects such as bowed jambs, racked frames, or inadequate anchoring can result in binding or sticking of movable components and increased operating forces.
5.4 This test method requires measurement of both breakaway and in-motion operating forces. Generally, breakaway force is higher than in-motion operating force due to the difference between static and dynamic friction coefficients or the presence of weather-stripping and sash pockets, or both. Traditional fenestration product stand...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method determines the operating forces for opening and closing horizontal and vertical sliding windows and horizontal sliding door systems. It does not address the forces required for opening pivoting, projecting, or other fenestration systems. This test method does not address the use or performance of add-on devices or mechanical operators that might be installed to reduce operating forces of sliding windows or doors. It deals only with the forces necessary to open and close a sash or panel through the direct application of force to the operable sash or panel.
1.2 This test method is suitable for laboratory product comparisons or for qualifying products, or both, as meeting window or door operating force specifications. This test method is also suitable for use in the field to determine the operating forces required to open and close installed sliding windows and doors.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see Section 7.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E2068 − 00 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Operating Force of Sliding Windows and
1
Doors
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2068; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method determines the operating forces for 3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology E631
opening and closing horizontal and vertical sliding windows unless otherwise specified.
and horizontal sliding door systems. It does not address the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
forces required for opening pivoting, projecting, or other
3.2.1 breakaway force—the force required to start a sash
fenestration systems.This test method does not address the use
(panel) in motion from a fully closed or fully open position.
or performance of add-on devices or mechanical operators that
3.2.2 fully closed position—the position of the sash or panel
might be installed to reduce operating forces of sliding
after being closed, latched, and unlatched, or where the sash or
windows or doors. It deals only with the forces necessary to
panel is closed to its maximum engagement within a frame or
open and close a sash or panel through the direct application of
pocket if no latching mechanism is provided.
force to the operable sash or panel.
3.2.3 fully open position—the point at the limits of the
1.2 This test method is suitable for laboratory product
operating hardware (if applicable) or the point at which the
comparisons or for qualifying products, or both, as meeting
sash or panel contacts a limiting device.
window or door operating force specifications. This test
3.2.4 in-motion operating force—theforcerequiredtomain-
method is also suitable for use in the field to determine the
tain a sash or panel in motion while moving the sash or panel
operating forces required to open and close installed sliding
between 1 in. from fully open to 1 in. from fully closed
windows and doors.
positions, or 1 in. from fully closed to 1 in. from fully open
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
position.
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
4. Summary of Test Method
and are not considered standard.
4.1 Two equivalent test methods for determining operating
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
force are described. Test Method A uses dead weights and a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
cable and pulley system to apply force to operate a sash or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
panel. Test Method B uses a force gage and hand-applied
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
pressure to operate a sash or panel. The test specimen is
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
mounted in a rigid support frame. After attaching the loading
precautionary statements, see Section 7.
system to the operating sash or panel, the weight or force is
applied and increased until the sash or panel is put into motion.
2. Referenced Documents
This determines breakaway force. Starting from 1 in. (25 mm)
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: from a closed or open position the minimum amount of weight
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
or force required to keep a sash in motion, once it is started
moving, is measured. This determines the in-motion operating
force. Forces required to operate a sliding window or patio
1 door in both opening and closing directions are determined by
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51
this test method.
on Performance of Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016. Published October 2016. Originally
5. Significance and Use
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E2068 – 00(2008).
DOI: 10.1520/E2068-00R16.
5.1 This test method determines the operational forces of
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
slidingwindowsanddoorsbysimulatingforceappliedbyhand
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
directly to movable sash or panels. Breakaway and in-motion
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. operating forces are measures of the ease of operation of
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2068 − 00 (Reapproved 2008) E2068 − 00 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Operating Force of Sliding Windows and
1
Doors
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2068; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method determines the operating forces for opening and closing horizontal and vertical sliding windows and
horizontal sliding door systems. It does not address the forces required for opening pivoting, projecting, or other fenestration
systems. This test method does not address the use or performance of add-on devices or mechanical operators that might be
installed to reduce operating forces of sliding windows or doors. It deals only with the forces necessary to open and close a sash
or panel through the direct application of force to the operable sash or panel.
1.2 This test method is suitable for laboratory product comparisons or for qualifying products, or both, as meeting window or
door operating force specifications. This test method is also suitable for use in the field to determine the operating forces required
to open and close installed sliding windows and doors.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see Section 7.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology E631 unless otherwise specified.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 breakaway force—the force required to start a sash (panel) in motion from a fully closed or fully open position.
3.2.2 fully open position—the point at the limits of the operating hardware (if applicable) or the point at which the sash or panel
contacts a limiting device.
3.2.2 fully closed position—the position of the sash or panel after being closed, latched, and unlatched, or where the sash or
panel is closed to its maximum engagement within a frame or pocket if no latching mechanism is provided.
3.2.3 fully open position—the point at the limits of the operating hardware (if applicable) or the point at which the sash or panel
contacts a limiting device.
3.2.4 in-motion operating force—the force required to maintain a sash or panel in motion while moving the sash or panel
between 1 in. from fully open to 1 in. from fully closed positions, or 1 in. from fully closed to 1 in. from fully open position.
4. Summary of Test Method
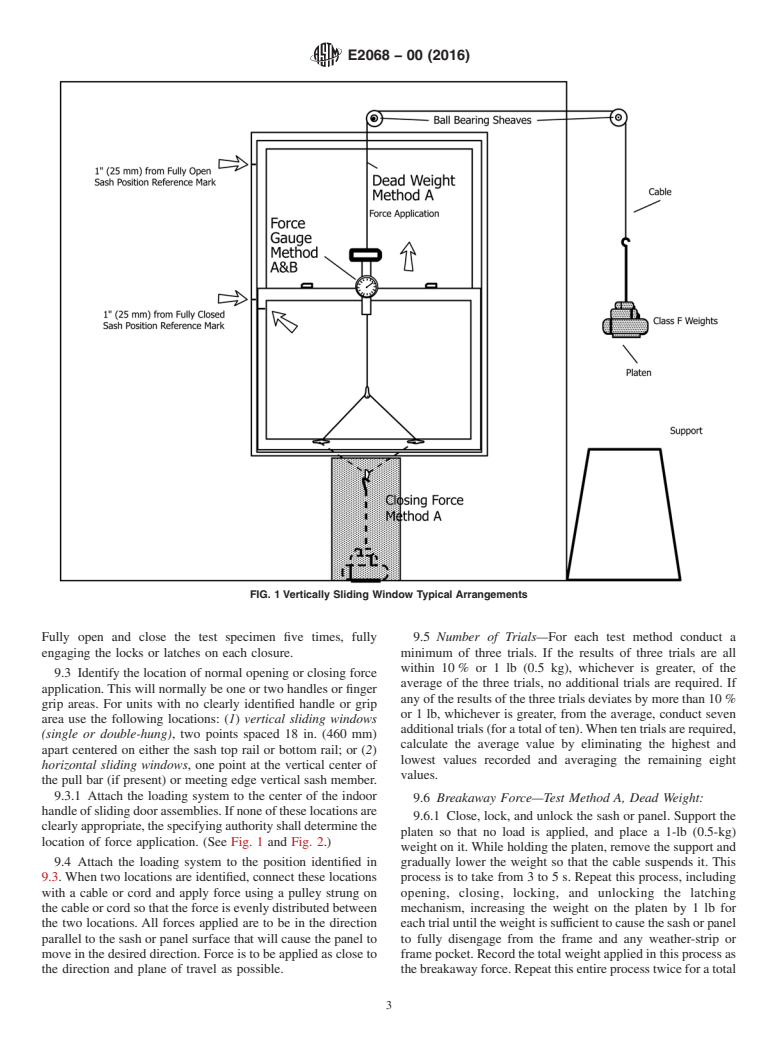
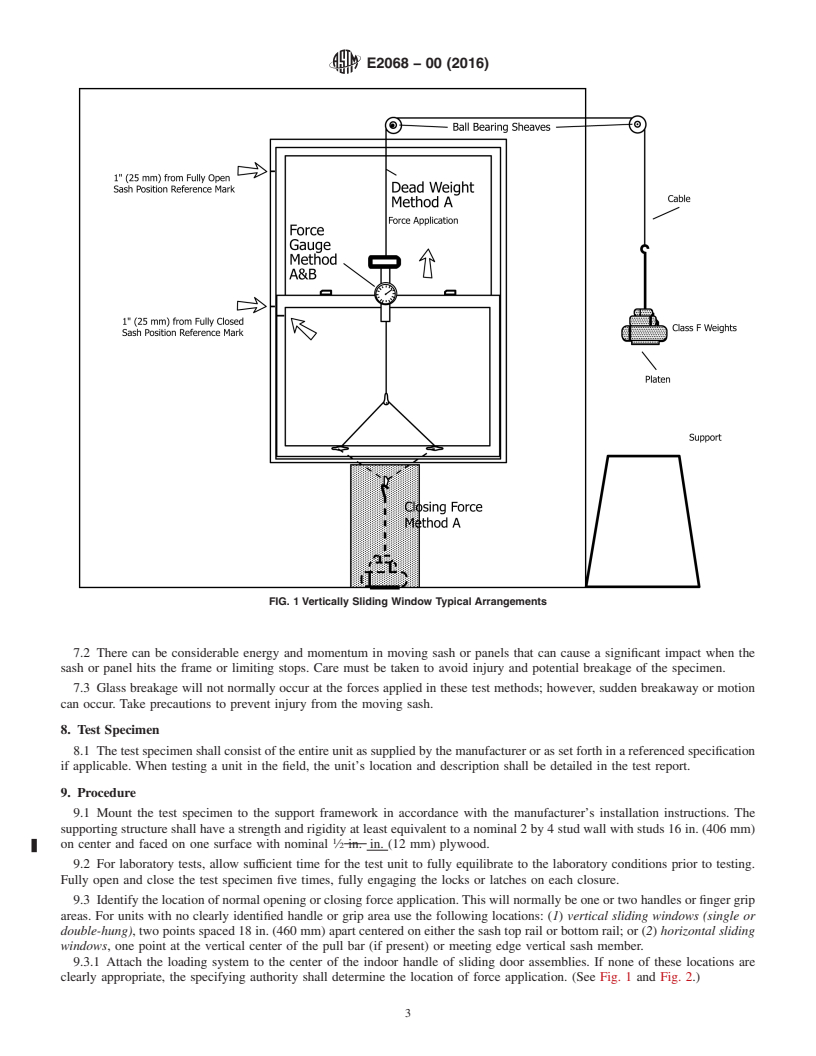
4.1 Two equivalent test methods for determining operating force are described. Test Method A uses dead weights and a cable
and pulley system to apply force to operate a sash or panel. Test Method B uses a force gage and hand-applied pressure to operate
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51 on Performance
of Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2008Oct. 1, 2016. Published October 2008October 2016. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20002008 as
E2068 – 00.E2068 – 00(2008). DOI: 10.1520/E2068-00R08.10.1520/E2068-00R16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2068 − 00 (2016)
a sash or panel. The test specimen is mounted in a rigid support frame. After attaching the loading system to the operating sash
or panel, the weight or force is applied and increased until the sash or panel is put into motion. This determines b
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.