ASTM D3576-04(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Cell Size of Rigid Cellular Plastics
Standard Test Method for Cell Size of Rigid Cellular Plastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Several physical properties of rigid cellular plastics are dependent on cell size and cell orientation. Measuring water absorption and open-cell content in accordance with Test Method D2842 and Test Method D2856 requires knowledge of surface cell volume, which uses cell size values in the calculations.
This test method provides an apparent cell size because it assumes that there is no measurable edge to edge or top to bottom variation in average cell size and that the cell size distribution about the average cell size is normal. If the analyst is concerned there may be significant variation in either the average cell size or the cell size distribution more detailed analysis may be required.
Before proceeding with this test method, reference should be made to the specification of the material being tested. Any test specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions, or testing parameters, or a combination thereof, covered in the materials specification shall take precedence over those mentioned in this test method. If there are no material specifications, then the default conditions apply.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent cell size of rigid cellular plastics by counting the number of cell-wall intersections in a specified distance.
1.2 Procedure A requires the preparation of a thin slice, not more than one half the average cell diameter in thickness, that is mechanically stable. For most rigid cellular plastics this limits the test method to materials with an average cell size of at least 0.2 mm.
1.3 Procedure B is intended for use with materials whose friable nature makes it difficult to obtain a thin slice for viewing.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—The annex to ISO 2896 is technically equivalent to this test method.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3576 − 04(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Cell Size of Rigid Cellular Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3576; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 ISO Standard:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the appar-
ISO 2896Cellular Plastics, Rigid—Determination of Water
entcellsizeofrigidcellularplasticsbycountingthenumberof
Absorption
cell-wall intersections in a specified distance.
1.2 ProcedureArequires the preparation of a thin slice, not 3. Terminology
more than one half the average cell diameter in thickness, that
3.1 Definitions of terms applicable to this test method are
is mechanically stable. For most rigid cellular plastics this
given in Terminology D883.
limits the test method to materials with an average cell size of
at least 0.2 mm. 4. Summary of Test Method
1.3 Procedure B is intended for use with materials whose
4.1 Procedure A—Thecellularplasticspecimeniscuttonot
friable nature makes it difficult to obtain a thin slice for more than one half the average cell diameter in thickness on a
viewing.
slicer and the shadowgraph is projected on a screen by the use
of a cell-size scale slide assembly and a projector.The average
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
chord length is obtained by counting the cells on cell-wall
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
intersections and converting this value to average cell size by
only.
mathematical derivation.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 Procedure B—The cellular plastic specimen is sliced to
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
provide a smooth surface. The cell walls are accented by the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
use of a marking pen.The average chord length is obtained by
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
countingthecellwallintersectionsandconvertingthisvalueto
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
average cell size by mathematical derivation.
NOTE 1—The annex to ISO 2896 is technically equivalent to this test
method.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Several physical properties of rigid cellular plastics are
2. Referenced Documents
dependent on cell size and cell orientation. Measuring water
2.1 ASTM Standards:
absorption and open-cell content in accordance with Test
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
MethodD2842andTestMethodD2856requiresknowledgeof
D2842Test Method for Water Absorption of Rigid Cellular
surface cell volume, which uses cell size values in the
Plastics
calculations.
D2856TestMethodforOpen-CellContentofRigidCellular
5.2 This test method provides an apparent cell size because
Plastics by the Air Pycnometer (Withdrawn 2006)
it assumes that there is no measurable edge to edge or top to
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
bottom variation in average cell size and that the cell size
distributionabouttheaveragecellsizeisnormal.Iftheanalyst
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlastics
is concerned there may be significant variation in either the
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials -
average cell size or the cell size distribution more detailed
Plastics and Elastomers.
analysis may be required.
Current edition approved April 15, 2010. Published June 2010. Originally
approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D3576-04. DOI:
5.3 Before proceeding with this test method, reference
10.1520/D3576-04R10.
2 shouldbemadetothespecificationofthematerialbeingtested.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Any test specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions, or
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
www.astm.org. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D3576 − 04 (2010)
FIG. 1 Razor Blade Cell Size Specimen Slicer
testing parameters, or a combination thereof, covered in the 7. Sampling
materials specification shall take precedence over those men-
7.1 Generally one specimen is sufficient to determine the
tioned in this test method. If there are no material
apparent cell size of a sample.
specifications, then the default conditions apply.
7.2 The number of samples may be dictated by the end-use
6. Apparatus
data needed.
6.1 The apparatus required to perform the test as defined by
Procedure A is listed as follows: 8. Procedures
6.1.1 Cell Size Specimen Slicer —Cutting blade apparatus
8.1 Procedure A:
capable of slicing thin specimens (0.02 mm) for cell size
8.1.1 Cut a specimen 50 by 50 mm by thickness (2 by 2 in.
viewing. Fig. 1 shows an acceptable alternative slicing appa-
by thickness) from the sample in the area to be tested.
ratus.
6.1.2 Cell Size Projector—Conventional 35-mm slide pro- 8.1.2 Prepare the cell size viewing specimen by cutting a
jector that accepts standard 50 by 50-mm (2 by 2-in.) slides. thin slice (less than monocellular) from one of the cut surfaces
6.1.3 Cell Size Scale Slide Assembly, consisting of two
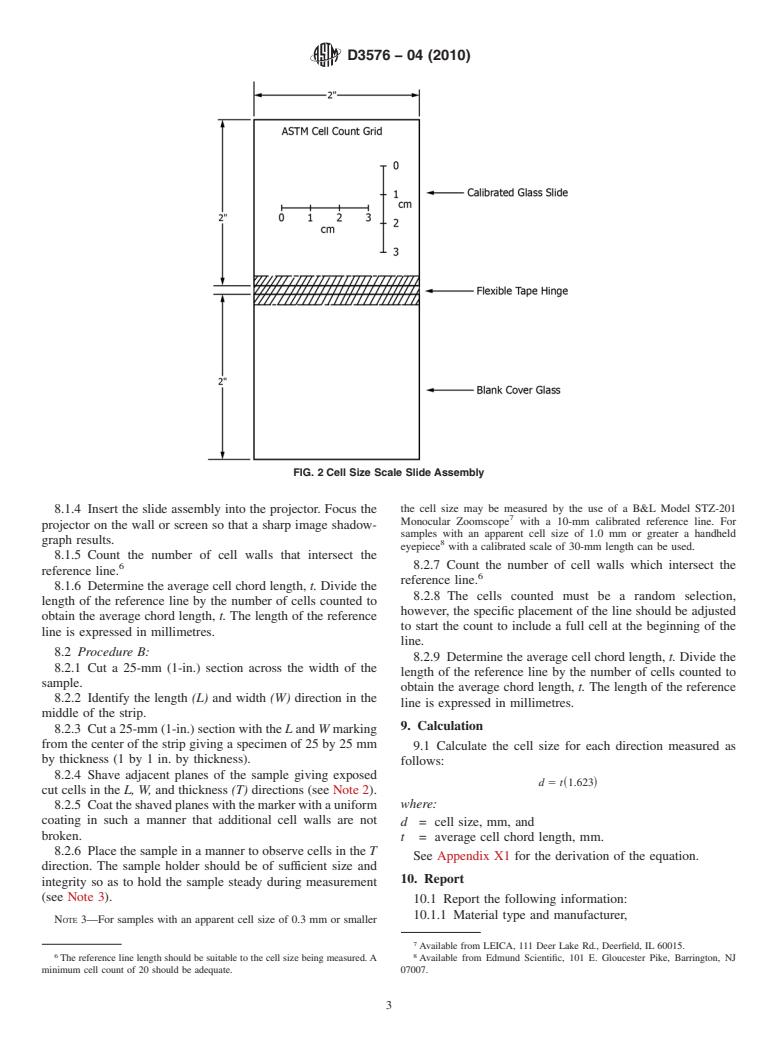
of the specimen. (Slice thickness should be as thin as practi-
pieces of slide glass hinged by tape along one edge, between cable; so that a shadowgraph will not be occluded by overlap-
which a calibrated scale (30 mm in length) printed on a thin
ping cell walls. Optimum slice thickness will vary with the
plastic sheet is placed (see Fig. 2).
averagecellsizeofthefoam,withsmallercellfoamsrequiring
thinner slices.)
6.2 The apparatus required to perform the test as defined by
Procedure B is listed as follows:
NOTE 2—One cell size measurement will provide a representative
6.2.1 Cell Size Specimen Slicer —Cutting blade apparatus
apparent cell size for cellular plastics having symmetric cells of relatively
capable of providing a smooth surface.
uniform size. However, if the cell size in the three normal directions is
6.2.2 Optical Magnification System, capable of 5 to 25× suspected of varying by a value greater than the precision of this test
method, all three directions should be measured and reported for maxi-
magnification with a calibrated scale of the appropriate length.
mum accuracy.An acceptable procedure, in this case, is to determine the
6.2.3 Highlighting Market, that does not contain a solvent
cell size in two planes perpendicular to each other.The size of the cells in
which will attack the polymer system. The ink used should
the three normal directions can then be compared and reported separately
contrast with the color of the foam.
if desired.
8.1.3 Insert the thin-sliced foam specimen into the cell size
5 slide assembly. Position the zero on the grid line at the top of
Hobart Model 610-1, an electrically operated slicer, available from the Hobart
Corp., 701 S. Ridge Ave., Troy, OH 45374. the area to be measured. Reassemble the slide.
D3576 − 04 (2010)
FIG. 2 Cell Size Scale Slide Assembly
the cell size may be measured by the use of a B&L Model STZ-201
8.1.4 Insert the slide assembly into the projector. Focus the
Monocular Zoomscope with a 10-mm calibrated reference line. For
projector on the wall or screen so that a sharp image shadow-
samples with an apparent cell size of 1.0 mm or greater a handheld
graph results.
eyepiece with a calibrated scale of 30-mm length can be used.
8.1.5 Count the number of cell walls that intersect the
6 8.2.7 Count the number of cell walls which intersect the
reference line.
reference line.
8.1.6 Determine the average cell chord length, t. Divide the
8.2.8 The cells counted must be a random selection,
length of the reference line by the number of cells counted to
however, the specific placement of the line should be adjusted
obtain the average chord length, t. The length of the reference
to start the count to include a full cell at the beginning of the
line is expressed in millimetre
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.