ASTM B387-90(2001)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire (Withdrawn 2010)
Standard Specification for Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire (Withdrawn 2010)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire. The following materials are covered: molybdenum 360, molybdenum 361, molybdenum 363, molybdenum 364, molybdenum 365, and molybdenum 366. These materials shall be manufactured with conventional extrusion, forging, swaging, rolling, and drawing equipment. These shall materials be made by vacuum arc-melted or powder metallurgy methods. The chemical composition shall conform to the required contents of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, iron, nickel, silicon, titanium, tungsten, zirconium, and molybdenum. Chemical analysis shall be done. Mechanical properties shall conform to the required tension properties: tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and diamond pyramid hardness. Tension test shall also be done.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire as follows:
1.1.1 Molybdenum 360—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum.
1.1.2 Molybdenum 361—Unalloyed powder metallurgy molybdenum.
1.1.3 Molybdenum Alloy 363—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum-0.5% titanium-0.1% zirconium (TZM) alloy.
1.1.4 Molybdenum Alloy 364—Powder metallurgy molybdenum-0.5% titanium-0.1% zirconium (TZM) alloy.
1.1.5 Molybdenum 365—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, low carbon.
1.1.6 Molybdenum Alloy 366—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, 30% tungsten alloy.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire as follows:
Molybdenum 360—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum.
Molybdenum 361—Unalloyed powder metallurgy molybdenum.
Molybdenum Alloy 363—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
Molybdenum Alloy 364—Powder metallurgy molybdenum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
Molybdenum 365—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, low carbon.
Molybdenum Alloy 366—Vacuum arc-cast molybdenum, 30 % tungsten alloy.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee B10 on Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys, this specification was withdrawn in January 2010 in accordance with section 10.5.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B387 – 90 (Reapproved 2001)
Standard Specification for
1
Molybdenum and Molybdenum Alloy Bar, Rod, and Wire
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B387; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
NOTE 1—This specification covers wire no smaller than 0.020 in. (0.51
1. Scope
mm) in diameter or of equivalent cross-sectional area. Specification F289
1.1 This specification covers unalloyed molybdenum and
covers diameters up to 0.020 in.
molybdenum alloy bar, rod, and wire as follows:
1.1.1 Molybdenum 360—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast mo-
4. Ordering Information
lybdenum.
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
1.1.2 Molybdenum 361—Unalloyed powder metallurgy mo-
the following information as applicable:
lybdenum.
4.1.1 Material number and temper designation (Section 1
1.1.3 Molybdenum Alloy 363—Vacuum arc-cast molybde-
and Table 3 ),
num–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
4.1.2 Product form (Section 3),
1.1.4 Molybdenum Alloy 364—Powder metallurgy molyb-
4.1.3 Chemical requirements (Table 1 and Table 2),
denum–0.5 % titanium–0.1 % zirconium (TZM) alloy.
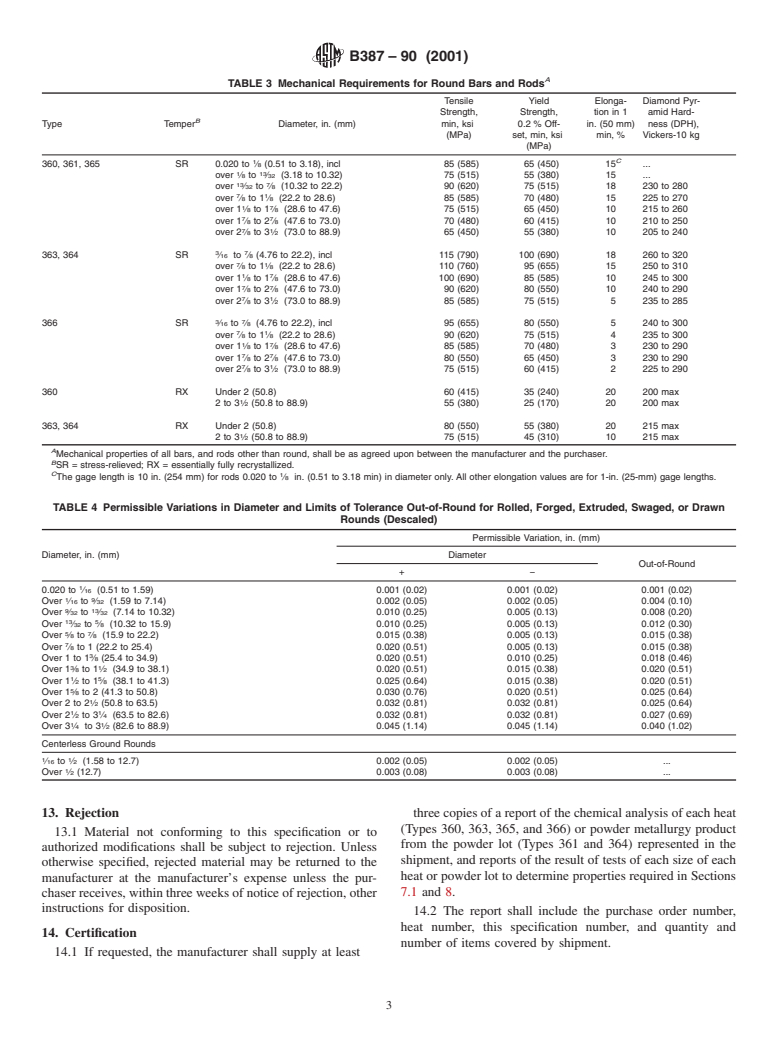
4.1.4 Mechanical requirements (Section 7),
1.1.5 Molybdenum 365—Unalloyed vacuum arc-cast mo-
4.1.5 Softening temperature (Section 8),
lybdenum, low carbon.
4.1.6 Tolerances (Section 9 and Table 4),
1.1.6 Molybdenum Alloy 366—Vacuum arc-cast molybde-
4.1.7 Workmanship and quality level requirements (Section
num, 30 % tungsten alloy.
10),
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
4.1.8 Packaging (Section 16),
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
4.1.9 Marking (Section 15),
for information purposes only.
4.1.10 Certification and reports (Section 14), and
4.1.11 Disposition of rejected material (Section 13).
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Materials and Manufacture
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
5.1 The various molybdenum mill products covered by this
F289 Specification for Molybdenum Wire and Rod for
specification shall be manufactured with the conventional
Electronic Applications
extrusion, forging, swaging, rolling, and drawing equipment
normally found in primary ferrous and nonferrous plants. The
3. Terminology
ingot metal for Molybdenum 360 and 365 and Molybdenum
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Alloys 363 and 366 is vacuum arc-melted in furnaces of a type
3.1.1 bar and rod—any straight product with a round,
suitable for reactive, refractory metals, and for Molybdenum
rectangular, hexagonal, or octagonal solid cross section, 4 in.
361 and 364 the metal is consolidated by powder metallurgy
(101.6 mm) in diameter or less, or of equivalent cross-sectional
methods.
area.
3.1.2 wire—any product furnished in coils or on spools or 6. Chemical Composition
reels.
6.1 The molybdenum and molybdenum alloy ingots and
billets for conversion to finished products covered by this
1
specification shall conform to the requirements of the chemical
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on
Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of composition prescribed in Table 1.
Subcommittee B10.04 on Molybdenum and Tungsten.
6.2 Check Analysis:
Current edition approved Sept. 28,1990. Published January 1991. Originally
6.2.1 Checkanalysisisananalysismadebythepurchaseror
published as B387 – 62 T. Last previous edition B387 – 85. DOI: 10.1520/B0387-
the manufacturer of the metal after it has been processed into
90R01.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
finished mill forms, and is either for the purpose of verifying
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
thecompositionofaheatorlotortodeterminevariationsinthe
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
composition within a heat or lot.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B387 – 90 (2001)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Element Material Number
360 361 363 364 365 366
C 0.030 max 0.010 max 0.010–0.030 0.010–0.040 0.010 max 0.030 max
A
O, max 0.0015 0.0070 0.0030 0.030 0.0015 0.0025
A
N, max 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002
Fe, max 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.010
Ni, max 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.005 0.002 0.002
Si, max 0.010 0.010 0.010 0.005 0.010 0.010
Ti . . 0.40–0.55 0.40–0.55 . .
W . . . . . 27–33
Zr . . 0.06–0.12 0.06–0.12 .
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.