ASTM E405-04(2018)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Wear Testing Rotary Operators for Windows
Standard Test Methods for Wear Testing Rotary Operators for Windows
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 These tests provide standard methods for evaluating the mechanical performance of the rotary-type window operators, while the operators are subjected to cyclic wear in opening and closing against the operating moment.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods describe the wear testing of gear-type rotary operating devices used for opening and closing windows (Note 1).
1.2 These test methods do not directly determine the effects of varying environmental conditions but may be employed after environmental exposure to evaluate the effect of such exposure.
1.3 These test methods are not intended to evaluate the structural adequacy of the operator in resisting the maximum force to which it may be subjected.
Note 1: Certain types of rotary window operators, such as torque-bar operators and telescopic operators cannot be tested by these test methods.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The metric equivalents of inch-pound units may be approximate.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement, see 9.1.2.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E405 − 04 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Test Methods for
Wear Testing Rotary Operators for Windows
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E405; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 These test methods describe the wear testing of gear- 3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
type rotary operating devices used for opening and closing nology E631 unless otherwise indicated.
windows (Note 1).
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 closing torque, n—a constant torque applied to the
1.2 These test methods do not directly determine the effects
input shaft when the operator is in the fully closed position,
of varying environmental conditions but may be employed
simulating the forces applied by a person tightly closing the
after environmental exposure to evaluate the effect of such
exposure. window and shall be expressed in pound-force-inches (or
newton metres).
1.3 These test methods are not intended to evaluate the
structural adequacy of the operator in resisting the maximum
3.2.2 fully closed position of the operator, n—the position of
force to which it may be subjected.
the operator with the window in a fully closed position.
NOTE 1—Certain types of rotary window operators, such as torque-bar
3.2.3 fully opened position of the operator, n—the position
operators and telescopic operators cannot be tested by these test methods.
ofthearmfrom2to5°shortoflockingthemechanismwiththe
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
window in an open position.
as the standard. The metric equivalents of inch-pound units
3.2.4 gear-type rotary operator, n—a mechanical operating
may be approximate.
device for opening and closing windows. It consists basically
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
of an operating handle turning an input shaft which drives a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
gear mechanism that causes an arm or arms to pivot, operating
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the window.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2.5 operating moment, n—the product of the applied force
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
and the length of the output lever arm from the point of load
For a specific hazard statement, see 9.1.2.
application to the pivot axis. It shall be expressed in pound-
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
force-inches (or newton metres). During a test cycle, the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
operating moment varies from a maximum value with the arm
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
in a centered position (peak operating moment) to some lesser
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
value as the arm is moved away from the centered position.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.2.6 operator test specimen, n—an entire, assembled gear-
type rotary operator, including the operating handle.
2. Referenced Documents
2 3.2.7 test cycle, n:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.7.1 Test Method A—fully opening and fully closing the
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
operator.
3.2.7.2 Test Method B—the number of rotations of the
1 handle to open and close the operator fully.
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51
3.2.8 test force, n, for Test Method A—the force applied to
on Performance of Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls.
the operator arm at the point of attachment. The required test
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2018. Published September 2018. Originally
force in pounds-force (or newtons) is equal to the specified
approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as E405–04 (2012). DOI:
10.1520/E0405-04R18.
peak operating moment in pound-force-inches (or newton
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
metres) divided by the distance in inches (or metres) measured
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
perpendicular to the line of action of the force from the pivot
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. axis to the point of attachment.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E405 − 04 (2018)
4. Summary of Test Methods
4.1 These test methods consist of subjecting the rotary
operator to an operating moment against which the operator
shall work in a cyclic function of opening and closing. Test
Method A evaluates the operator for its ability to resist wear
through a given number of cycles against the test moment with
a specified torque applied to the input shaft. Test Method B
evaluates only the rotating fingergrip portion of handle assem-
blies having rotating fingergrips.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 These tests provide standard methods for evaluating the
mechanical performance of the rotary-type window operators,
while the operators are subjected to cyclic wear in opening and
closing against the operating moment.
6. Apparatus
6.1 The apparatus described is general in nature and any
arrangement of equipment capable of performing the test
procedure within the allowable tolerances is permitted.
6.2 Test Method A:
6.2.1 The test apparatus for Test Method A shall consist of
a frame for mounting the rotary operator with the operator
arm(s) centered (approximately the center of travel); test
weights up to 5 lb (2280 g) accurate to within 61.0 % or test
weights above 5 lb (2280 g) accurate to within 60.5 %,
attached by flexible cable to the arm(s) to provide the required
test forces; an attachment bolt fastening the cable to the arm; a
torque-limiting clutch, whose output is within 615 % of the
specified closing torque, attached to the handle drive mecha-
nism in line with the operator input shaft and driven by a
reversible motor; and limit switching devices to effect reversal
of rotation at the fully open and fully closed operator positions FIG. 1 Typical Operator Test Apparatus
(see Fig. 1).
6.2.2 The arm or the test attachment bolt through the arm
shall bear against the test frame, if necessary, to prevent the
reversible motor drives a horizontal shaft to which the test
arm from closing beyond the nominal fully closed position.
handle is attached.The shaft shall be obtained by removing the
The cables shall be adjustable to provide an equal tension force
input shaft from an operator or as an additionally supplied part.
in both the cables when the test attachment point and pivot are
The handle end of the shaft shall be identical to the input shafts
centered.
of the test operators. The timing device effects a reversal of the
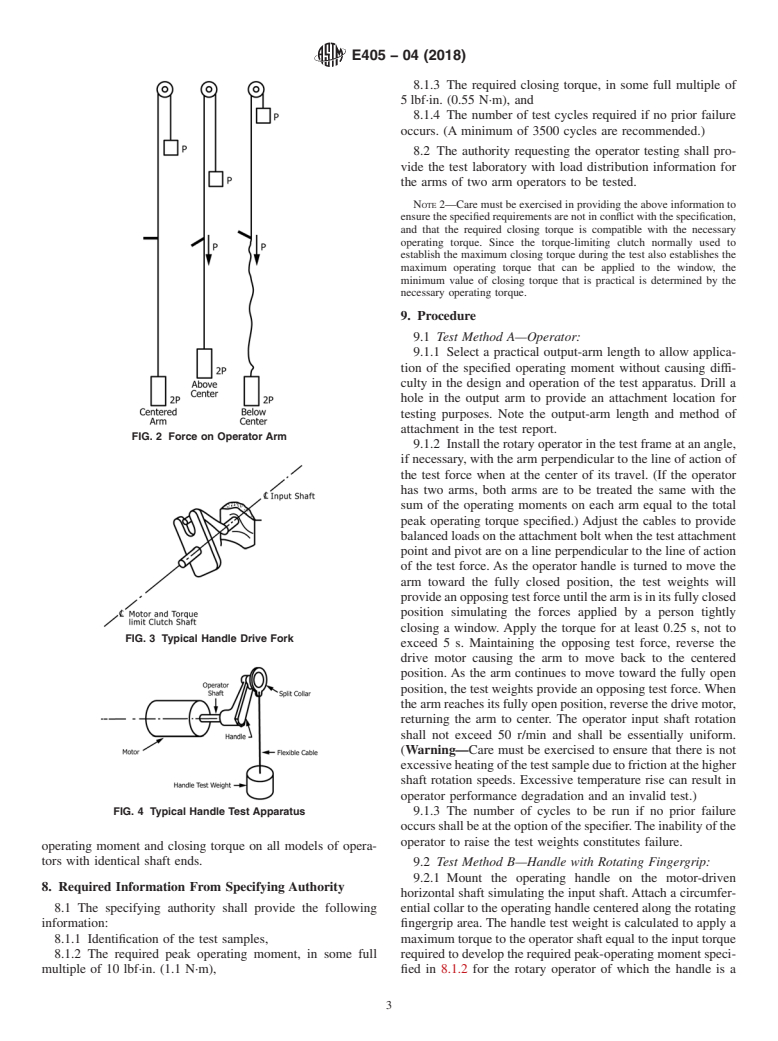
6.2.3 Fig. 2 shows how, if a vertical arrangement were used,
motor at required intervals. The split collar carries the test
to test a single-arm operator, a system of two test weights, an
weight and attaches to the rotating fingergrip of the handle
upper weight equal to the test force, and a lower weight of
causing one revolution of the fingergrip with respect to the
twice the test force would act to provide the required down-
handle for each revolution of the handle (see Fig. 4).
ward force when the arm is above the center position of its
travel and the same force upward when the arm is below the
7. Test Specimens
centerofitstravel.Foroperatorswithtwoarms,sumofthe
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.