ASTM D2235-04(2011)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Solvent Cement for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe and Fittings
Standard Specification for Solvent Cement for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe and Fittings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers solvent cement for joining acrylonitrile-butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic pipe and fittings for pressure and nonpressure systems.
1.2 Recommendation for using solvent cement for joining acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) plastic pipe and fittings is given in Appendix X1. Satisfactory joining of pipe and fittings cannot be made in the presence of water, as water destroys the bonding ability of solvent cement; therefore, all materials must be dry for satisfactory joining.
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2235 −04 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Specification for
Solvent Cement for Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS)
Plastic Pipe and Fittings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2235; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1084 Test Methods for Viscosity of Adhesives
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
1.1 This specification covers solvent cement for joining
tics
acrylonitrile-butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic pipe and fittings
D3965 ClassificationSystemandBasisforSpecificationsfor
for pressure and nonpressure systems.
Rigid Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Materials
1.2 Recommendation for using solvent cement for joining
for Pipe and Fittings
acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) plastic pipe and fittings
F402 Practice for Safe Handling of Solvent Cements,
is given in Appendix X1. Satisfactory joining of pipe and
Primers, and Cleaners Used for Joining Thermoplastic
fittings cannot be made in the presence of water, as water
Pipe and Fittings
destroys the bonding ability of solvent cement; therefore, all
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
materials must be dry for satisfactory joining.
F493 Specification for Solvent Cements for Chlorinated
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes,
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Plastic Pipe and Fittings
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
2.2 Federal Standard:
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall 3
Fed. Std. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
2.3 Military Standard:
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
MIL STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
2.4 National Sanitation Foundation Standards:
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Standard No. 14 Plastic Piping Components and Related
and are not considered standard.
Materials
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
Standard No. 61 for DrinkingWater Systems Components—
test methods portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
Health Effects
standarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,
ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuser
3. Terminology
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
3.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminologies D883
tions prior to use.
and F412. Abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology
D1600 unless otherwise indicated. The abbreviation for
2. Referenced Documents
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene plastic is ABS.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D329 Specification for Acetone
3.2.1 solventcement—adhesivemadebydissolvingaplastic
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
resin or compound in a suitable solvent or mixture of solvents.
D740 Specification for Methyl Ethyl Ketone
The solvent cement dissolves the surfaces of the pipe and
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
fittings to form a bond between the mating surfaces provided
the proper cement is used for the particular materials and
proper techniques are followed.
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2011. Published March 2011. Originally
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved 2004 as D2235 – 04. DOI:
10.1520/D2235-04R11. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM dodssp.daps.dla.mil.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd.,Ann
the ASTM website. Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.nsf.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D2235−04 (2011)
4. Classification 7.1.2 TestConditions—Conduct tests at 73.4 6 3.6°F (23 6
2°C), unless otherwise specified in the test methods or in this
4.1 Solvent Cement shall be acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene
specification.
plastic resin dissolved in either of the following solvents:
(1) methyl ethyl ketone 7.2 Viscosity:
(2) a blend of methyl ethyl ketone and acetone, with acetone 7.2.1 The samples for test shall be representative of the
constituting no more than 25 % of the solvent blend by weight. material under consideration. One sample for every batch shall
be tested in accordance with 7.2.2.
NOTE 1—It is recommended that solvent cements made to this speci-
7.2.2 MeasuretheviscosityinaccordancewithMethodBof
ficationnot be orange since that color is recommended for use with CPVC
Test Methods D1084, except that conditioning to temperature
solvent cement under Specification F493.
equilibrium only is required. For qualification purposes, use a
Model RVF viscometer, a speed of 10 r/min, and the spindle
5. Materials
that, by trial, gives the closest reading to center range of scale
5.1 Material Specification—Virgin ABS material shall con-
for the cement being tested. Other speeds are used for
form to the requirements prescribed in Specification D3965
qualification purposes.
withaminimumcellclassificationof1-1-2-2-2orequivalentto
7.3 Total Solids:
the cell classification for the material being joined.
7.3.1 Apparatus:
5.2 Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic—
7.3.1.1 Ointment Tins—Style No. 12, 1 oz (30 mL) all
Plastic containing polymers in which the minimum butadiene
metal.
content is 6 %, the minimum acrylonitrile content is 15 %, the
7.3.1.2 Vacuum Oven.
minimum styrene or substituted styrene content, or both, is
7.3.1.3 Desiccator.
15 %, and the maximum content of all other monomers is not
7.3.1.4 Analytical Balance.
more than 5 %.
7.3.2 Procedure—Stir the sample thoroughly with a spatula
5.3 Rework Material—Only clean regrind material con-
before weighing. Weigh 3.0 6 0.5 g of the sample into a tared
forming to the requirements of this specification may be used.
ointment tin. Place tin into the vacuum oven and heat at 248°F
(120°C) for 45 min. Vacuum must be continually in operation
5.4 MethylEthyl-Ketone— Commercial or industrial grade
todrawoffflammablesolventsandshouldbemaintainedat0.6
of MEK shall be used which complies with Specification
in. Hg (15 mm Hg) minimum. Remove the tin from the oven
D740.
andcapimmediately.Placeinadesiccatoruntilcooledtoroom
5.5 Acetone—Commercial or industrial grade of acetone
temperature. Weigh the tin and dried sample to the nearest
shall be used which complies with Specification D329.
0.015 grains (1 mg).
NOTE 3—This material is usually nonhomogeneous and shall be
6. Requirements
thoroughly stirred before weighing. The weighing shall also be accom-
6.1 Resin Content—The ABS resin content shall be 15 %
plished quickly to avoid loss of solvent by volatization.
minimum when tested in accordance with 7.3.
7.3.3 The use of a vacuum oven is mandatory for drying the
specimen because it has no exposed heating surface nor an
6.2 Dissolution—The cement shall be capable of dissolving
10 % by weight of the plastic compound used in the pipe or openflame,thusavoidingthedangerofflashing.Theovenalso
provides an open vacuum to exhaust solvent fumes.
fitting, and still be free flowing and not contain lumps or
undissolved resin particles. 7.3.4 The specimen shall be left in the oven for 45 min and
no longer. Specimens left in for1hor more show a definite
6.3 The cement shall be free flowing and shall not contain
increase in weight.
lumps,undissolvedparticles,orforeignmatter.Itshallshowno
7.3.5 Calculation—Calculate the percentage total solids,
gelation or separation that cannot be removed by stirring.
TS, as follows:
6.4 Viscosity—The minimum viscosity shall be 100 cP (100
TS,%= ((B − A)/(C − A)) × 100
mPa·s) when tested in accordance with 7.2.2.
where:
6.5 Lap Shear Strength—The minimum average lap shear
A = weight of ointment tin,
strength shall be 800 psi (5.5 MPa) when tested in accordance
B = weight of tin and specimen after drying, and
with 7.4.
C = weight of tin and specimen before drying.
NOTE 2—The specified shear strength value is used to evaluate the
7.3.6 Precision—Duplicate samples shall be tested for best
cement and should not be used for designing pipe joints.
results. Duplicate results obtained by the same analyst, on the
same material, on the same day, in the same laboratory are
7. Test Methods
suspect if they differ by more than 0.52 % absolute. This
7.1 The properties enumerated in this specification shall be
procedure has a standard deviation of 0.13.
determined in accordance with the following methods:
7.4 Lap Shear Strength (Qualification Tests):
7.1.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 73.4 6
3.6°F (23 6 2°C) for not less than 40 h prior to test in
accordance with Procedure A of Practice D618, for those tests
Labline Duo-Vac vacuum oven, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory for
where conditioning is required. this purpose.
D2235−04 (2011)
7.4.1 Number of Specimens—A minimum of seven speci-
mens shall be tested for the requirement specified in 6.5.
7.4.2 Cut sections 1 by 1 in. (25 by 25 mm) and 1 by 2 in.
(25 by 50 mm) from 0.25-in. (6-mm) thick ABS sheets. One
section of each size is required for each specimen (Fig. 1).
7.4.3 Clean the surfaces to be adhered with a cloth damp-
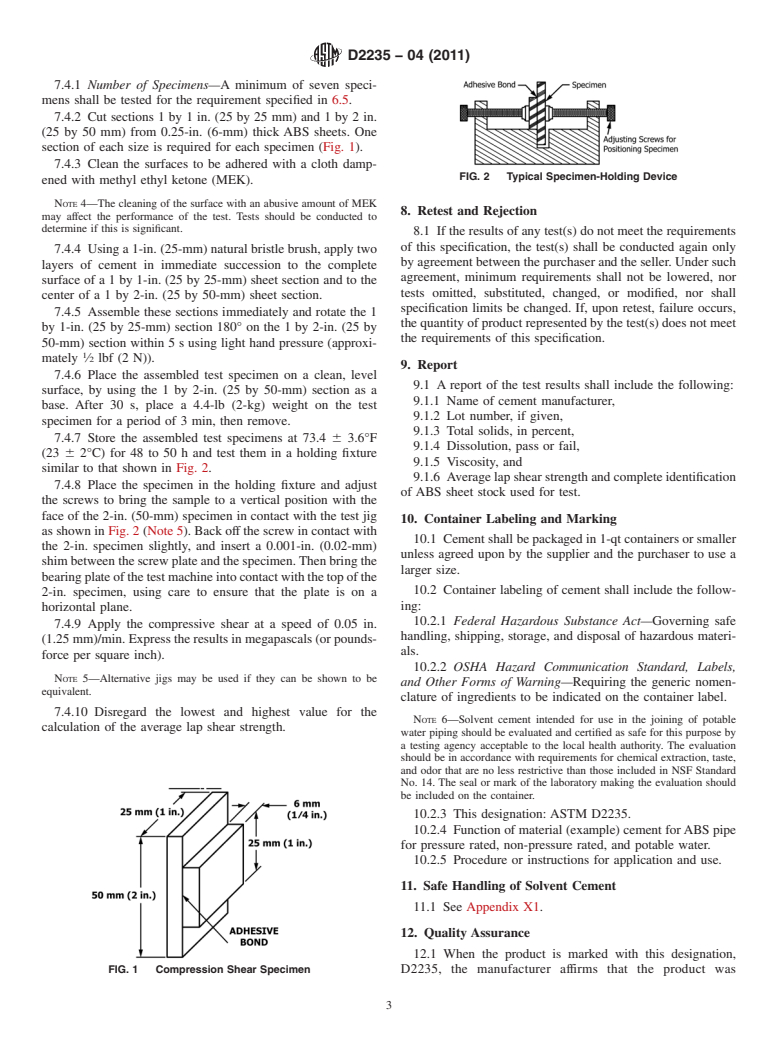
FIG. 2 Typical Specimen-Holding Device
ened with methyl ethyl ketone (MEK).
NOTE 4—The cleaning of the surface with an abusive amount of MEK
8. Retest and Rejection
may affect the performance of the test. Tests should be conducted to
determine if this is significant.
8.1 If the results of any test(s) do not meet the requirements
of this specification, the test(s) shall be conducted again only
7.4.4 Using a 1-in. (25-mm) natural bristle brush, apply two
by agreement between the purchaser and the seller. Under such
layers of cement in immediate succession to the complete
agreement, minimum requirements shall not be lowered, nor
surface ofa1by 1-in. (25 by 25-mm) sheet section and to the
tests omitted, substituted, changed, or modified, nor shall
center ofa1by 2-in. (25 by 50-mm) sheet section.
specification limits be changed. If, upon retest, failure occurs,
7.4.5 Assemble these sections immediately and rotate the 1
the quantity of product represented by the test(s) does not meet
by 1-in. (25 by 25-mm) section 180° on the 1 by 2-in. (25 by
the requirements of this specification.
50-mm) section within 5 s using light hand pressure (approxi-
mately ⁄2 lbf (2 N)).
9. Report
7.4.6 Place the assembled test specimen on a clean, level
9.1 A report of the test results shall include the following:
surface, by using the 1 by 2-in. (25 by 50-mm) section as a
9.1.1 Name of cement manufacturer,
base. After 30 s, place a 4.4-lb (2-kg) weight on the test
9.1.2 Lot number, if given,
specimen for a period of 3 min, then remove.
9.1.3 Total solids, in percent,
7.4.7 Store the assembled test specimens at 73.4 6 3.6°F
9.1.4 Dissolution, pass or fail,
(23 6 2°C) for 48 to 50 h and test them in a holding fixture
9.1.5 Viscosity, and
similar to that shown in Fig. 2.
9.1.6 Average lap shear strength and complete identification
7.4.8 Place the specimen in the holding fixture and adjust
of ABS sheet stock used for test.
the screws to bring the sample to a vertical position with the
face of the 2-in. (50-mm) specimen in contact with the test jig
10. Container Labeling and Marking
as shown in Fig. 2 (Note 5). Back off the screw in contact with
10.1 Cement shall be packaged in 1-qt containers or smaller
the 2-in. specimen slightly, and insert a 0.001-in. (0.02-mm)
unless agreed upon by the supplier and the purchaser to use a
shimbetweenthescrewplateandthespecimen.Thenbringthe
larger size.
bearingplateofthetestmachineintocontactwiththetopofthe
10.2 Container labeling of cement shall include the follow-
2-in. specimen, using care to ensure that the plate is on a
ing:
horizontal plane.
10.2.1 Federal Hazardous Substance Act—Governing safe
7.4.9 Apply the compressive shear at a speed of 0.05 in.
handling, shipping, storage, and disposal of hazardous materi-
(1.25 mm)/min. Express the results in megapascals (or pounds-
als.
force per square inch).
10.2.2 OSHA Hazard Communication Standard, Labels,
NOTE 5—Alternative jigs may be used if they can be shown to be
and Other Forms of Warning—Requiring the generic nomen-
equivalent.
clature of ingredients to be indicated on the container label.
7.4.10 Disregard the lowest and highest value for the
NOTE 6—Solvent cement intended for use in the joining of potable
calculation of the average lap shear strength.
water piping should be evaluated and certified as safe for this purpose by
a testing agency acceptable to the local health authority. The evaluation
should be in accordance with requirements for chemical extraction, taste,
and odor that are no less restrictive than those included in NSF Standard
No. 14. The seal or mark of the laboratory making the evaluation should
be included on the container.
10.2.3 This designation: ASTM D2235.
10.2.4 Function of material (example) cement forABS pipe
for pressure rated, non-pressure rated, and potable water.
10.2.5 Procedure or instructions for application and use.
11. Safe Handling of Solvent Cement
11.1 See Appendix X1.
12. Quality Assurance
12.1 When the product is marked with this designation,
FIG. 1 Compression Shear Specimen D2235, the manufacturer affirms that the product was
D2235−04 (2011)
manufactured, inspected, sampled, and tested in accordance
with this specification and has been found to meet the
requirements of this specification.
SUPPLEMENTARY REQUIREMENTS
This requirement applies whenever a regulatory authority or user calls for the product to be used to
convey or to be in contact with potable water.
NOTE S2.1—In U.S. federal contracts, the contractor is responsible for
S1. Potable Water Requirement—Products intended for
inspection.
contact with potable water shall be evaluated, tested, and
S3. Packaging and Product Marking for U.S. Government
certified for conformance with ANSI/NSF Standard No.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.