ASTM E911-98(2004)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Glass Stopcocks with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Plugs
Standard Specification for Glass Stopcocks with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Plugs
ABSTRACT
This specification covers dimensional interchangeability requirements of glass stopcocks with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plugs for use in ordinary laboratory and industrial applications. However, it does not cover the design characteristics of the stopcock-plug assembly nor the physical or chemical properties of the materials used. Glass stopcocks with glass plugs or stopcocks for use in high-vacuum applications are not covered as well. The plug shall be manufactured from PTFE material of Types I and IV, extrusion and molding grade resins. Stopcocks, on the other hand, shall be manufactured from glass into one of various types: single straight-bore stopcock, single oblique-bore stopcock, double oblique-bore (three-way) stopcock, T-bore stopcock, or angled-bore stopcock. Tests for dimension conformity, taper, leak rate, and performance shall be performed and shall conform to the requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers standard dimensional requirements for obtaining, within practical limits, interchangeability in glass stopcocks (Note 1) with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plugs for ordinary laboratory and industrial applications. It covers dimensional interchangeability only and does not involve design characteristics of the item except where specified, nor does it involve physical or chemical characteristics of the material used. It does not cover glass stopcocks with glass plugs (Note 2) or stopcocks intended for use in high-vacuum work.
Note 1—A stopcock is defined as consisting of a plug and barrel in assembled configuration.
Note 2—Glass stopcocks with glass plugs are covered by Specification E 675.
Note 3—The dimensions pertaining to stopcocks were taken from the now obsolete Commercial Standard CS 21-58 of the U.S. Department of Commerce and Product Standard PS 28-70 published by the National Bureau of Standards.
Note 4—Although glass is the most common material for stopcocks, other materials may be used as specified. Stopcocks constructed from glass shall be in accordance with Specifications E 438 and E 671.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: E911 – 98 (Reapproved 2004)
Standard Specification for
Glass Stopcocks with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Plugs
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E911; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope E920 Specification for Commercially Packaged Laboratory
Apparatus
1.1 This specification covers standard dimensional require-
E921 Specification for Export Packaged Laboratory Appa-
ments for obtaining, within practical limits, interchangeability
ratus
in glass stopcocks (Note 1) with polytetrafluoroethylene
E1133 Practice for Performance Testing of Packaged Labo-
(PTFE) plugs for ordinary laboratory and industrial applica-
ratory Apparatus for United States Government Procure-
tions. It covers dimensional interchangeability only and does
ments
not involve design characteristics of the item except where
E1157 Specification for Sampling and Testing of Reusable
specified, nor does it involve physical or chemical character-
Laboratory Glassware
istics of the material used. It does not cover glass stopcocks
2.2 Other Standard:
with glass plugs (Note 2) or stopcocks intended for use in
PS 28-70 Glass Stopcocks With Polytetrafluoroethylene
high-vacuum work.
(PTFE) Plugs
NOTE 1—A stopcock is defined as consisting of a plug and barrel in
assembled configuration.
3. Material
NOTE 2—Glass stopcocks with glass plugs are covered by Specification
3.1 The PTFE material used to manufacture the plugs shall
E675.
be in accordance with the requirements of Specification D1457
NOTE 3—The dimensions pertaining to stopcocks were taken from the
Types I and IV, extrusion and molding grade resins.
now obsolete Commercial Standard CS 21-58 of the U.S. Department of
Commerce and Product Standard PS 28-70 published by the National
4. Requirements for Single Straight-Bore Stopcocks
Bureau of Standards.
NOTE 4—Although glass is the most common material for stopcocks,
4.1 The designations and dimensions for single straight-
other materials may be used as specified. Stopcocks constructed from
bore stopcocks are shown in Fig. 1 and Table 1.
glass shall be in accordance with Specifications E438 and E671.
4.2 Taper (Note 3)—All straight-bore stopcocks shall have
a taper of 2 6 0.006 mm of diameter per 10 mm of length (1
2. Referenced Documents
to 5).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insu- NOTE 5—The lines of contact of the mating surfaces should form a
conical section having a taper of 2 6 0.006 mm per 1 cm of axial length
lation
(before compression of the plug surface) for an axial distance of at least
D1457 Specification for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
10 mm on each side of the bore.
Molding and Extrusion Materials
E438 Specification for Glasses in Laboratory Apparatus
5. Requirements for Single Oblique-Bore Stopcocks
E671 Specification for Maximum Permissible Thermal Re-
5.1 The designations and dimensions for single oblique-
sidual Stress in Annealed Glass Laboratory Apparatus
bore stopcocks are shown in Fig. 2 and Table 2.
E675 Specification for Interchangeable Taper-Ground Stop-
5.2 Taper (Note 4)—All single oblique-bore stopcocks shall
cocks And Stoppers
have a taper of 2 6 0.006 mm of diameter per 10 mm of length
(1 to 5).
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E41 on
Laboratory Apparatus and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E41.01 on 6. Requirements for Double Oblique-Bore (3-Way)
Apparatus.
Stopcocks
Current edition approved May 1, 2004. Published May 2004. Originally
6.1 The designations and dimensions for double-oblique-
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as E911 – 98. DOI:
10.1520/E0911-98R04.
bore stopcocks are shown in Fig. 3 and Table 3.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Commercial Standards and Product Standards are available from National
the ASTM website. Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100 Bureau Dr., Stop 3460,
Withdrawn. Gaithersburg, MD 20899-3460.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E911 – 98 (2004)
FIG. 1 Stopcock
FIG. 3 Double Oblique-Bore (3-Way) Stopcock
TABLE 1 Single Straight-Bore Stopcocks
8. Test Methods
Stopcock Designation Diameter of Plug at
and Bore of Hole in Centerline of Bore Length of Shell E,mm 8.1 Dimensions—Determine dimensions in accordance with
Plug B,mm D,mm
Method B of Test Methods D374, except that micrometre
111 6 0.06 25 6 0.5
calipers graduated to 0.01 mm shall be used.
211 6 0.06 25 6 0.5
8.2 Taper —Measure taper by using a sine bar and plate or
3 15.2 6 0.10 30 6 0.5
an air gage.
4 15.2 6 0.10 30 6 0.5
616 6 0.20 35 6 0.5
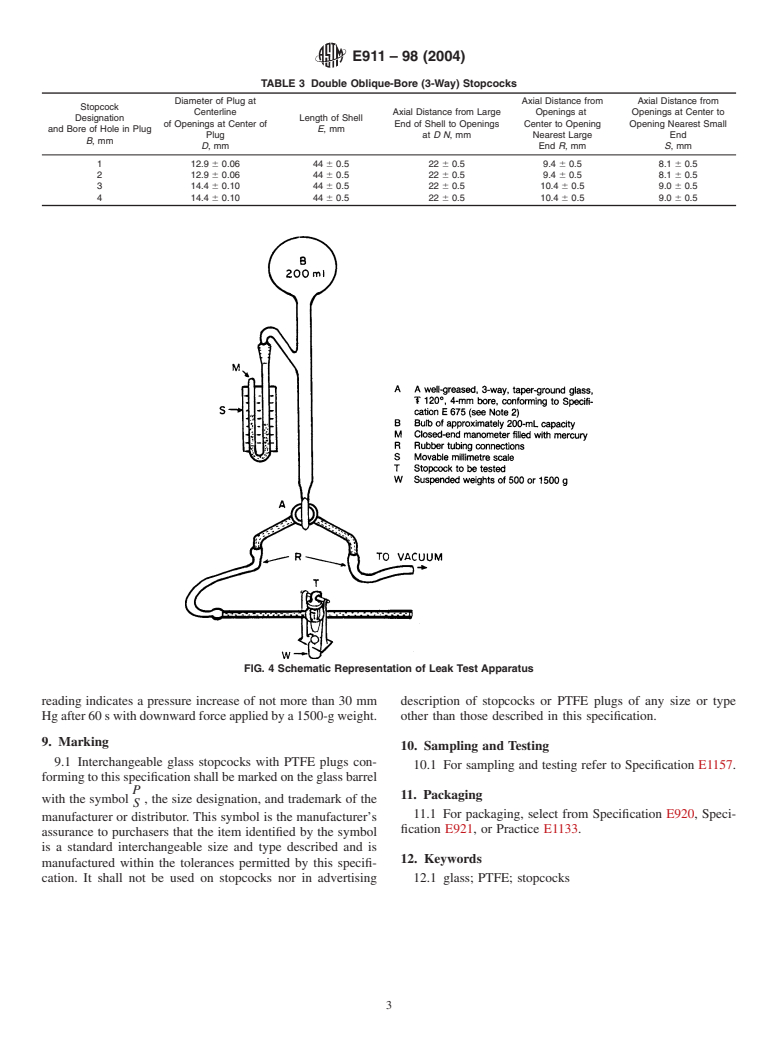
8.3 Leak Rate—Use the leak test apparatus illustrated in
Fig.4,oronefunctionallysimilartoit.Suspendweightsof500
to 1500 g from the test plug to apply downward force for
properly seating the plug in the barrel. Conduct the test as
follows:
8.3.1 Check the apparatus setup, Fig. 1, for any leakage
under the test conditions before testing any stopcocks, T.
8.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.