ASTM E283-04(2012)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Specimen
Standard Test Method for Determining Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Specimen
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is a standard procedure for determining the air leakage characteristics under specified air pressure differences at ambient conditions.
Note 2—The air pressure differences acting across a building envelope vary greatly. The factors affecting air pressure differences and the implications or the resulting air leakage relative to the environment within buildings are discussed in the literature. , , These factors should be fully considered in specifying the test pressure differences to be used.
Rates of air leakage are sometimes used for comparison purposes. Such comparisons may not be valid unless the components being tested and compared are of essentially the same size, configuration, and design.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a standard laboratory procedure for determining the air leakage rates of exterior windows, curtain walls, and doors under specified differential pressure conditions across the specimen. The test method described is for tests with constant temperature and humidity across the specimen.
1.2 This laboratory procedure is applicable to exterior windows, curtain walls, and doors and is intended to measure only such leakage associated with the assembly and not the installation. The test method can be adapted for the latter purpose.
Note 1—Performing tests at non-ambient conditions or with a temperature differential across the specimen may affect the air leakage rate. This is not addressed by this test method.
1.3 This test method is intended for laboratory use. Persons interested in performing field air leakage tests on installed units should reference Test Method E783.
1.4 Persons using this procedure should be knowledgeable in the areas of fluid mechanics, instrumentation practices, and shall have a general understanding of fenestration products and components.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statement see Section 7.
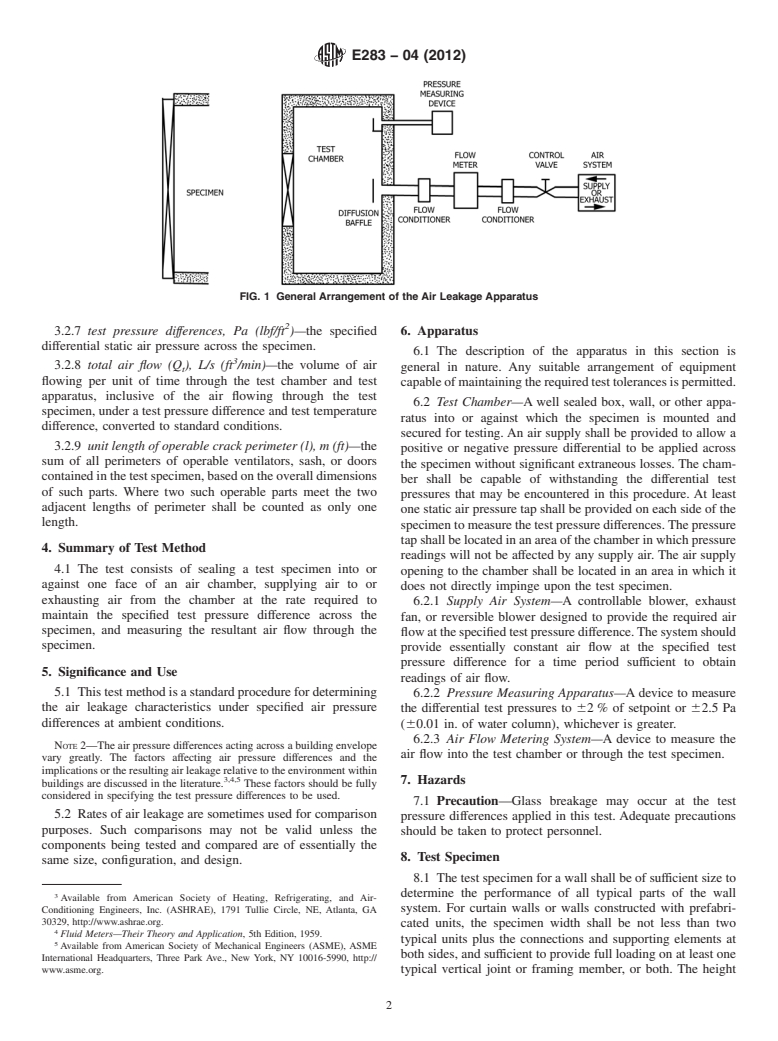
FIG. 1 General Arrangement of the Air Leakage Apparatus
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E283 −04 (Reapproved 2012)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows,
Curtain Walls, and Doors Under Specified Pressure
1
Differences Across the Specimen
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E283; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversastandardlaboratoryprocedure 2.1 ASTM Standards:
for determining the air leakage rates of exterior windows, E631Terminology of Building Constructions
curtain walls, and doors under specified differential pressure E783Test Method for Field Measurement of Air Leakage
conditions across the specimen. The test method described is Through Installed Exterior Windows and Doors
for tests with constant temperature and humidity across the
3. Terminology
specimen.
3.1 Definitions—Terms used in this standard are defined in
1.2 This laboratory procedure is applicable to exterior
Terminology E631.
windows, curtain walls, and doors and is intended to measure
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
only such leakage associated with the assembly and not the
2 3 2
3.2.1 air leakage rate (q or q), L/(s·m ) (ft /min·ft ), or
A l
installation. The test method can be adapted for the latter
3
L/(s·m) (ft /min·ft) —the air leakage per unit of specimen area
purpose.
(A) or per unit length of operable crack perimeter (l).
NOTE 1—Performing tests at non-ambient conditions or with a tem-
3 3
3.2.2 extraneous air leakage (Q ), m /s (ft /min)—the vol-
e
perature differential across the specimen may affect the air leakage rate.
ume of air flowing per unit of time through the test chamber
This is not addressed by this test method.
and test apparatus, exclusive of the air flowing through the test
1.3 This test method is intended for laboratory use. Persons
specimen, under a test pressure difference and test temperature
interestedinperformingfieldairleakagetestsoninstalledunits
difference, converted to standard conditions.
should reference Test Method E783.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—Extraneous leakage is the sum of all
1.4 Persons using this procedure should be knowledgeable
leakage other than that intended to be measured by the test.
in the areas of fluid mechanics, instrumentation practices, and
3.2.3 specimen—theentireassembledunitsubmittedfortest
shallhaveageneralunderstandingoffenestrationproductsand
as described in Section 7.
components.
3
3.2.4 specimen air leakage (Q ), L/s (ft /min)—the volume
s
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
of air flowing per unit of time through the specimen under a
standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
test pressure difference and test temperature difference, con-
conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for informa-
verted to standard conditions.
tion only and are not considered standard.
2 2
3.2.5 specimen area (A), m (ft )—the area determined by
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the overall dimensions of the frame that fits into the rough
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
opening.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.6 standard test conditions—in this test method, dry air
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
at:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
Pressure—101.3 kPa (29.92 in. Hg)
statement see Section 7.
Temperature—20.8°C (69.4°F)
3 3
Air Density—1.202 kg/m (0.075 lbm/ft )
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51
2
on Performance of Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2012. Published May 2012. Originally contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as E283–2004. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/E0283-04R12. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E283−04 (Reapproved 2012)
1
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
E283−04 (2012)
FIG. 1 General Arrangement of the Air Leakage Apparatus
2
3.2.7 test pressure differences, Pa (lbf/ft )—the specified
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.