ASTM D4282-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by Microdiffusion
Standard Test Method for Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by Microdiffusion
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is useful in distinguishing between the potentially available free cyanide (total cyanide) and the free cyanide actually present.
5.2 This test method provides a convenient technique for making on-site free cyanide determinations.
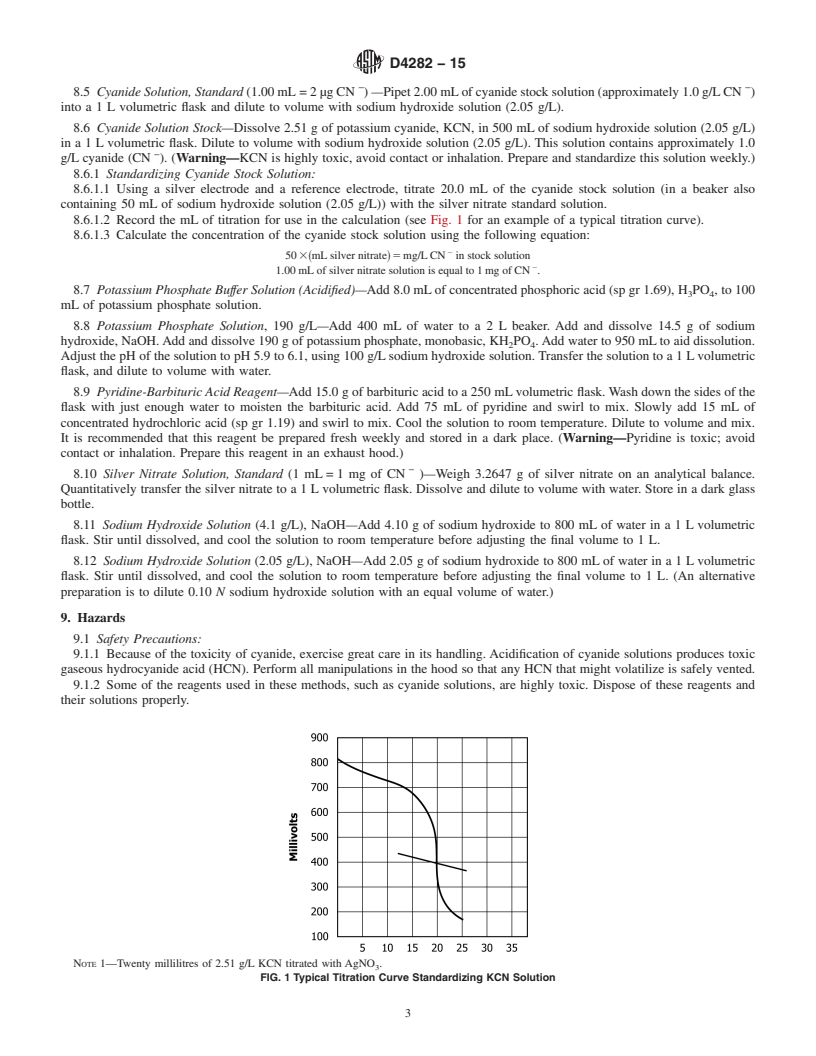
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of free cyanides in waters and wastewaters. Free cyanide is here defined as the cyanide which diffuses as cyanide (HCN), at room temperature, from a solution at pH 6.2
1.2 This test method does not include complexes that resist dissociation, such as hexacyanoferrates and gold cyanide, nor does it include thiocyanate and cyanohydrin.
1.3 This test method may be applied to water and wastewater samples containing free cyanide from 10 to 150 μg/L. Greater concentrations may be determined by appropriate dilution.
1.4 This test method has been fully validated by collaborative testing as specified by Practice D2777.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 8.6, 8.9, Section 9, and 12.2.1.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4282 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by
1
Microdiffusion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4282; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1192Guide for Equipment for Sampling Water and Steam
4
in Closed Conduits (Withdrawn 2003)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of free
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
cyanides in waters and wastewaters. Free cyanide is here
D2777Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
defined as the cyanide which diffuses as cyanide (HCN), at
2 Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
room temperature, from a solution at pH 6.
D3370Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
1.2 This test method does not include complexes that resist
D3856Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories
dissociation, such as hexacyanoferrates and gold cyanide, nor
Engaged in Analysis of Water
does it include thiocyanate and cyanohydrin.
D4210Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Proce-
dures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
1.3 This test method may be applied to water and wastewa-
4
ter samples containing free cyanide from 10 to 150 µg/L. (Withdrawn 2002)
D5788Guide for Spiking Organics into Aqueous Samples
Greater concentrations may be determined by appropriate
dilution. D5789Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
for Standard Test Methods for Organic Constituents
1.4 This test method has been fully validated by collabora-
4
(Withdrawn 2002)
tive testing as specified by Practice D2777.
D5847Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
E275PracticeforDescribingandMeasuringPerformanceof
standard.
Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3. Terminology
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1 Definitions:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
Terminology D1129.
statements, see 8.6, 8.9, Section 9, and 12.2.1.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 free cyanide—those simple cyanides or loosely held
2. Referenced Documents
cyanide complexes that diffuse at pH 6, at room temperature.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129Terminology Relating to Water
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The reactions are carried out in a microdiffusion cell.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D19 on Water
4.2 The sample is treated with cadmium ion to precipitate
andisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.06onMethodsforAnalysisfor
the hexacyanoferrates.
Organic Substances in Water.
Current edition approved July 15, 2015. Published July 2015. Originally
4.3 The sample is buffered at pH 6 and allowed to stand for
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D4282–02 (2015).
4h.
DOI: 10.1520/D4282-R15.
2
The paper by J. M. Kruse and L. E. Thibault “Determination of Free Cyanide
4.4 The HCN diffuses into sodium hydroxide solution.
in Ferro- and Ferricyanides,”Analytical Chemistry, 45(13): 2260–2261; 1973 Nov.,
recommendsadiffusionatpH7.TheANSImodification(ANSIPH4.41-1978)uses 4.5 An aliquot of the sodium hydroxide solution is treated
pH 6. Using the conditions of the ANSI method, diffusion is completed within 4
with chloramine-T, and the cyanogen chloride formed is
hoursatpH6.LongerdiffusiontimewasrequiredatpH7onthesamplesanalyzed.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4282 − 15
reacted with barbituric acid in pyridine. The absorbance of the 8.3 Cadmium Chloride Solution (10 g/L), CdCl —Dissolve
2
color formed is measured using a spectrophotometer at a 10.0 g of anhydrous cadmium chloride in 750 mL of water in
wavelength of 580 nm. a 1 L volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with water.
8.4 Chloramine-T
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4282 − 02 (Reapproved 2015) D4282 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Free Cyanide in Water and Wastewater by
1
Microdiffusion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4282; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of free cyanides in waters and wastewaters. Free cyanide is here defined as the
2
cyanide which diffuses as cyanide (HCN), at room temperature, from a solution at pH 6.
1.2 This test method does not include complexes that resist dissociation, such as hexacyanoferrates and gold cyanide, nor does
it include thiocyanate and cyanohydrin.
1.3 This test method may be applied to water and wastewater samples containing free cyanide from 10 to 150 μg/L. Greater
concentrations may be determined by appropriate dilution.
1.4 This test method has been fully validated by collaborative testing as specified by Practice D2777.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 8.6, 8.9, Section 9, and 12.2.1.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
4
D1192 Guide for Equipment for Sampling Water and Steam in Closed Conduits (Withdrawn 2003)
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D3856 Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories Engaged in Analysis of Water
D4210 Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Procedures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data (Withdrawn
4
2002)
D5788 Guide for Spiking Organics into Aqueous Samples
D5789 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Organic Constituents (Withdrawn
4
2002)
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
E275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions: For a definition of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D1129.
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to Terminology D1129.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.06 on Methods for Analysis for
Organic Substances in Water.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2015July 15, 2015. Published March 2015July 2015. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 20102015 as
D4282 – 02 (2010).(2015). DOI: 10.1520/D4282-02R15.10.1520/D4282-R15.
2
The paper by J. M. Kruse and L. E. Thibault “Determination of Free Cyanide in Ferro- and Ferricyanides,” Analytical Chemistry, 45(13): 2260–2261; 1973 Nov.,
recommends a diffusion at pH 7. The ANSI modification (ANSI PH 4.41-1978) uses pH 6. Using the conditions of the ANSI method, diffusion is completed within 4 hours
at pH 6. Longer diffusion time was required at pH 7 on the samples analyzed.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4282 − 15
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 free cyanide—refers to those simple cyanides or loosely held cyanide complexes of cyanide that diffuse at pH 6, at room
temperature.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The reactions are carried out in a microdiffusion cell.
4.2 The sample is treated with cadmium ion to precipitate the hexacyanoferrates.
4.3 The sample is buffered at pH
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.