ASTM E331-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Skylights, Doors, and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure Difference
Standard Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Skylights, Doors, and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure Difference
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is a standard procedure for determining the resistance to water penetration under uniform static air pressure differences. The air-pressure differences acting across a building envelope vary greatly. These factors should be fully considered prior to specifying the test pressure difference to be used.
Note 1—In applying the results of tests by this test method, note that the performance of a wall or its components, or both, may be a function of proper installation and adjustment. In service, the performance will also depend on the rigidity of supporting construction and on the resistance of components to deterioration by various causes, vibration, thermal expansion and contraction, etc. It is difficult to simulate the identical complex wetting conditions that can be encountered in service, with large wind-blown water drops, increasing water drop impact pressures with increasing wind velocity, and lateral or upward moving air and water. Some designs are more sensitive than others to this upward moving water.
Note 2—This test method does not identify unobservable liquid water which may penetrate into the test specimen.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance of exterior windows, curtain walls, skylights, and doors to water penetration when water is applied to the outdoor face and exposed edges simultaneously with a uniform static air pressure at the outdoor face higher than the pressure at the indoor face.
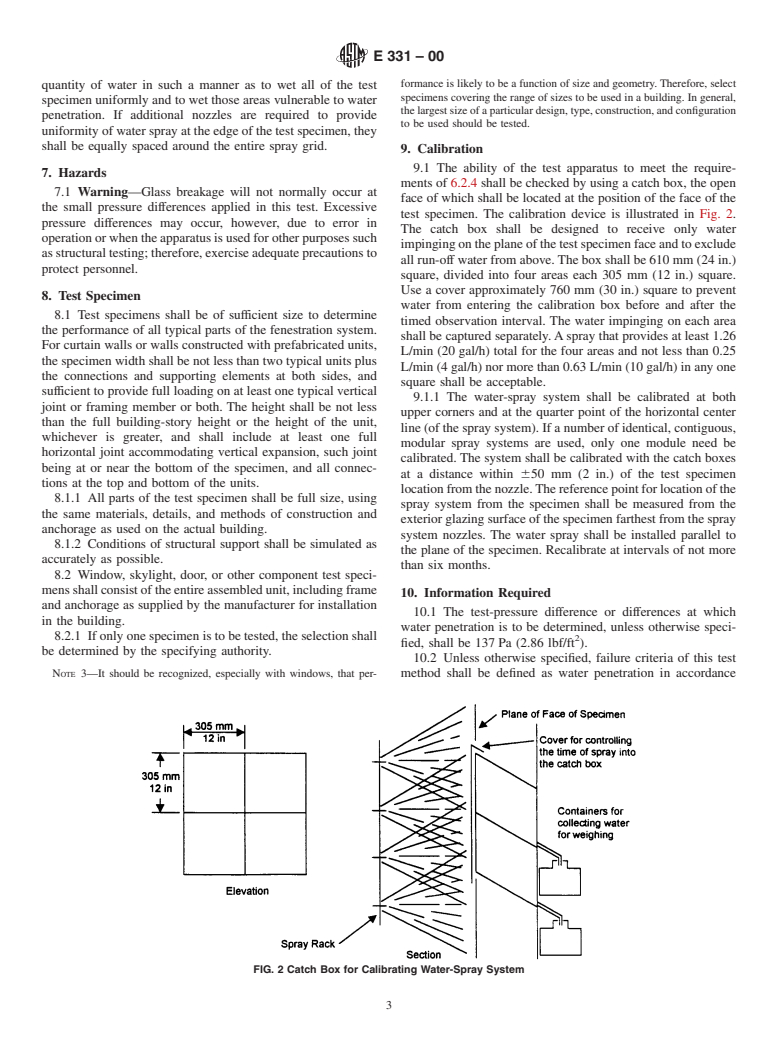
1.2 This test method is applicable to any curtain-wall area or to windows, skylights, or doors alone.
1.3 This test method addresses water penetration through a manufactured assembly. Water that penetrates the assembly, but does not result in a failure as defined herein, may have adverse effects on the performance of contained materials such as sealants and insulating or laminated glass. This test method does not address these issues.
1.4 The proper use of this test method requires a knowledge of the principles of pressure measurement.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound equivalents of SI units may be approximate.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements see 7.1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E331–00
Standard Test Method for
Water Penetration of Exterior Windows, Skylights, Doors,
and Curtain Walls by Uniform Static Air Pressure
1
Difference
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 331; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resis- 3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms relating to
tance of exterior windows, curtain walls, skylights, and doors buildingconstructionusedinthistestmethod,seeTerminology
to water penetration when water is applied to the outdoor face E 631.
and exposed edges simultaneously with a uniform static air 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
pressure at the outdoor face higher than the pressure at the 3.2.1 specimen, n—the entire assembled unit submitted for
indoor face. test as described in Section 8.
1.2 Thistestmethodisapplicabletoanycurtain-wallareaor 3.2.2 test pressure difference, n—the specified difference in
to windows, skylights, or doors alone. static air pressure across the closed and locked or fixed
2
1.3 This test method addresses water penetration through a specimen expressed as pascals (lbf/ft ).
manufactured assembly. Water that penetrates the assembly, 3.2.3 water penetration, n—penetration of water beyond a
but does not result in a failure as defined herein, may have plane parallel to the glazing (the vertical plane) intersecting the
adverse effects on the performance of contained materials such innermost projection of the test specimen, not including
as sealants and insulating or laminated glass. This test method interiortrimandhardware,underthespecifiedconditionsofair
does not address these issues. pressure difference across the specimen. For products with
1.4 The proper use of this test method requires a knowledge non-planer glazing surfaces (domes, vaults, pyramids, etc.) the
of the principles of pressure measurement. plane defining water penetration is the plane defined by the
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the innermost edges of the unit frame.
standard. The inch-pound equivalents of SI units may be
4. Summary of Test Method
approximate.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4.1 This test method consists of sealing the test specimen
into or against one face of a test chamber, supplying air to or
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- exhausting air from the chamber at the rate required to
maintainthetestpressuredifferenceacrossthespecimen,while
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard spraying water onto the outdoor face of the specimen at the
required rate and observing any water penetration.
statements see 7.1.
2. Referenced Documents 5. Significance and Use
5.1 Thistestmethodisastandardprocedurefordetermining
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
E 631 Terminology of Building Constructions the resistance to water penetration under uniform static air
pressure differences. The air-pressure differences acting across
a building envelope vary greatly. These factors should be fully
1 considered prior to specifying the test pressure difference to be
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51 used.
on Performance of Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls.
NOTE 1—In applying the results of tests by this test method, note that
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 2000. Published December 2000 . Originally
the performance of a wall or its components, or both, may be a function
published as E 331 – 67. Last previous edition E 331 – 96.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.11. ofproperinstallationandadjustment.Inservice,theperformancewillalso
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E331–00
depend on the rigidity of supporting construction and on the resistance of
supply opening into the chamber shall be arranged so that the
components to deterioration by various causes, vibration, thermal expan-
air does not impinge directly on the test specimen with any
sion and contraction, etc. It is difficult to simulate the identical complex
significant velocity. A means of access into the chamber may
wetting conditions tha
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.