ASTM D6110-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Determining the Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched Specimens of Plastics
Standard Test Methods for Determining the Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched Specimens of Plastics
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods are used to determine the resistance of plastics to breakage by flexural shock as indicated by the energy extracted from standardized (see Note 2) pendulum-type hammers, mounted in standardized machines, in breaking standard specimens with one pendulum swing. These test methods require specimens to be made with a milled notch (see Note 3). The notch produces a stress concentration which promotes a brittle, rather than a ductile, fracture. The results of these test methods are reported in terms of energy absorbed per unit of specimen width (see Note 4). Note 1—This standard resembles ISO 179 in title only. The content is significantly different.
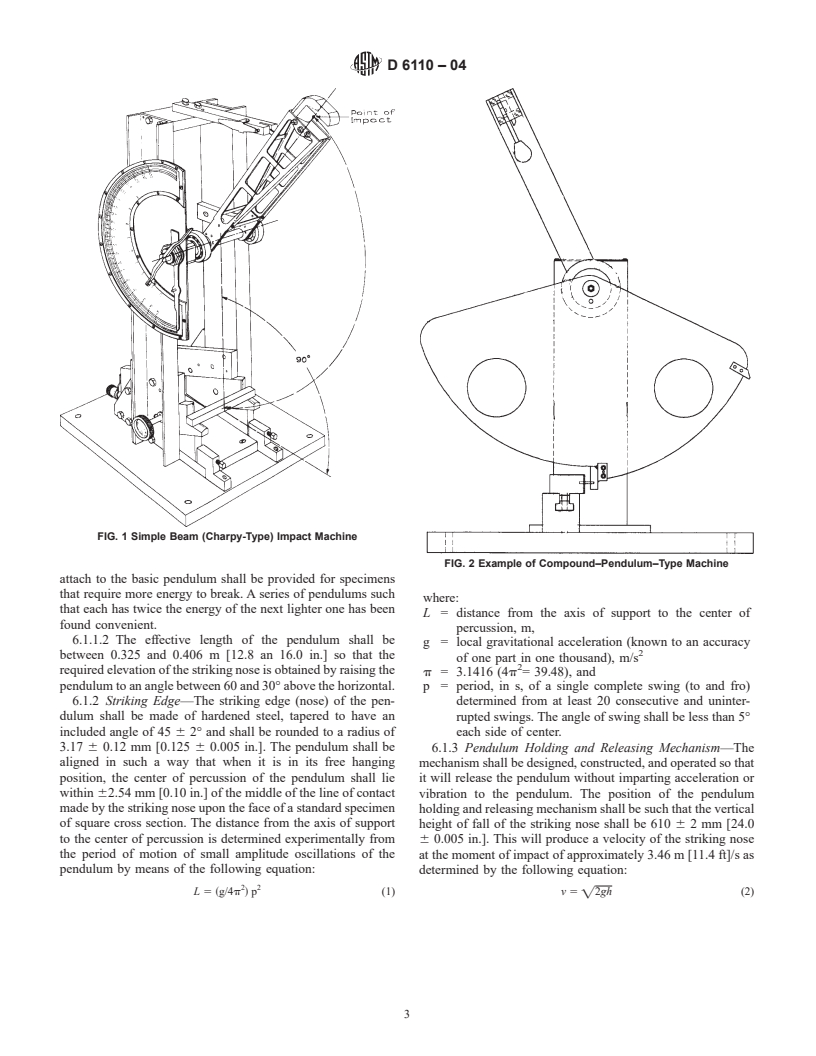
Note 2—The machines with pendulum-type hammers have been standardized in that they must comply with certain requirements including a fixed height of hammer fall, which results in a substantially fixed velocity of the hammer at the moment of impact. Hammers of different initial energies (produced by varying their effective weights), however, are recommended for use with specimens of different impact resistance. Moreover, manufacturers of the equipment are permitted to use different designs of pendulums, which may result in different pendulum rigidities (see Section 5), plus other differences in machine design.
Note 3—The specimens are standardized in that they have a fixed length and fixed depth, however, the width of the specimens is permitted to vary between limits. One design of milled notch is allowed. The notch in the specimen serves to concentrate the stress, minimize plastic deformation, and direct the fracture to the part of the specimen behind the notch. Scatter in energy-to-break is thus reduced. Because of differences in the elastic and viscoelastic properties of plastics, however, response to a given notch varies among materials.
Note 4—Caution must be exercised in interpreting the results of these test methods. The following testing parameters may affect test results significantly: method of specimen fabrication, including but not limited to processing technology, molding conditions, mold design, and thermal treatment; method of notching; speed of notching tool; design of notching apparatus; quality of the notch; time between notching and test; test specimen thickness; and environmental conditioning.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 6110 – 04
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Charpy Impact Resistance of Notched
1
Specimens of Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6110; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method is used to determine the resistance of
plastics to breakage by flexural shock as indicated by the
NOTE 4—This standard resembles ISO 179 in title only. The content is
energy extracted from standardized (see Note 1) pendulum-
significantly different.
type hammers, mounted in standardized machines, in breaking
2. Referenced Documents
standard specimens with one pendulum swing. This test
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
method requires specimens to be made with a milled notch (see
Note 2). The notch produces a stress concentration which D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D 647 Practice for Design of Molds for Test Specimens of
promotes a brittle, rather than a ductile, fracture. The results of
3
this test method are reported in terms of energy absorbed per Plastic Molding Materials
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
unit of specimen width (see Note 3).
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Mate-
NOTE 1—The machines with pendulum-type hammers have been stan-
rials
dardized in that they must comply with certain requirements including a
D 4066 Classification System for Nylon Injection and Ex-
fixed height of hammer fall, which results in a substantially fixed velocity
trusion Materials
of the hammer at the moment of impact. Hammers of different initial
energies (produced by varying their effective weights), however, are
D 5942 Test Method for Determination of Charpy Impact
recommended for use with specimens of different impact resistance.
Strength
Moreover, manufacturers of the equipment are permitted to use different
D 5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid
lengths and constructions of pendulums with possible differences in
Plastics Specimens
pendulum rigidities resulting (see Section 5). Be aware that other
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Test Pro-
differences in machine design do exist.
gram to Determine the Precision of Test Methods
NOTE 2—The specimens are standardized in that they have a fixed
length and fixed depth, however, the width of the specimens is permitted
3. Terminology
to vary between limits. One design of milled notch is allowed. The notch
in the specimen serves to concentrate the stress, minimize plastic
3.1 Definitions—For definitions related to plastics, see Ter-
deformation, and direct the fracture to the part of the specimen behind the
minology D 883.
notch. Scatter in energy-to-break is thus reduced. Because of differences
in the elastic and viscoelastic properties of plastics, however, response to
4. Summary of Test Method
a given notch varies among materials.
4.1 A notched specimen is supported as a horizontal simple
NOTE 3—Caution must be exercised in interpreting the results of this
beam and is broken by a single swing of the pendulum with the
test method. The following testing parameters have been shown to affect
test results significantly: method of specimen fabrication, including but impact line midway between the supports and directly opposite
not limited to processing technology, molding conditions, mold design,
the notch.
and thermal treatment; method of notching; speed of notching tool; design
of notching apparatus; quality of the notch; time between notching and
5. Significance and Use
test; test specimen thickness; test specimen width under notch; and
5.1 Before proceeding with this test method, refer to the
environmental conditioning.
material specification for the material being tested. Any test
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions and testing
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
parameters required by the materials specification shall take
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1 2
This test method are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Plastics and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Properties. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved March 1, 2004. Published April 2004. Originally the ASTM webs
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.