ASTM F1276-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Creep Relaxation of Laminated Composite Gasket Materials
Standard Test Method for Creep Relaxation of Laminated Composite Gasket Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is designed to compare related materials under controlled conditions and their ability to maintain a given compressive stress as a function of time. A portion of the torque loss on the bolted flange is a result of creep relaxation. Torque loss can also be caused by elongation of the bolts, distortion of the flanges, and vibration; therefore, the results obtained should be correlated with field results. This test method may be used as a routine test when agreed upon between the user and the producer.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides a means of measuring the amount of creep relaxation of a laminated composite gasket material at a predetermined time after a compressive stress has been applied.
1.2 Creep relaxation is measured by means of a calibrated bolt with dial indicator.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1276 − 23
Standard Test Method for
1
Creep Relaxation of Laminated Composite Gasket Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1276; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F104 Classification System for Nonmetallic Gasket Materi-
als
1.1 This test method provides a means of measuring the
F436 Specification for Hardened Steel Washers (Metric)
amount of creep relaxation of a laminated composite gasket
F0436_F0436M
material at a predetermined time after a compressive stress has
F868 Classification for Laminated Composite Gasket Mate-
been applied.
rials
1.2 Creep relaxation is measured by means of a calibrated
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
bolt with dial indicator. 3
Relaxometer, Method B (Adjunct to Test Method F38)
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3. Summary of Test Method
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
3.1 In this test method, the specimen is subjected to a
compressive stress between two platens, with the stress applied
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
by a nut and bolt. Run at room or elevated temperatures, the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
stress is determined by measuring the change in length of the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
calibrated bolt with a dial indicator. The bolt length is
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
measured at the beginning of the test and at the end of the test.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
The percent relaxation is calculated from this.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Significance and Use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- 4.1 This test method is designed to compare related mate-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical rials under controlled conditions and their ability to maintain a
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. given compressive stress as a function of time. A portion of the
torque loss on the bolted flange is a result of creep relaxation.
2. Referenced Documents
Torque loss can also be caused by elongation of the bolts,
2
distortion of the flanges, and vibration; therefore, the results
2.1 ASTM Standards:
obtained should be correlated with field results. This test
A193/A193M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless
method may be used as a routine test when agreed upon
Steel Bolting for High Temperature or High Pressure
between the user and the producer.
Service and Other Special Purpose Applications
B637 Specification for Precipitation-Hardening and Cold
5. Apparatus
Worked Nickel Alloy Bars, Forgings, and Forging Stock
4
5.1 Relaxometer, composed of two platens, special drilled
for Moderate or High Temperature Service
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to and calibrated bolt, washer and nut composed of Specification
A193/A193M Grade B7 or Specification B637 Grade UNS
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
F38 Test Methods for Creep Relaxation of a Gasket Material N07718, or other alloys of construction that would satisfy the
calibration Procedure (see Annex) for the test temperature
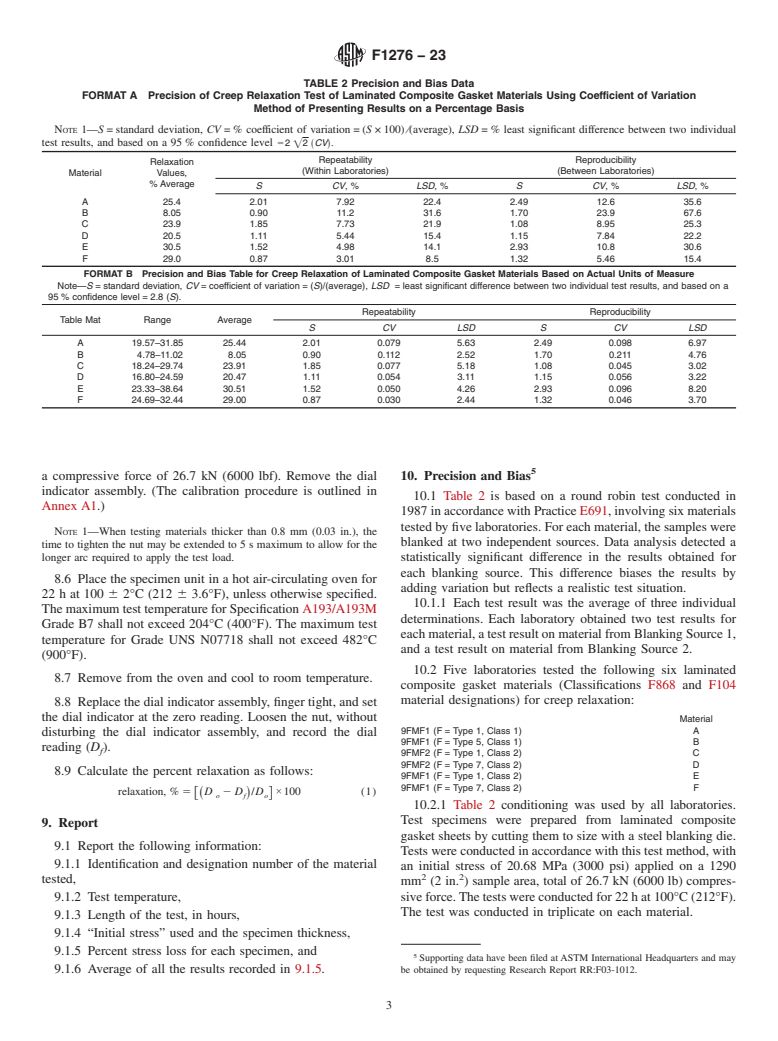
specified and a dial indicator assembly as shown in Fig. 1.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F03 on Gaskets
5.2 Box End Wrench.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F03.20 on Mechanical Test
Methods.
Current edition approved April 1, 2023. Published May 2023. Originally
3
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as F1276 – 99 (2016). Detailed working drawings of this apparatus are available from ASTM
DOI: 10.1520/F1276-23. Headquarters, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428–2959 USA.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Order Adjunct No. 12-600-381-00.
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Dario P. Bernasconi, 40 Farrington St., Stoughton, MA 02072, and Donald G.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Johnson, Metal Samples, P.O. Box 8, Munford, AL 36268, are suppliers of the
the ASTM website. relaxometer.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1276 − 99 (Reapproved 2016) F1276 − 23
Standard Test Method for
1
Creep Relaxation of Laminated Composite Gasket Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1276; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method provides a means of measuring the amount of creep relaxation of a laminated composite gasket material at
a predetermined time after a compressive stress has been applied.
1.2 Creep relaxation is measured by means of a calibrated bolt with dial indicator.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A193/A193M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for High Temperature or High Pressure Service and Other
Special Purpose Applications
B637 Specification for Precipitation-Hardening and Cold Worked Nickel Alloy Bars, Forgings, and Forging Stock for Moderate
or High Temperature Service
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
F38 Test Methods for Creep Relaxation of a Gasket Material
F104 Classification System for Nonmetallic Gasket Materials
F436 Specification for Hardened Steel Washers (Metric) F0436_F0436M
F868 Classification for Laminated Composite Gasket Materials
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
3
Relaxometer, Method B (Adjunct to Test Method F38)
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 In this test method, the specimen is subjected to a compressive stress between two platens, with the stress applied by a nut
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F03 on Gaskets and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F03.20 on Mechanical Test Methods.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016April 1, 2023. Published October 2016May 2023. Originally approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 20092016 as
F1276 – 99 (2009).(2016). DOI: 10.1520/F1276-99R16.10.1520/F1276-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Detailed working drawings of this apparatus are available from ASTM Headquarters, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428–2959 USA. Order Adjunct
No. 12-600-381-00.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1276 − 23
and bolt. Run at room or elevated temperatures, the stress is determined by measuring the change in length of the calibrated bolt
with a dial indicator. The bolt length is measured at the beginning of the test and at the end of the test. The percent relaxation is
calculated from this.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is designed to compare related materials under controlled conditions and their ability to maintain a given
compressive stress as a function of time. A portion of the torque loss on the bolted flange is a result of creep relaxation. Torque
loss can also be caused by elongation of the bolts, distortion of the flanges, and vibration; therefore, the results obtained should
be correlated with field results. This test method may be used as a routine test when agreed upon between the user and the producer.
5. Apparatus
4
5.1 Relaxometer, composed of two platens, special drilled and calibrated bolt, washer and nut composed of Specification
A193/A193M Grade B7 or Specification B637 Grade UNS N07718, or other alloys of construction that would satisfy the
calib
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.