ASTM C1058/C1058M-10
(Practice)Standard Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
Standard Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The various methods for measuring and calculating thermal properties provide data and information for manufacturer's published information, for comparison of related products, and for designers and users to evaluate insulation products for particular applications. For these purposes it is advisable to provide basic data and information produced under standard temperature conditions.
It is possible that thermal properties of a specimen will change with mean temperature, with temperature difference across the specimens, and with high temperature exposure. Data and information at standard temperatures are necessary for valid comparison of thermal properties.
The mean test temperatures to measure thermal properties shall be selected from those listed in Table 1. It is recommended that thermal properties of insulation materials be evaluated over a mean temperature range that represents the intended end use. For this situation, the lowest and greatest mean temperatures need to be within 10°C of the maximum and minimum mean temperature of interest. The temperature differences for any chosen mean temperature will depend upon both the thermal insulation application (see appropriate materials specification), the method of evaluation, and the limitations of the apparatus. Temperature differences or relevant temperatue conditions required by ASTM material specifications shall take precedence over those recommended in this practice.
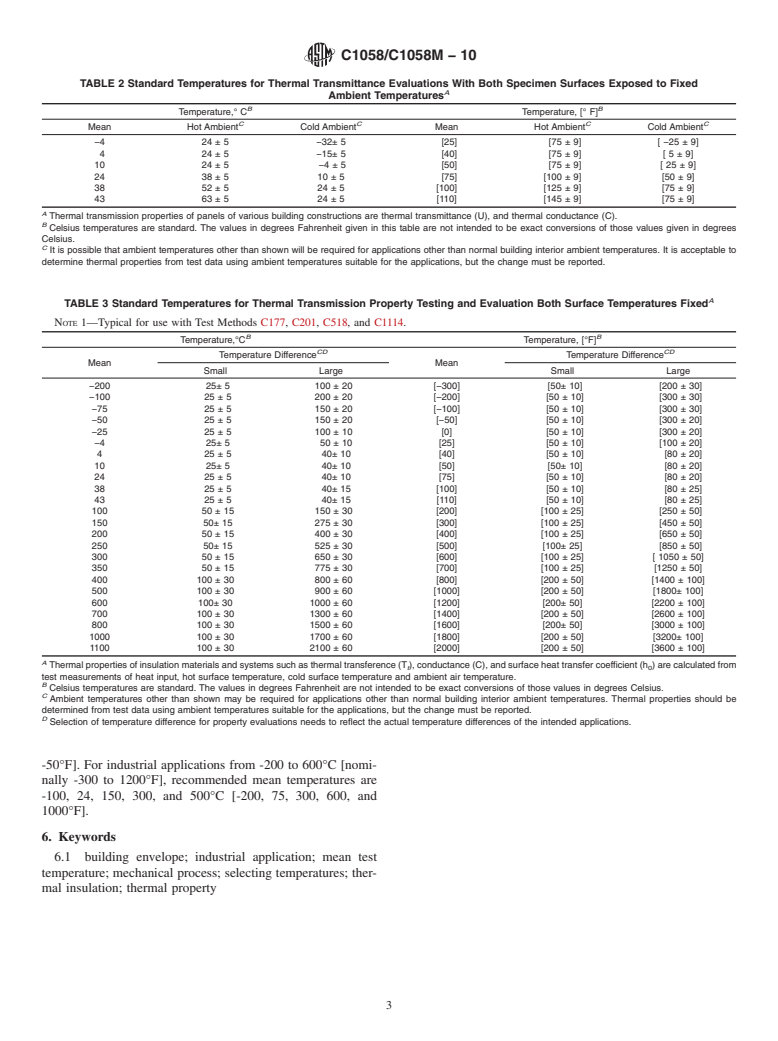
Standard conditions are presented where both surfaces are exposed to fixed ambient temperatures that are typical for testing building constructions, both insulated and uninsulated (Table 2).
Standard conditions are presented where the temperatures of the two surfaces are fixed and surface coefficients are not considered (Table 3).
For conditions where the temperature of only one surface is fixed with the other exposed to fixed ambient temperature, use the mean temperatures of Table 1.
These conditions must be stated to describe accurately...
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers standard mean temperatures for reporting thermal properties of thermal insulations, products, and materials, and of related systems and components, both insulated and uninsulated.
1.2 Thermal properties shall be determined as a function of temperature by standard test methods. (Test Methods C177, C201, C335, C518, C745, C1114, C1363, Guide C653, and Practice C687, all in combination with Practice C1045.)
Note 1—Standard referenced materials are needed to span the temperature range of the tests.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This practice recommends standard conditions for use in testing and evaluating thermal properties as a function of temperature by standard test methods.
1.5 General applications of thermal insulations include:
1.5.1 Building envelopes,
1.5.2 Mechanical systems or processes, and
1.5.3 Building and industrial insulations.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1058/C1058M − 10
StandardPractice for
Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating and Reporting
1
Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1058/C1058M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This practice covers standard mean temperatures for
2.1 ASTM Standards:
reporting thermal properties of thermal insulations, products,
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
and materials, and of related systems and components, both
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
insulated and uninsulated.
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
1.2 Thermal properties shall be determined as a function of
C201 Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Refractories
temperature by standard test methods. (Test Methods C177,
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Properties
C201, C335, C518, C745, C1114, C1363, Guide C653, and
of Pipe Insulation
Practice C687, all in combination with Practice C1045.)
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
NOTE 1—Standard referenced materials are needed to span the tem-
Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
perature range of the tests.
C653 Guide for Determination of the Thermal Resistance of
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
Low-Density Blanket-Type Mineral Fiber Insulation
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
C687 Practice for Determination of Thermal Resistance of
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
Loose-Fill Building Insulation
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
C745 Test Method for Heat Flux Through Evacuated Insu-
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
lations Using a Guarded Flat Plate Boiloff Calorimeter
3
with the standard.
(Withdrawn 2008)
1.4 Thispracticerecommendsstandardconditionsforusein C1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission Prop-
testing and evaluating thermal properties as a function of
erties Under Steady-State Conditions
temperature by standard test methods. C1114 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission
Properties by Means of the Thin-Heater Apparatus
1.5 General applications of thermal insulations include:
C1363 Test Method for Thermal Performance of Building
1.5.1 Building envelopes,
Materials and Envelope Assemblies by Means of a Hot
1.5.2 Mechanical systems or processes, and
Box Apparatus
1.5.3 Building and industrial insulations.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3. Terminology
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3.1 Definitions— For definitions of terms and symbols used
in this practice, refer to Terminology C168.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1 2
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.30 on Thermal contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Measurement. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved June 1, 2010. Published September 2010. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved 2008 as C1058 – 03 (2008). DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/C1058-10. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1058/C1058M − 10
4. Significance and Use 4.3.1 Standard conditions are presented where both surfaces
are exposed to fixed ambient temperatures that are typical for
4.1 The various methods for measuring and calculating
testing building constructions, both insulated and uninsulated
thermal properties provide data and information for manufac-
(Table 2).
turer’s published information, for comparison of related
4.3.2 Standard conditions are presented where the tempera-
products, and for designers and users to evaluate insulation
tures of the two surfaces are fixed and surface coefficients are
products for particular applications. For these purposes it is
not considered (Table 3).
advisable to provide basic data and information produced
4.3.3 For conditions where the
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C1058–03 (Reapproved 2008) Designation:C1058/C1058M–10
Standard Practice for
Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating and Reporting
1
Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1058/C1058M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers standard mean temperatures for reporting thermal properties of thermal insulations, products, and
materials, and of related systems and components, both insulated and uninsulated.
1.2 Thermal properties shall be determined as a function of temperature by standard test methods. (Test Methods C177, C201,
C236, , C335, C518, C745, C976, , C1114, C1363, Guide C653, and Practice C687, all in combination with Practice C1045.)
NOTE 1—Standard referenced materials are needed to span the temperature range of the tests.
1.3This practice recommends standard conditions for use in testing and evaluating thermal properties as a function of
temperature by standard test methods.
1.4General applications of thermal insulations include:
1.4.1Building envelopes,
1.4.2Mechanical systems or processes, and
1.4.3Building and industrial insulations.
1.5The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
Approximate inch-pound units are provided in the tables.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This practice recommends standard conditions for use in testing and evaluating thermal properties as a function of
temperature by standard test methods.
1.5 General applications of thermal insulations include:
1.5.1 Building envelopes,
1.5.2 Mechanical systems or processes, and
1.5.3 Building and industrial insulations.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the
Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
C201 Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Refractories
C335 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Transfer Properties of Pipe Insulation
C518 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus
C653 Guide for Determination of the Thermal Resistance of Low-Density Blanket-Type Mineral Fiber Insulation
C687 Practice for Determination of Thermal Resistance of Loose-Fill Building Insulation
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C16 onThermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.30 onThermal Measurement.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2008. Published August 2008. Originally approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved 2003 as C1058–03. DOI:
10.1520/C1058-03R08.
Current edition approved June 1, 2010. Published September 2010. Originally approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved 2008 as C1058 – 03 (2008). DOI:
10.1520/C1058-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1058/C1058M–10
C745 Test Method for Heat Flux Through Evacuated Insulations Using a Guarded Flat Plate Boiloff Calorimeter
C1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission Properties Under Steady-State Conditions
C1114 Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Thin-Heater Apparatus
C1363 Test Method for Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Envelope Assemblies by Means of a H
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.