ASTM C1199-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring the Steady-State Thermal Transmittance of Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box Methods
Standard Test Method for Measuring the Steady-State Thermal Transmittance of Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box Methods
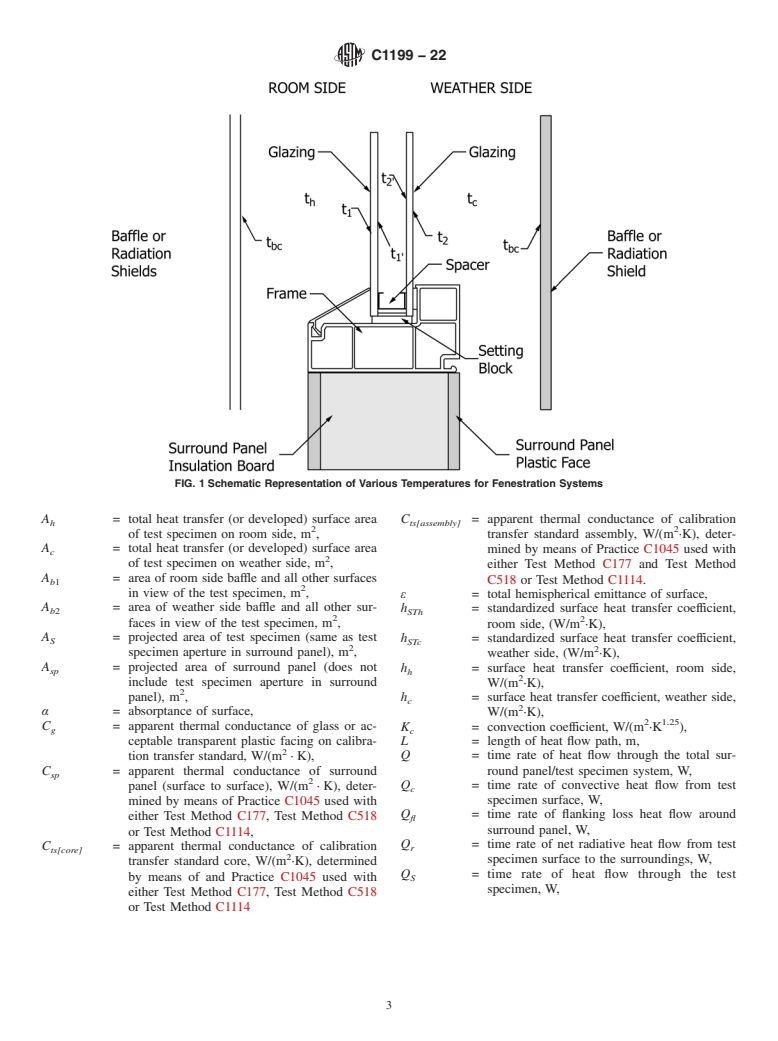
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method details the calibration and testing procedures and necessary additional temperature instrumentation required in applying Test Method C1363 to measure the thermal transmittance of fenestration systems mounted vertically in the thermal chamber.
4.2 The thermal transmittance of a test specimen is affected by its size and three-dimensional geometry. Care must be exercised when extrapolating to product sizes smaller or larger than the test specimen. Therefore, it is recommended that fenestration systems be tested at the recommended sizes specified in Practice E1423 or NFRC 100.
4.3 Since both temperature and surface heat transfer coefficient conditions affect results, use of recommended conditions will assist in reducing confusion caused by comparing results of tests performed under dissimilar conditions. Standardized test conditions for determining the thermal transmittance of fenestration systems are specified in Practice E1423 and Section 6.2. The performance of a test specimen measured at standardized test conditions is potentially different than the performance of the same fenestration product when installed in the wall of a building located outdoors. Standardized test conditions often represent extreme summer or winter design conditions, which are potentially different than the average conditions typically experienced by a fenestration product installed in an exterior wall. For the purpose of comparison, it is essential to calibrate with surface heat transfer coefficients on the Calibration Transfer Standard (CTS) which are as close as possible to the conventionally accepted values for building design; however, this procedure can be used at other conditions for research purposes or product development.
4.4 Similarly, it would be desirable to have a surround panel that closely duplicates the actual wall where the fenestration system would be installed. Since there are such a wide variety of fenestration system openings in North American...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers requirements and guidelines and specifies calibration procedures required for the measurement of the steady-state thermal transmittance of fenestration systems installed vertically in the test chamber. This test method specifies the necessary measurements to be made using measurement systems conforming to Test Method C1363 for determination of fenestration system thermal transmittance.
Note 1: This test method allows the testing of projecting fenestration products (that is, garden windows, skylights, and roof windows) installed vertically in a surround panel. Current research on skylights, roof windows, and projecting products hopefully will provide additional information that can be added to the next version of this test method so that skylight and roof windows can be tested horizontally or at some angle typical of a sloping roof.
1.2 This test method refers to the thermal transmittance, U of a fenestration system installed vertically in the absence of solar radiation and air leakage effects.
Note 2: The methods described in this document may also be adapted for use in determining the thermal transmittance of sections of building wall, and roof and floor assemblies containing thermal anomalies, which are smaller than the hot box metering area.
1.3 This test method describes how to determine the thermal transmittance, US of a fenestration product (also called test specimen) at well-defined environmental conditions. The thermal transmittance is also a reported test result from Test Method C1363. If only the thermal transmittance is reported using this test method, the test report must also include a detailed description of the environmental conditions in the thermal chamber during the test as outlined in 10.1.14.
1.4 For rating purposes, this test method also describes how to calculate a standardized thermal transmittance, UST, which can be used to compare test results from labor...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1199 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Measuring the Steady-State Thermal Transmittance of
1
Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1199; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope the comparison to results from computer programs that use
standard heat transfer coefficients to determine the thermal
1.1 This test method covers requirements and guidelines
transmittance of fenestration products. Although this test
and specifies calibration procedures required for the measure-
method specifies two methods of calculating the standardized
ment of the steady-state thermal transmittance of fenestration
thermal transmittance, only the standardized thermal transmit-
systems installed vertically in the test chamber. This test
tance result from one method is reported for each test. One
methodspecifiesthenecessarymeasurementstobemadeusing
standardizedthermaltransmittancecalculationprocedureisthe
measurement systems conforming to Test Method C1363 for
CalibrationTransferStandard(CTS)Methodandanotheristhe
determination of fenestration system thermal transmittance.
Area Weighting (AW) Method (see Section 9 for further
NOTE 1—This test method allows the testing of projecting fenestration
descriptions of these two methods). The Area Weighting
products (that is, garden windows, skylights, and roof windows) installed
method requires that the surface temperatures on both sides of
vertically in a surround panel. Current research on skylights, roof
the test specimen be directly measured as specified in Practice
windows, and projecting products hopefully will provide additional
E1423 in order to determine the surface heat transfer coeffi-
information that can be added to the next version of this test method so
thatskylightandroofwindowscanbetestedhorizontallyoratsomeangle
cients on the fenestration product during the test. The CTS
typical of a sloping roof.
Method does not use the measured surface temperatures on the
1.2 This test method refers to the thermal transmittance, U test specimen and instead utilizes the calculation of equivalent
of a fenestration system installed vertically in the absence of surfacetemperaturesfromcalibrationdatatodeterminethetest
solar radiation and air leakage effects. specimen surface heat transfer coefficients. The AW shall be
used whenever the thermal transmittance, U , is greater than
S
NOTE 2—The methods described in this document may also be adapted
2 2
3.4 W/(m ·K) [0.6 Btu/(hr·ft ·°F)], or when the ratio of test
for use in determining the thermal transmittance of sections of building
specimen projected surface area to wetted (that is, total heat
wall, and roof and floor assemblies containing thermal anomalies, which
are smaller than the hot box metering area.
transfer or developed) surface area on either side of the test
specimenislessthan0.80.OtherwisetheCTSMethodshallbe
1.3 Thistestmethoddescribeshowtodeterminethethermal
used to standardize the thermal transmittance results.
transmittance, U of a fenestration product (also called test
S
specimen) at well-defined environmental conditions. The ther-
1.5 Adiscussionoftheterminologyandunderlyingassump-
mal transmittance is also a reported test result from Test
tions for measuring the thermal transmittance are included.
Method C1363. If only the thermal transmittance is reported
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
using this test method, the test report must also include a
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
detailed description of the environmental conditions in the
information purposes only.
thermal chamber during the test as outlined in 10.1.14.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.4 For rating purposes, this test method also describes how
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to calculate a standardized thermal transmittance, U , which
ST
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
can be used to compare test results from laboratories with
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
vastly different thermal chamber configurations, and facilitates
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
1
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC16onTh
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1199 − 14 C1199 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Measuring the Steady-State Thermal Transmittance of
1
Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box Methods
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1199; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers requirements and guidelines and specifies calibration procedures required for the measurement of the
steady-state thermal transmittance of fenestration systems installed vertically in the test chamber. This test method specifies the
necessary measurements to be made using measurement systems conforming to Test Method C1363 for determination of
fenestration system thermal transmittance.
NOTE 1—This test method allows the testing of projecting fenestration products (that is, garden windows, skylights, and roof windows) installed vertically
in a surround panel. Current research on skylights, roof windows, and projecting products hopefully will provide additional information that can be added
to the next version of this test method so that skylight and roof windows can be tested horizontally or at some angle typical of a sloping roof.
1.2 This test method refers to the thermal transmittance, U of a fenestration system installed vertically in the absence of solar
radiation and air leakage effects.
NOTE 2—The methods described in this document may also be adapted for use in determining the thermal transmittance of sections of building wall, and
roof and floor assemblies containing thermal anomalies, which are smaller than the hot box metering area.
1.3 This test method describes how to determine the thermal transmittance, U of a fenestration product (also called test specimen)
S
at well-defined environmental conditions. The thermal transmittance is also a reported test result from Test Method C1363. If only
the thermal transmittance is reported using this test method, the test report must also include a detailed description of the
environmental conditions in the thermal chamber during the test as outlined in 10.1.14.
1.4 For rating purposes, this test method also describes how to calculate a standardized thermal transmittance, U , which can be
ST
used to compare test results from laboratories with vastly different thermal chamber configurations, and facilitates the comparison
to results from computer programs that use standard heat transfer coefficients to determine the thermal transmittance of fenestration
products. Although this test method specifies two methods of calculating the standardized thermal transmittance, only the
standardized thermal transmittance result from one method is reported for each test. One standardized thermal transmittance
calculation procedure is the Calibration Transfer Standard (CTS) Method and another is the Area Weighting (AW) Method (see
Section 9 for further descriptions of these two methods). The Area Weighting method requires that the surface temperatures on both
sides of the test specimen be directly measured as specified in Practice E1423 in order to determine the surface heat transfer
coefficients on the fenestration product during the test. The CTS Method does not use the measured surface temperatures on the
test specimen and instead utilizes the calculation of equivalent surface temperatures from calibration data to determine the test
specimen surface heat transfer coefficients. The AW shall be used whenever the thermal transmittance, U , is greater than 3.4
S
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.30 on Thermal
Measurement.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2014March 1, 2022. Published February 2014March 2022. Originally approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 20122014
as C1199 – 12.C1199 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/C1199-14.10.1520/C1199-22.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1199 − 22
2 2
W/(m ·K) [0.6 Btu/(hr·ft ·°F)], or when the ratio of test specimen projected surface area to wetted (that is, total heat transfer or
developed) surface area on either side of the test specimen is less than 0.80. Otherwise the CTS Method shall be used to standardize
the ther
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.