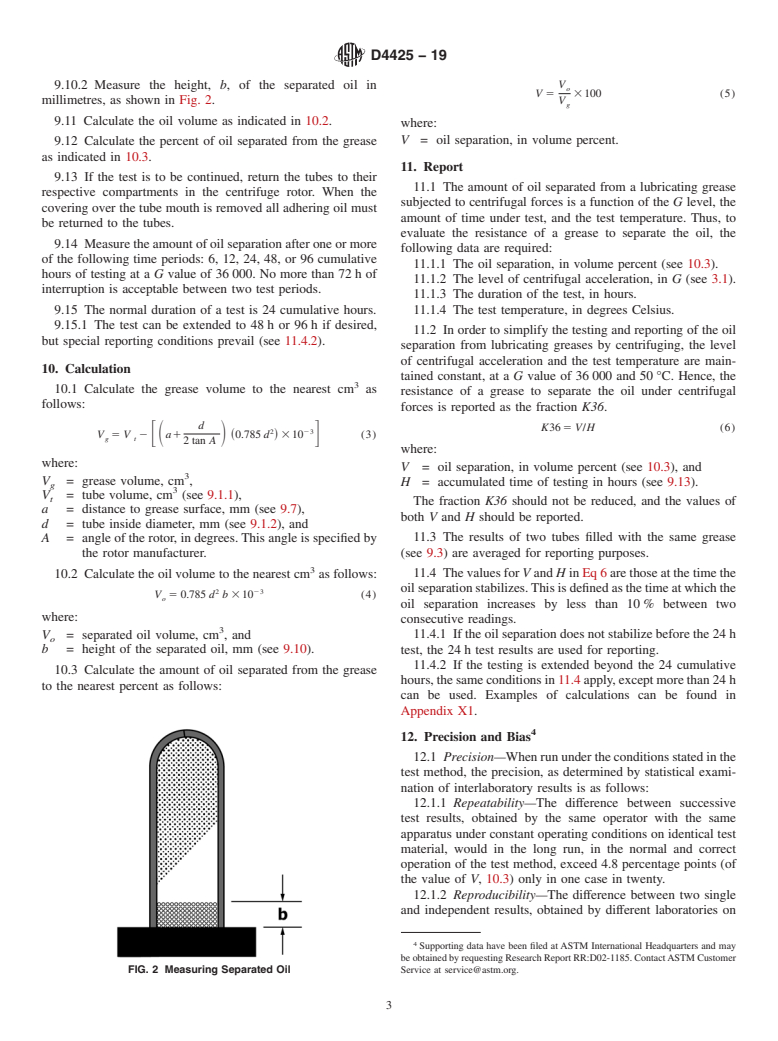
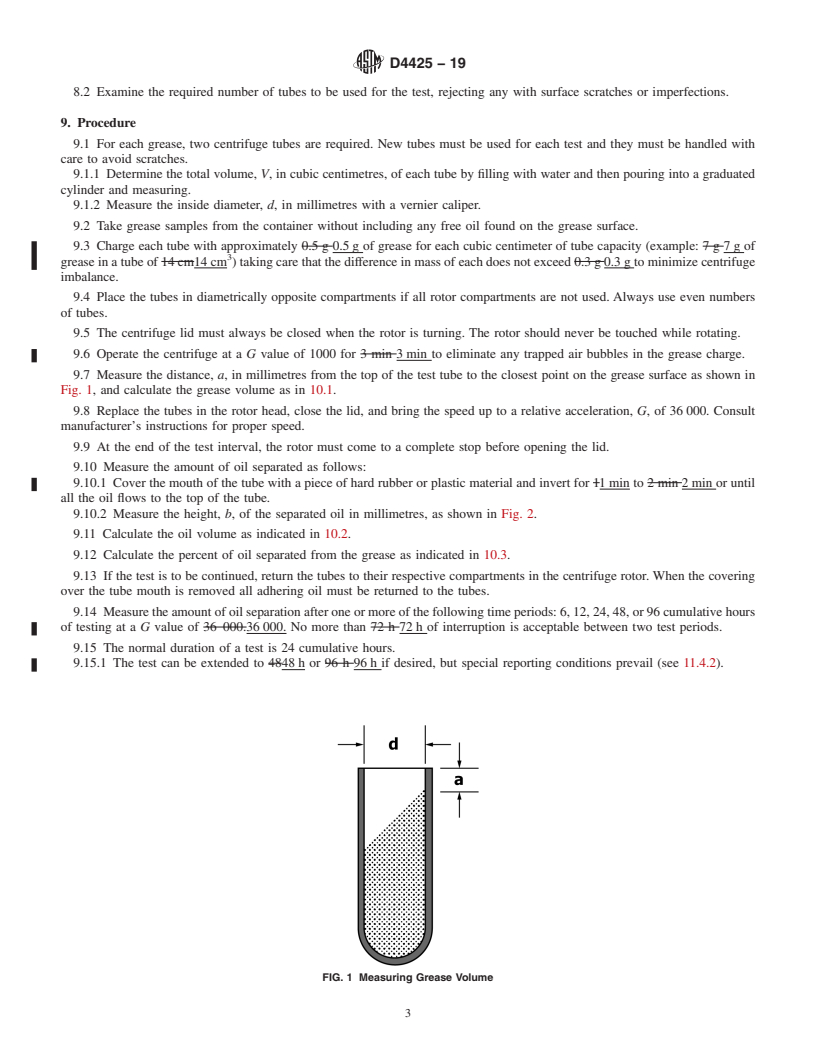
ASTM D4425-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease by Centrifuging (Koppers Method)
Standard Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease by Centrifuging (Koppers Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is useful in evaluating the degree to which a grease would separate into fluid and solid components when subjected to high centrifugal forces. Flexible shaft couplings, universal joints, and rolling element thrust bearings are examples of machinery which subject lubricating greases to large and prolonged centrifugal forces. This test method has been found to give results that correlate well with results from actual service. The test method may be run at other conditions with agreement between parties but the precision noted in this test method will no longer apply.3
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the tendency of lubricating grease to separate oil when subjected to high centrifugal forces.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4425 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease by Centrifuging
1
(Koppers Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4425; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3.1.2 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance com-
posed of finely-divided particles dispersed in a liquid to form
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the
the products’s structure.
tendencyoflubricatinggreasetoseparateoilwhensubjectedto
high centrifugal forces. 3.1.2.1 Discussion—Thickeners can be fibers (such as vari-
ous metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
non-soapthickeners),whichareinsolubleor,atmost,onlyvery
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
slightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general require-
standard.
ments are that the solid particles be extremely small, uniformly
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
dispersed, and capable of forming a relatively stable, gel-like
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
structure with the liquid lubricant.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2 Symbols:
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
a = distance from top of grease surface to tube mouth
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
(mm).
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
b = height of liquid column in an inverted test tube (mm).
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
d = test tube inside diameter (mm).
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
H = accumulated test time at a given reading (h).
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
K36 = resistance to centrifugal separation (V/H).
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
r = measured at the maximum radius of rotation (mm).
rpm = rotational speed (r/min).
2. Referenced Documents
V = volume of separated oil, as a percentage of the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
original grease volume (%).
3
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating
V = grease volume in a test tube (cm ).
g
3
Grease
V = volume of separated oil (cm ).
o
3
V = test tube total volume (cm ).
t
3. Terminology
A = angle of rotor, between the test tube axis and axis of
rotation (degrees).
3.1 Definitions:
ω = rotational speed (rad/s).
3.1.1 lubricating grease, n—a semi-fluid to solid product of
G = relative centrifugal acceleration.
a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—The dispersion of the thickener forms a
3.3 The relative effect of centrifugal forces, when related to
2
two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by
the gravitational standard acceleration (9.81 m⁄s ), is noted
surface tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are
with the symbol G. It can be calculated as follows:
commonly included to impart special properties. D217
24 2
G 5 1.02 310 3r 3ω (1)
or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum
26 2
G 5 1.12 310 3r 3rpm¯ (2)
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
mittee D02.G0.03 on Physical Tests.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2019.PublishedJuly2019.Originallyapproved 4. Summary of Test Method
in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D4425 – 09 (2014). DOI:
10.1520/D4425-19. 4.1 Pairs of centrifuge tubes are charged with grease
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
samples and are placed in the centrifuge. The grease samples
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
are subjected to a centrifugal force equivalent to a G value of
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 36 000, at 50 °C 6 1 °C, for specific periods of time. The
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4425 − 19
resistance of the grease to separate the oil is then defined as a 8.2 Examine the required number of tubes to be used for the
ratioofthepercentofoilseparatedtothetotalnumberofhours test, rej
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4425 − 09 (Reapproved 2014) D4425 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease by Centrifuging
1
(Koppers Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4425; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the tendency of lubricating grease to separate oil when subjected to
high centrifugal forces.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating Grease
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 lubricating grease, n—a semi-fluid to solid product of a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface tension and other
physical forces. Other ingredients are commonly included to impart special properties. D217
3.1.2 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance composed of finely-divided particles dispersed in a liquid to form the
products’s structure.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
Thickeners can be fibers (such as various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain non-soap thickeners), which are
insoluble or, at most, only very slightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general requirements are that the solid particles be
extremely small, uniformly dispersed, and capable of forming a relatively stable, gel-like structure with the liquid lubricant.
3.2 Symbols:
a = distance from top of grease surface to tube mouth (mm).
b = height of liquid column in an inverted test tube (mm).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.G0.03 on Physical Tests.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014June 1, 2019. Published November 2014July 2019. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 20092014 as
D4425 – 09.D4425 – 09 (2014). DOI: 10.1520/D4425-09R14.10.1520/D4425-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4425 − 19
d = test tube inside diameter (mm).
H = accumulated test time at a given reading (h).
K36 = resistance to centrifugal separation (V/H).
r = measured at the maximum radius of rotation (mm).
rpm = rotational speed (r/min).
V = volume of separated oil, as a percentage of the original grease volume (%).
3
V = grease volume in a test tube (cm ).
g
3
V = volume of separated oil (cm ).
o
3
V = test tube total volume (cm ).
t
A = angle of rotor, between the test tube axis and axis of rotation (degrees).
ω = rotational speed (rad/s).
G = relative centrifugal acceleration.
2
3.3 The relative effect of centrifugal forces, when related to the gravitational standard acceleration (9.81 (9.81 m m/s⁄s ), is
noted with the symbol G. It can be calculated as follows:
24 2
G 5 1.02 310 3r 3ω (1)
or
26 2
G 5 1.12 310 3r 3rpm¯ (2)
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Pairs of centrifuge tubes are charged with grease samples and are placed in the centrifuge. The grease samples are subjected
to a centrifugal force equivalent to a G valu
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.