ASTM C1339-02e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flowability and Bearing Area of Chemical-Resistant Polymer Machinery Grouts
Standard Test Method for Flowability and Bearing Area of Chemical-Resistant Polymer Machinery Grouts
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Chemical-resistant polymer machinery grouts are used to provide precision support for machinery or equipment.
The machinery or equipment or support bases or plates, or combination thereof, are positioned to the precise elevation and location required. The bases or plates are typically placed on prepared foundations and supported on temporary shims or support bolts (jack screws). Forms are installed to contain the flowable grout. The grout is poured around the perimeter in such a manner as to allow the grout to flow around and under the equipment base or plates. The grout subsequently hardens to provide a strong rigid support layer capable of withstanding the stresses transferred by the equipment to the foundation.
In addition to the required physical properties of the grout, the flow and bearing area achieved are important considerations for effective grout installation. The two characteristics measured by this test method are flow and bearing area.
The flow test simulates typical application conditions for a flowable polymer machinery grout. It may be used to evaluate the suitability of a particular grout for a specific application, to compare the flowability and bearing area of two or more grouts, or to evaluate the effects of formulation changes, temperature, mixing techniques, or other factors on flowability.
The estimated amount of upper grout surface contact in percent can be used to compare two or more grouts or show the effects of temperature, formulation changes, or other factors on bearing area. Because of the limited accuracy in estimating the percent of contact, a limited set of results is suggested (see 9.9.1). Visual guides are provided for comparative purposes (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measure of flowability of chemical-resistant polymer machinery grouts as evaluated in a 2-in. (5-cm) or 1-in. (2.5-cm) pour thickness. The test method provides for the assessment of upper surface plate contact area (bearing area). These grouts will typically be two- or three-component formulations that may be used for installations where grout thickness will range from 1 to 6 in. (2.5 to 15 cm) underneath the base or plates being grouted.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
e1
Designation:C1339–02
Standard Test Method for
Flowability and Bearing Area of Chemical-Resistant Polymer
1
Machinery Grouts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1339; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—Fig. 3 was editorially corrected in April 2004.
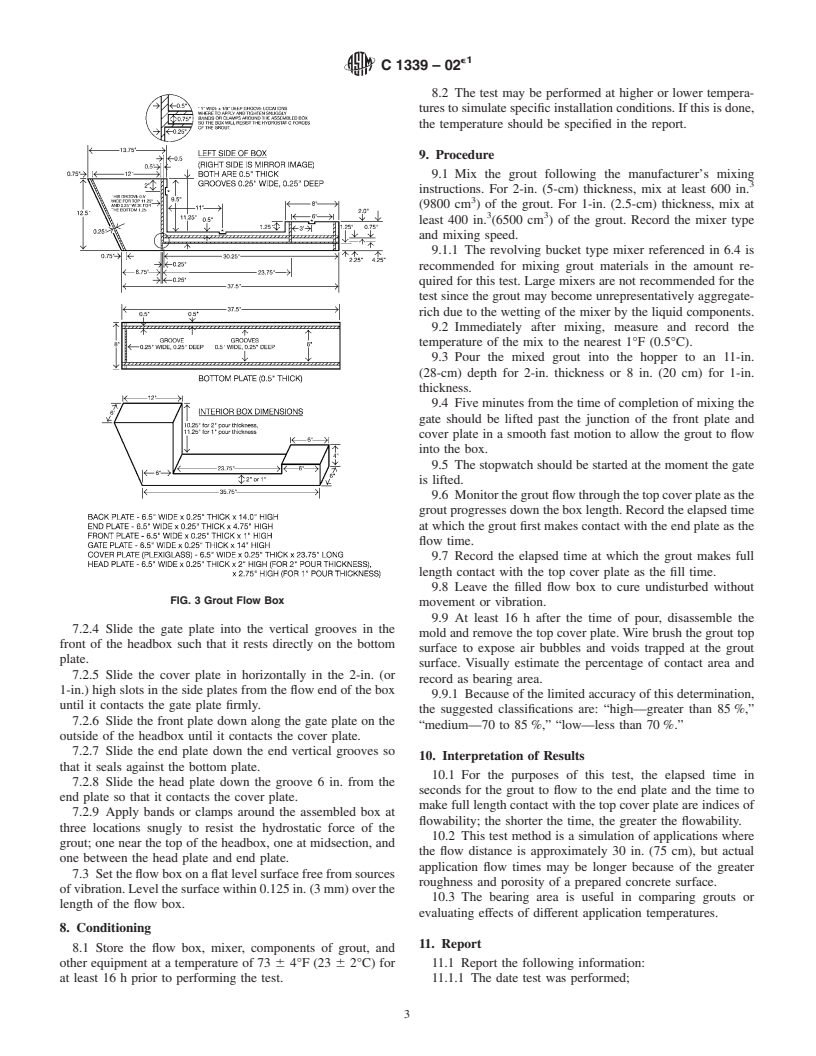
1. Scope 4.2 A movable gate is raised, allowing the grout to flow
from the hopper into the trough. The times for the grout to first
1.1 This test method covers the measure of flowability of
contact the end plate and to establish full length contact with
chemical-resistant polymer machinery grouts as evaluated in a
the top cover plate are recorded and used as indices of
2-in. (5-cm) or 1-in. (2.5-cm) pour thickness. The test method
flowability.
provides for the assessment of upper surface plate contact area
4.3 After the grout hardens, the mold and top plate are
(bearing area). These grouts will typically be two- or three-
removed.Thetopsurfaceofthegroutiswirebrushedtoexpose
component formulations that may be used for installations
any surface air bubbles or voids, and a visual estimate is made
where grout thickness will range from 1 to 6 in. (2.5 to 15 cm)
of the percentage of grout top surface area that is in contact
underneath the base or plates being grouted.
with the plate. Visual guides are provided for comparative
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
purposes (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 Chemical-resistant polymer machinery grouts are used
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
to provide precision support for machinery or equipment.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
5.2 The machinery or equipment or support bases or plates,
as standard. The values given in parentheses are for informa-
or combination thereof, are positioned to the precise elevation
tion only.
and location required. The bases or plates are typically placed
2. Referenced Documents on prepared foundations and supported on temporary shims or
support bolts (jack screws). Forms are installed to contain the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
flowable grout. The grout is poured around the perimeter in
C 904 Terminology Relating to Chemical-Resistant Non-
2 such a manner as to allow the grout to flow around and under
metallic Materials
the equipment base or plates. The grout subsequently hardens
3. Terminology to provide a strong rigid support layer capable of withstanding
the stresses transferred by the equipment to the foundation.
3.1 Definitions—For definition of terms used in this test
5.3 In addition to the required physical properties of the
method, see Terminology C 904.
grout, the flow and bearing area achieved are important
4. Summary of Test Method
considerations for effective grout installation. The two charac-
teristics measured by this test method are flow and bearing
4.1 Polymer machinery grout of a flowable consistency is
area.
pouredintoahopperatoneendofashallowplastictroughwith
5.4 The flow test simulates typical application conditions
a clear plastic cover plate.
for a flowable polymer machinery grout. It may be used to
evaluate the suitability of a particular grout for a specific
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C03 on
application, to compare the flowability and bearing area of two
Chemical-Resistant Nonmetallic Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee C03.01 on Test Methods.
or more grouts, or to evaluate the effects of formulation
Current edition approved April 10, 2002. Published June 2002. Originally
changes, temperature, mixing techniques, or other factors on
published as C 1339 – 96. Last previous edition C 1339 – 96a.
2 flowability.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.05.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
e1
C1339–02
FIG. 2 Grout Top Surface
FIG. 1 Grout Top Surface
6.4 Mixer, a commercial mixing device that is able to rotate
5.5 The estimated amount of upper grout surface contact in
a 5-gal metal or plastic pail with a stationary mixing blade to
percent can be used to compare two or more grouts or show the
stir the grout mix. Typical operating speed is 30 to 100 rpm
effects of temperature, formulation changes, or other factors on
(see Fig. 4).
bearing area. Because of the limited accuracy in estimating t
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.