ASTM D6919-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Dissolved Alkali and Alkaline Earth Cations and Ammonium in Water and Wastewater by Ion Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Dissolved Alkali and Alkaline Earth Cations and Ammonium in Water and Wastewater by Ion Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
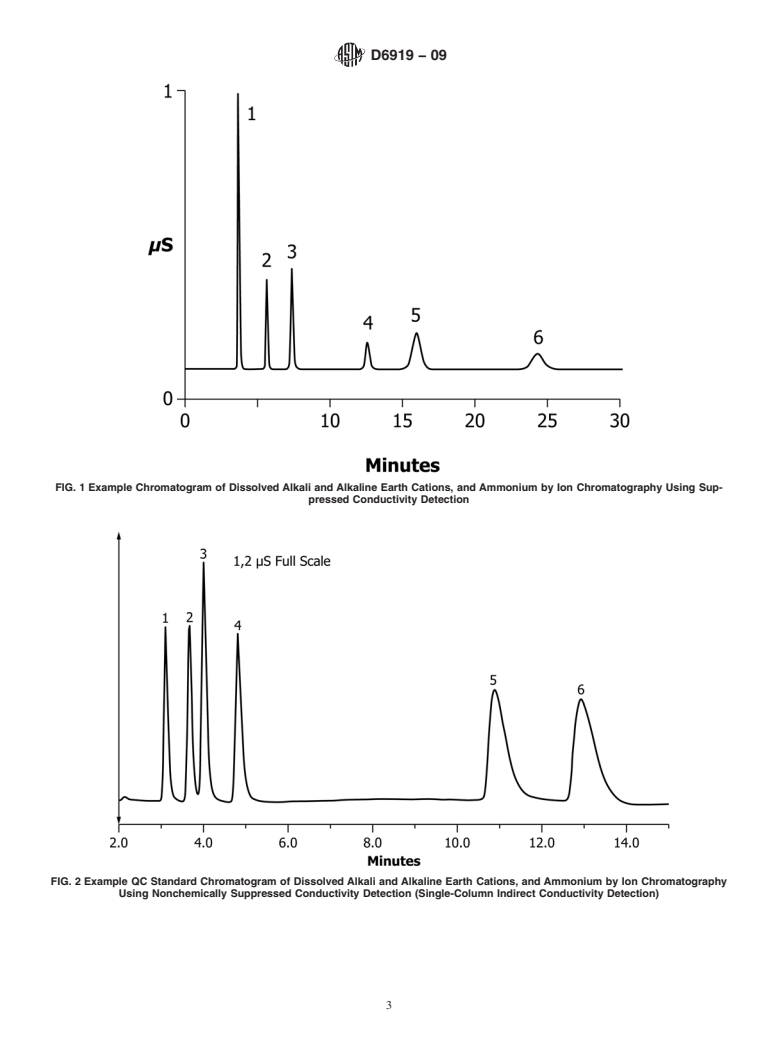
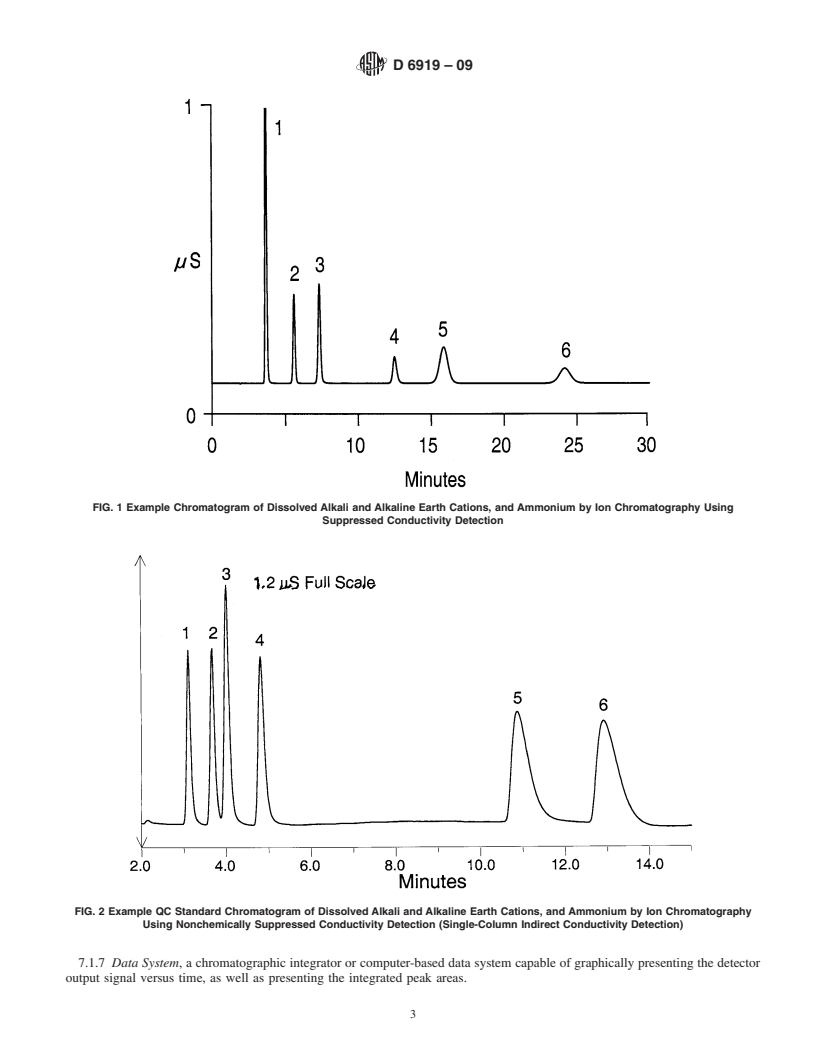
This method is applicable to the simultaneous determination of dissolved alkali and alkaline earth cations and ammonium in water and wastewaters. Alkali and alkaline earth cations are traditionally determined by using spectroscopic techniques, such as AAS or ICP; whereas ammonium can be measured by using a variety of wet chemical methods, including colorimetry, ammonia-selective electrode, and titrimetry. However, ion chromatography provides a relatively straightforward method for the simultaneous determination of cations, such as lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and ammonium, in fewer than 20–30 min.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is valid for the simultaneous determination of the inorganic alkali and alkaline earth cations, lithium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium, as well as the ammonium cation in reagent water, drinking water, and wastewaters by suppressed and nonsuppressed ion chromatography.
1.2 The anticipated range of the method is 0.05–200 mg/L. The specific concentration ranges tested for this method for each cation were as follows (measured in mg/L): Lithium0.4–10.0 Sodium4.0–40.0 Ammonium0.4–10.0 Potassium1.2–20.0 Magnesium2.4–20.0 Calcium4.0–40.0
1.2.1 The upper limits may be extended by appropriate dilution or by the use of a smaller injection volume. In some cases, using a larger injection loop may extend the lower limits.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 It is the user's responsibility to ensure the validity of these test methods for waters of untested matrices.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For hazards statements specific to this test method, see 8.3.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6919 − 09
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Dissolved Alkali and Alkaline Earth
Cations and Ammonium in Water and Wastewater by Ion
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6919; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method is valid for the simultaneous determi- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
nation of the inorganic alkali and alkaline earth cations, D1129Terminology Relating to Water
lithium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium, as well D1193Specification for Reagent Water
as the ammonium cation in reagent water, drinking water, and D2777Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
wastewaters by suppressed and nonsuppressed ion chromatog- Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
raphy. D3370Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D3856Guide for Management Systems in Laboratories
1.2 The anticipated range of the method is 0.05–200 mg/L.
Engaged in Analysis of Water
The specific concentration ranges tested for this method for
D4210Practice for Intralaboratory Quality Control Proce-
each cation were as follows (measured in mg/L):
dures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
Lithium 0.4–10.0
3
(Withdrawn 2002)
Sodium 4.0–40.0
Ammonium 0.4–10.0 D5810Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
Potassium 1.2–20.0
D5847Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
Magnesium 2.4–20.0
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
Calcium 4.0–40.0
D5905Practice for the Preparation of SubstituteWastewater
1.2.1 The upper limits may be extended by appropriate
dilution or by the use of a smaller injection volume. In some
3. Terminology
cases,usingalargerinjectionloopmayextendthelowerlimits.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
method, refer to Terminology D1129.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4. Summary of Test Method
standard.
4.1 Inorganic cations and the ammonium cation, hereafter
1.4 It is the user’s responsibility to ensure the validity of
referred to as ammonium, are determined by ion chromatog-
these test methods for waters of untested matrices.
raphy in water and wastewater samples from a fixed sample
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
volume, typically 10–50 µL. The cationic analytes are sepa-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
rated using a cation-exchange material, which is packed into
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
guardandanalyticalcolumns.Adiluteacidsolutionistypically
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
used as the eluent.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For hazards
4.1.1 The separated cations are detected by using conduc-
statements specific to this test method, see 8.3.
tivity detection. To achieve sensitive conductivity detection, it
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D19 on Water For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
in Water. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved May 15, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D6919–03. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D6919-09. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6919 − 09
is essential that the background signal arising from the eluent (pH 1.3), such as the IonPac® CS16 column. The columns
have low baseline noise. One means to achieve low back- used with nonsuppressed conductivity detection typically have
ground noise is to combine the conductivity detector with a
lower capacity and can tolerate acid concentrations up to 10
+
suppressor device that will reduce the conductance of the
mM H (pH 2.0), such as the trademarked IC-Pak C/MD
eluent, hence background noise, and also transform the sepa-
column.
4
rated cations into their more conductive corresponding bases.
6.2 A slight decrease or increase in eluent strength often
4.1.2 Detection can also be achieved without chemical
allows in
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D6919–03 Designation:D6919–09
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Dissolved Alkali and Alkaline Earth
Cations and Ammonium in Water and Wastewater by Ion
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6919; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method is valid for the simultaneous determination of the inorganic alkali and alkaline earth cations, lithium,
sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium, as well as the ammonium cation in reagent water, drinking water, and wastewaters
by suppressed and nonsuppressed ion chromatography.
1.2 The anticipated range of the method is 0.05–200 mg/L. The specific concentration ranges tested for this method for each
cation were as follows (measured in mg/L):
Lithium 0.4–10.0
Sodium 4.0–40.0
Ammonium 0.4–10.0
Potassium 1.2–20.0
Magnesium 2.4–20.0
Calcium 4.0–40.0
1.2.1 Theupperlimitsmaybeextendedbyappropriatedilutionorbytheuseofasmallerinjectionvolume.Insomecases,using
a larger injection loop may extend the lower limits.
1.3It is the user’s responsibility to ensure the validity of these test methods for waters of untested matrices.
1.4
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 It is the user’s responsibility to ensure the validity of these test methods for waters of untested matrices.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For hazards statements specific to this test method, see 8.3.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D 1193 Specifications for Reagent Water
D 2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
2
D 3370 Practices for Sampling Water Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D 3856 Guide for Good Laboratory Practices in Laboratories Engaged in Sampling and Analysis of Water
D 4210 Practice for Interalaboratory Quality Control Procedures and a Discussion on Reporting Low-Level Data
D 5810 Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
D 5847 Practice for the Writing of Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
D 5905 Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Wastewater
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D 1129.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Inorganic cations and the ammonium cation, hereafter referred to as ammonium, are determined by ion chromatography in
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD19onWaterandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.05onInorganicConstituentsinWater.
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2003. Published September 2003.
Current edition approved May 15, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 6919 – 03.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 11.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6919–09
water and wastewater samples from a fixed sample volume, typically 10–50 µL. The cationic analytes are separated using a
cation-exchange material, which is packed into guard and analytical columns.Adilute acid solution is typically used as the eluent.
4.1.1 The separated cations are detected by using conductivity detection. To achieve sensitive conductivity detection, it is
essential that the background signal arising from the eluent have low baseline noise. One means to achieve low background noise
is to combine the conductivity detector with a suppressor device that will reduce the conductance of the eluent, hence background
3
noise, and also transform the separated cations into t
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.