ASTM E3012-16
(Guide)Standard Guide for Characterizing Environmental Aspects of Manufacturing Processes
Standard Guide for Characterizing Environmental Aspects of Manufacturing Processes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide provides manufacturers a systematic approach for characterizing the environmental aspects of manufacturing processes utilizing formal representations.
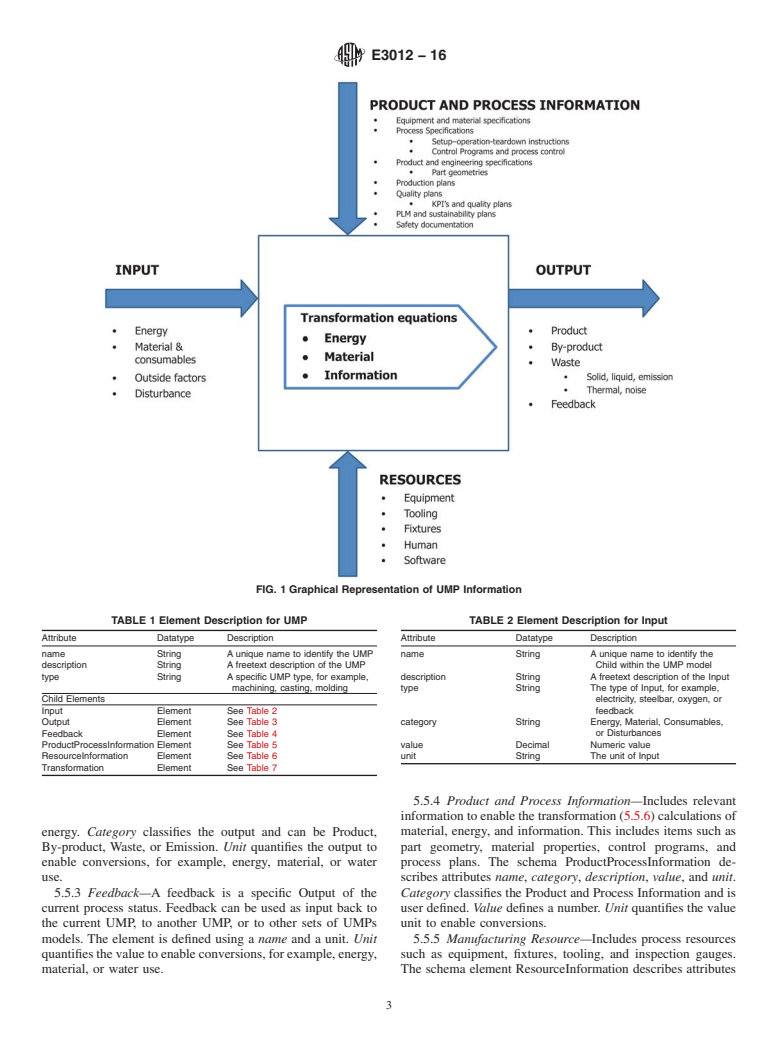
Note 1: A UMP is formally represented using languages such as eXtensible Markup Language (XML), Unified Modeling Language (UML), or Systems Modeling Language (SysML) to facilitate data exchange, computability, sharing, and communication with other manufacturing and analysis applications. These capabilities support manufacturers in evaluating, documenting, and improving performance.
4.2 This guide provides the required structure and formalism to ensure consistency in characterizing manufacturing processes in a computer-interpretable way enabling effective communication, computational analytics, and exchange of performance information.
Note 2: This guide will promote new tool development that can link manufacturing information and analytics for calculating the desired environmental performance measures.
4.3 The guide supports the development of tools to improve decision support capabilities while facilitating the development and extension of standardized data and information bases such as Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) (ISO 14040 series).
Note 3: Data collected within manufacturing enterprises can be used to build enterprise-or-sector-specific databases that complement or extend LCI databases (ULE 880). This approach will improve the relevancy and completeness of the data while retaining key links to Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides manufacturers an approach to characterize any category of manufacturing process and to systematically capture and describe relevant environmental information.
1.2 This guide defines a Process Characterization Methodology that uses graphical and formal representations to support the construction of unit manufacturing process (UMP) information models for characterizing the environmental aspects of manufacturing processes.
1.3 This guide defines the graphical UMP information model as being comprised of four elements (input, output, product and process information, and resources) that supports manufacturers in systematically identifying, collecting, structuring, and visualizing manufacturing information.
1.4 This guide defines the formal representation of the UMP information model through the use of a modeling method and language that can effectively convey the meaning and intent of processes they characterize.
1.5 This guide provides the necessary structure and formality for identifying and capturing key information needs to assess manufacturing performance, yet provides no details about an actual assessment of the process performance.
1.6 This guide provides an approach to link individual UMP information models together to create a network or system of UMP models that extends the characterization of environmental aspects beyond an individual process to a production system or the product itself.
1.7 This guide may be used to complement other standards that address sustainability and the product life cycle. This guide most closely relates to the inventory component as discussed in the ISO 14040 series (ISO 14044) standards, and resource management as discussed in the ISO 55000 series (ISO 55001) standards.
1.8 This guide does not purport to address all of the security issues and the risks associated with manufacturing information. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to follow practices and establish appropriate information technology related security measures.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E3012 − 16
Standard Guide for
Characterizing Environmental Aspects of Manufacturing
1
Processes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E3012; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.8 This guide does not purport to address all of the security
issues and the risks associated with manufacturing informa-
1.1 This guide provides manufacturers an approach to
tion. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to follow
characterize any category of manufacturing process and to
practices and establish appropriate information technology
systematically capture and describe relevant environmental
related security measures.
information.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.2 This guide defines a Process Characterization Method-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ology that uses graphical and formal representations to support
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the construction of unit manufacturing process (UMP) infor-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
mation models for characterizing the environmental aspects of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
manufacturing processes.
1.3 This guide defines the graphical UMP information
2. Referenced Documents
model as being comprised of four elements (input, output,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
product and process information, and resources) that supports
E2114 Terminology for Sustainability Relative to the Perfor-
manufacturers in systematically identifying, collecting,
mance of Buildings
structuring, and visualizing manufacturing information.
E2986 Guide for Evaluation of Environmental Aspects of
1.4 This guide defines the formal representation of the UMP
Sustainability of Manufacturing Processes
information model through the use of a modeling method and
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
language that can effectively convey the meaning and intent of
ISO 22400-1:2014 Automation systems and integration—
processes they characterize.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for manufacturing
1.5 This guide provides the necessary structure and formal-
operations management; Part 1: Overview, concepts, and
ity for identifying and capturing key information needs to
terminology
assess manufacturing performance, yet provides no details
ISO 14040 Environmental management—Life cycle assess-
about an actual assessment of the process performance.
ment—Principles and framework
ISO 14044 Environmental management—Life cycle assess-
1.6 This guide provides an approach to link individual UMP
ment—Requirements and guidelines
information models together to create a network or system of
ISO 55000:2014 Asset management—Overview, principles
UMP models that extends the characterization of environmen-
and terminology
talaspectsbeyondanindividualprocesstoaproductionsystem
ISO 55001:2014 Asset management—Management systems
or the product itself.
—Requirements
1.7 This guide may be used to complement other standards
4
2.3 UL Standard:
that address sustainability and the product life cycle. This
ULE 880 Sustainability for Manufacturing Organizations
guide most closely relates to the inventory component as
discussed in the ISO 14040 series (ISO 14044) standards, and
resource management as discussed in the ISO 55000 series
(ISO 55001) standards. 2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
1 3
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E60 on Sustainability Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E60.13 on Sustainable Manufac- Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier,
turing. Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
4
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published March 2016. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from Underwriters Laboratories (UL), 2600 N.W. Lake Rd., Camas,
E3012-16. WA 98607-8542, http://www.ul.com.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E3012 − 16
2.4 World Wide Web Consortium (W3C): 5. Unit Manufacturing Process Representation
eXtensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0 Recommenda-
5.1 The UMP representation utilizes graphical and formal
5
tion
methods in constructing UMP information models for charac-
6
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.