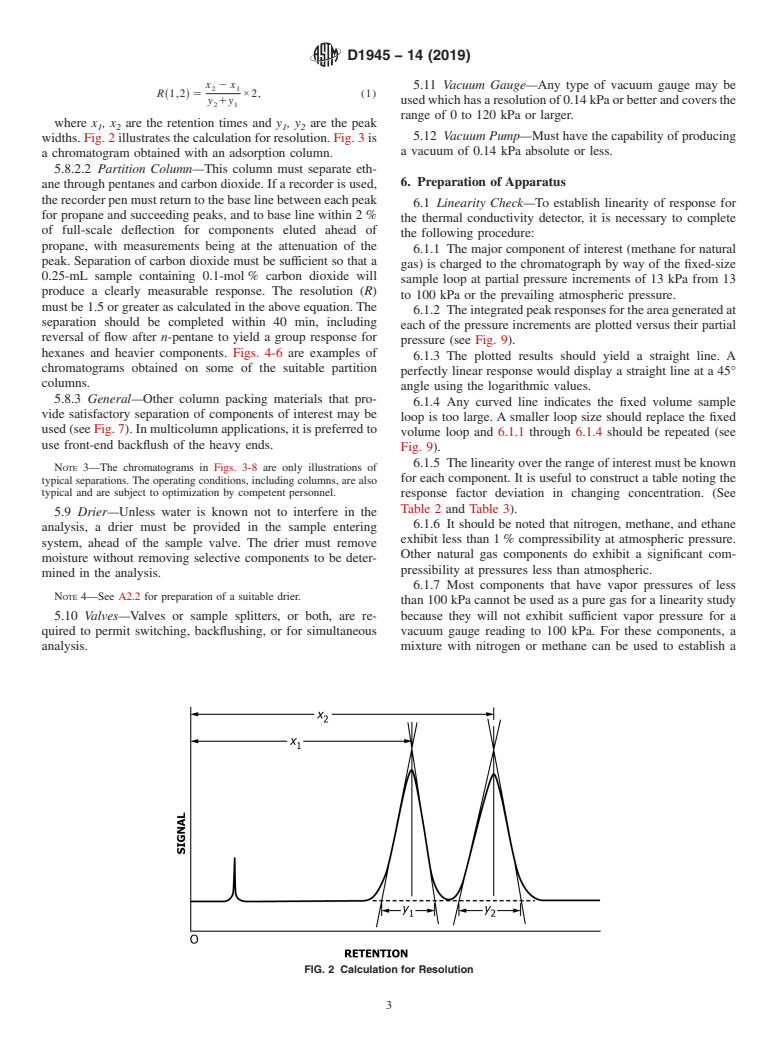
ASTM D1945-14(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is of significance for providing data for calculating physical properties of the sample, such as heating value and relative density, or for monitoring the concentrations of one or more of the components in a mixture.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the chemical composition of natural gases and similar gaseous mixtures within the range of composition shown in Table 1. This test method may be abbreviated for the analysis of lean natural gases containing negligible amounts of hexanes and higher hydrocarbons, or for the determination of one or more components, as required.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D1945 − 14 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
1
Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1945; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* calibration data obtained under identical operating conditions
from a reference standard mixture of known composition. The
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the chemi-
numerous heavy-end components of a sample can be grouped
cal composition of natural gases and similar gaseous mixtures
into irregular peaks by reversing the direction of the carrier gas
within the range of composition shown in Table 1. This test
through the column at such time as to group the heavy ends
method may be abbreviated for the analysis of lean natural
either as C and heavier, C and heavier, or C and heavier. The
5 6 7
gases containing negligible amounts of hexanes and higher
composition of the sample is calculated by comparing either
hydrocarbons, or for the determination of one or more
the peak heights, or the peak areas, or both, with the corre-
components, as required.
sponding values obtained with the reference standard.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4. Significance and Use
standard.
4.1 This test method is of significance for providing data for
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
calculating physical properties of the sample, such as heating
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
value and relative density, or for monitoring the concentrations
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of one or more of the components in a mixture.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Apparatus
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
5.1 Detector—The detector shall be a thermal-conductivity
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
type, or its equivalent in sensitivity and stability. The thermal
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
conductivity detector must be sufficiently sensitive to produce
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
a signal of at least 0.5 mV for 1 mol % n-butane in a 0.25-mL
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
sample.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.2 Recording Instruments—Either strip-chart recorders or
2. Referenced Documents
electronic integrators, or both, are used to display the separated
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
components. Although a strip-chart recorder is not required
D2597 Test Method for Analysis of Demethanized Hydro-
when using electronic integration, it is highly desirable for
carbon Liquid Mixtures Containing Nitrogen and Carbon
evaluation of instrument performance.
3
Dioxide by Gas Chromatography (Withdrawn 2016)
5.2.1 The recorder shall be a strip-chart recorder with a
E260 Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography
full-range scale of 5 mV or less (1 mV preferred). The width of
the chart shall be not less than 150 mm. A maximum pen
3. Summary of Test Method
response time of 2 s (1 s preferred) and a minimum chart speed
3.1 Components in a representative sample are physically
of 10 mm/min shall be required. Faster speeds up to 100 mm-
separated by gas chromatography (GC) and compared to
⁄min are desirable if the chromatogram is to be interpreted
using manual methods to obtain areas.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous
5.2.2 Electronic or Computing Integrators—Proof of sepa-
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.06.01 on Analysis of
ration and response equivalent to that for a recorder is required
Major Constituents by Gas Chromatography.
for displays other than by chart recorder. Baseline tracking
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published January 2020. Originally
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D1945 – 14. DOI:
with tangent skim peak detection is recommended.
10.1520/D1945-14R19.
2
5.3 Attenuator—If the chromatogram is to be interpreted
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
using manual methods, an attenuator must be used with the
Standards volume information, re
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.