ASTM C1287-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Uranium Compounds by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Standard Test Method for Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Uranium Compounds by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of 67 elements in uranium dioxide samples and nuclear grade uranium compounds and solutions without matrix separation by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The elements are listed in Table 1. These elements can also be determined in uranyl nitrate hexahydrate (UNH), uranium hexafluoride (UF6), triuranium octoxide (U3O8) and uranium trioxide (UO3) if these compounds are treated and converted to the same uranium concentration solution.
1.2 The elements boron, sodium, silicon, phosphorus, potassium, calcium and iron can be determined using different techniques. The analyst's instrumentation will determine which procedure is chosen for the analysis.
1.3 The test method for technetium-99 is given in Annex A1.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. WarningThe ICP-MS is a source of intense ultra-violet radiation from the radio frequency induced plasma. Protection from radio frequency radiation and UV radiation is provided by the instrument under normal operation.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1287 − 10
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Uranium
Compounds by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass
1
Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1287; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C753Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium
Dioxide Powder
1.1 This test method covers the determination of 67 ele-
C776Specification for Sintered Uranium Dioxide Pellets
ments in uranium dioxide samples and nuclear grade uranium
C787Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride for Enrich-
compounds and solutions without matrix separation by induc-
ment
tively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The
C788Specification for Nuclear-Grade Uranyl Nitrate Solu-
elements are listed in Table1. These elements can also be
tion or Crystals
determined in uranyl nitrate hexahydrate (UNH), uranium
C967Specification for Uranium Ore Concentrate
hexafluoride (UF ), triuranium octoxide (U O ) and uranium
6 3 8
C996Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride Enriched to
trioxide(UO )ifthesecompoundsaretreatedandconvertedto
3
235
Less Than 5 % U
the same uranium concentration solution.
,
C1346Practice for Dissolution of UF from P-10 Tubes
6
1.2 The elements boron, sodium, silicon, phosphorus,
C1347Practice for Preparation and Dissolution of Uranium
potassium, calcium and iron can be determined using different
Materials for Analysis
techniques. The analyst’s instrumentation will determine
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
which procedure is chosen for the analysis.
1.3 The test method for technetium-99 is given in Annex 3. Summary of Test Method
A1.
3.1 The sample is dissolved in acid if it is not already a
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as solution. A fixed quantity of internal standard is added to
standard. monitor and correct for signal instability. The level of impuri-
ties in the solution is measured by ICP-MS. Customized
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
software calculates the concentration of each element.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Uranium-concentration-matched standard solutions are
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
used to calibrate the ICP-MS instrument. The calibration is
3,4
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Warning—The
linear up to at least 0.2 µg/ml (100 µg/g U) for each analyte.
ICP-MS is a source of intense ultra-violet radiation from the
3.3 Microwave dissolution may be used as an alternate
radio frequency induced plasma. Protection from radio fre-
dissolution method.
quency radiation and UV radiation is provided by the instru-
ment under normal operation.
4. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 This test method is capable of measuring the elements
2
listed in Table 1, some of which are required by Specifications
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C753, C776, C787, C788, C967 and C996.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC26onNuclear
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
3
Test. “ICP-MSVersus Conventional Methods for theAnalysis ofTrace Impurities in
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2010.PublishedJuly2010.Originallyapproved Nuclear Fuel,” by Allenby, P., Clarkson, A. S., Makinson, P. R., presented at 2nd
in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as C1287–03. DOI: 10.1520/ Surrey Conference on Plasma Source Mass Spectrometry, Guildford, UK, July
C1287-10. 1987.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or “Trace Metals in NBL Uranium Standard CRM 124 Using ICP-MS,” by
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Aldridge, A. J., Clarkson, A. S., Makinson, P. R., Dawson, K. W., presented at 1st
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Durham International Conference on Plasma Source Mass Spectrometry, Durham,
the ASTM website. UK, September 1988.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1287 − 10
TABLE 1 Continued
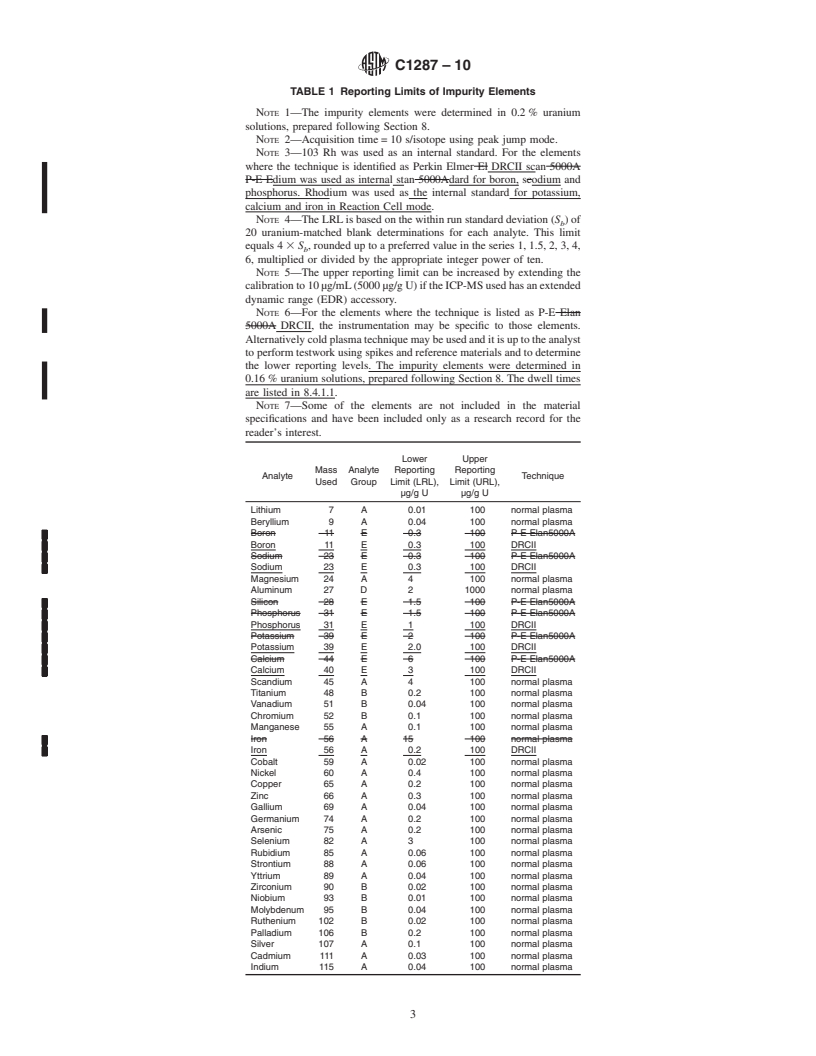
TABLE 1 Reporting Limits of Impurity Elements
Lower Upper
NOTE 1—The impurity elements were determined in 0.2% uranium
Mass Analyte Reporting Reporting
Analyte Technique
solutions, prepared following Section 8.
Used Group Limit (LRL), Limit (URL),
µg/g U µg/g U
NOTE 2—Acquisition time=10 s/isotope using peak jump mode.
Barium 138 A 0.02 100 normal plasma
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C1287–03 Designation:C1287–10
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Uranium
Compounds by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass
1
Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1287; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of 67 elements in uranium dioxide samples and nuclear grade uranium
compoundsandsolutionswithoutmatrixseparationbyinductivelycoupledplasmamassspectrometry(ICP-MS).Theelementsare
listed in Table1. These elements can also be determined in uranyl nitrate hexahydrate (UNH), uranium hexafluoride (UF ),
6
triuranium octoxide (U O ) and uranium trioxide (UO ) if these compounds are treated and converted to the same uranium
3 8 3
concentration solution.
1.2This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For a specific warning statement, see Note 1.
NOTE1—Warning:The ICP-MS is a source of intense ultra-violet radiation from the radio frequency induced plasma. Protection from radio frequency
radiation and UV radiation is provided by the instrument under normal operation.
1.3Theelementsboron,sodium,silicon,phosphorus,potassium,calciumandironcanbedeterminedusingdifferenttechniques.
The analyst’s instrumentation will determine which procedure is chosen for the analysis.
1.4The test method for technetium-99 is given in
1.2 Theelementsboron,sodium,silicon,phosphorus,potassium,calciumandironcanbedeterminedusingdifferenttechniques.
The analyst’s instrumentation will determine which procedure is chosen for the analysis.
1.3 The test method for technetium-99 is given in Annex A1.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Warning—The ICP-MS is a source of intense ultra-violet radiation from the radio frequency induced
plasma. Protection from radio frequency radiation and UV radiation is provided by the instrument under normal operation.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C753 Specification for Nuclear-Grade, Sinterable Uranium Dioxide Powder
C776 Specification for Sintered Uranium Dioxide Pellets
C787 Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride for Enrichment
C788 Specification for Nuclear-Grade Uranyl Nitrate Solution or Crystals
C967 Specification for Uranium Ore Concentrate
235
C996 Specification for Uranium Hexafluoride Enriched to Less Than 5 % U
,
C1346 Practice for Dissolution of UF from P-10 Tubes from P-10 Tubes
6
C1347 Practice for Preparation and Dissolution of Uranium Materials for Analysis
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The sample is dissolved in acid if it is not already a solution.Afixed quantity of internal standard is added to monitor and
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods ofTest.
Current edition approved July 10, 2003. Published August 2003. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as C1287–95(2001). DOI:
10.1520/C1287-03.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2010.PublishedJuly2010.Originallyapprovedin1994.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2003asC1287–03.DOI:10.1520/C1287-10.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1287–10
correct for signal instability. The level of impurities in the solution is measured by ICP-MS. Customized software calculates the
concentration of each element.
3.2 Uranium-concentration-matchedstandardsolutionsareusedtoca
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.