ASTM D7702/D7702M-14(2021)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Considerations When Evaluating Direct Shear Results Involving Geosynthetics
Standard Guide for Considerations When Evaluating Direct Shear Results Involving Geosynthetics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The shear strength of soil-geosynthetic interfaces and geosynthetic-geosynthetic interfaces is a critical design parameter for many civil engineering projects, including, but not limited to: waste containment systems, mining applications, dam designs involving geosynthetics, mechanically stabilized earth structures, reinforced soil slopes, and liquid impoundments. Since geosynthetic interfaces often serve as a weak plane on which sliding may occur, shear strengths of these interfaces are needed to assess the stability of earth materials resting on these interfaces, such as a waste mass or ore body over a lining system or the ability of a final cover to remain on a slope. Accordingly, project-specific shear testing using representative materials under conditions similar to those expected in the field is recommended for final design. Shear strengths of geosynthetic interfaces are obtained by either Test Method D5321/D5321M (geosynthetics) or D6243/D6243M (geosynthetic clay liners). This guide touches upon some of the issues that should be considered when evaluating shear strength data. Because of the large number of potential conditions that could exist, there may be other conditions not identified in this guide that could affect interpretation of the results. The seemingly infinite combinations of soils, geosynthetics, hydration and wetting conditions, normal load distributions, strain rates, creep, pore pressures, etc., will always require individual engineering evaluations by qualified practitioners. Along the same lines, the list of references provided in this guide is not exhaustive, nor are the findings and suggestions of any particular reference meant to be considered conclusive. The references and their related findings are presented herein only as examples available in the literature of the types of considerations that others have found useful when evaluating direct shear test results.
4.2 The figures included in this guide are only examples intended t...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide presents a summary of available information related to the evaluation of direct shear test results involving geosynthetic materials.
1.2 This guide is intended to assist designers and users of geosynthetics. This guide is not intended to replace education or experience and should only be used in conjunction with professional judgment. This guide is not intended to represent or replace the standard of care by which the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without consideration of a project’s many unique aspects. Not all aspects of this practice may be applicable in all circumstances. The word “Standard” in the title of this document means only that the document has been approved through the ASTM consensus process.
1.3 This guide is applicable to soil-geosynthetic and geosynthetic-geosynthetic direct shear test results, obtained using either Test Method D5321/D5321M or D6243/D6243M.
1.4 This guide does not address selection of peak or large-displacement shear strength values for design. References on this topic include Thiel (1),2 Gilbert (2), Koerner and Bowman (3), and Stark and Choi (4).
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardizatio...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7702/D7702M − 14 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Guide for
Considerations When Evaluating Direct Shear Results
1
Involving Geosynthetics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7702/D7702M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This guide presents a summary of available information
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
related to the evaluation of direct shear test results involving
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
geosynthetic materials.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 This guide is intended to assist designers and users of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
geosynthetics. This guide is not intended to replace education
or experience and should only be used in conjunction with 2. Referenced Documents
professional judgment. This guide is not intended to represent
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
or replace the standard of care by which the adequacy of a
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
given professional service must be judged, nor should this
Fluids
document be applied without consideration of a project’s many
D4439 Terminology for Geosynthetics
unique aspects. Not all aspects of this practice may be
D5321/D5321M Test Method for Determining the Shear
applicable in all circumstances. The word “Standard” in the
Strength of Soil-Geosynthetic and Geosynthetic-
title of this document means only that the document has been
Geosynthetic Interfaces by Direct Shear
approved through the ASTM consensus process.
D6243/D6243M Test Method for Determining the Internal
1.3 This guide is applicable to soil-geosynthetic and
and Interface Shear Strength of Geosynthetic Clay Liner
geosynthetic-geosynthetic direct shear test results, obtained by the Direct Shear Method
using either Test Method D5321/D5321M or D6243/D6243M.
3. Terminology
1.4 This guide does not address selection of peak or
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms relating to soil and
large-displacement shear strength values for design. Refer-
2
rock, refer to Terminology D653. For definitions of terms
ences on this topic include Thiel (1), Gilbert (2), Koerner and
relating to geosynthetics and GCLs, refer to Terminology
Bowman (3), and Stark and Choi (4).
D4439.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
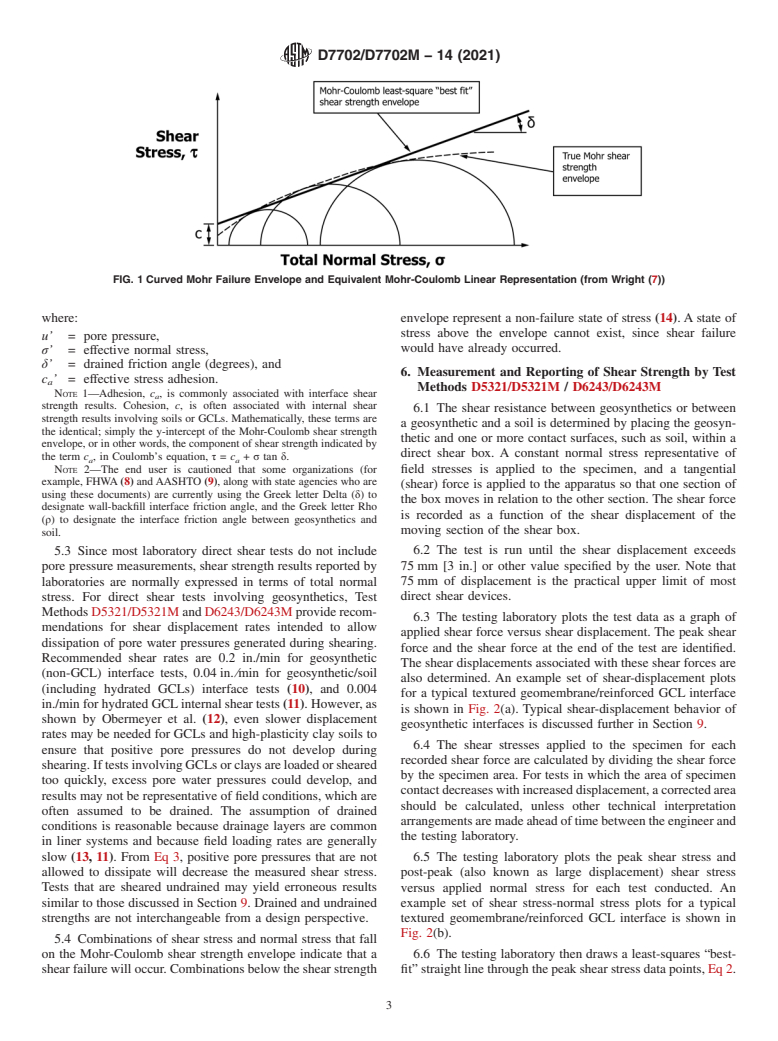
3.2.1 adhesion, c or c, n—the y-intercept of the Mohr-
each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to a
Coulomb shear strength envelope; the component of shear
ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be
strength indicated by the term c , in Coulomb’s equation, τ =
used independently of the other, and values from the two a
c + σ tan δ.
systems shall not be combined. a
3.2.2 failure envelope, n—curvi-linear line on the shear
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
stress-normal stress plot representing the combination of shear
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and normal stresses that define a selected shear failure criterion
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(for example, peak and post-peak). Also referred to as shear
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
strength envelope.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.2.3 Mohr-Coulomb friction angle δ,n—angle of friction
of a material or between two materials (degrees), the angle
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D35 on Geosynthetics
defined by the least-squares, “best-fit” straight line through a
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.04 on Geosynthetic Clay
Liners.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2021. Published August 2021. Originally
3
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D7702_D7702 – 14. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI:10.1520/D7702_D7702M-14R21. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
this standard. the ASTM website.
Copyright © A
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.