ASTM A290/A290M-05
(Specification)Standard Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Rings for Reduction Gears
Standard Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Rings for Reduction Gears
ABSTRACT
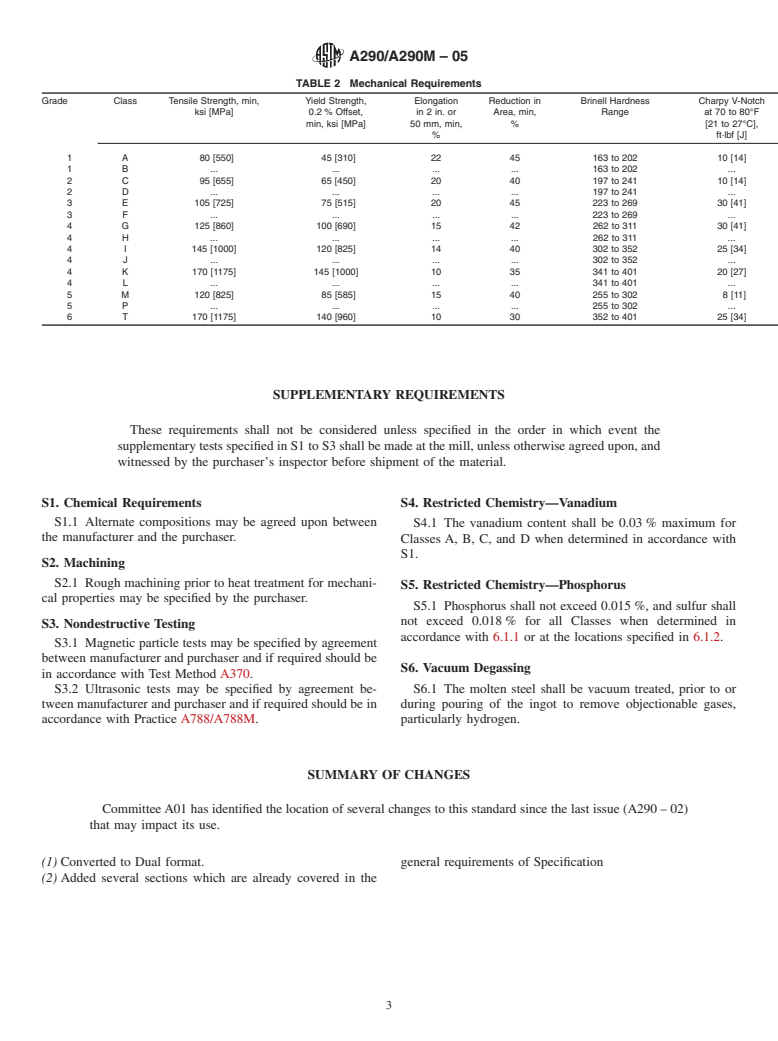
This specification deals with normalized and tempered, and quenched and tempered, carbon and alloy steel forged or rolled rings for reduction gears. The grades and classes of steels covered here are: Grade 1, Classes A and B, and Grade 2, Classes C and D, which are carbon steels; and Grade 3, Classes E and F, Grade 4, Classes G, H, I, J, K and L, Grade 5, Classes M and P, and Grade 6, Class T, which are alloy steels. Materials shall be manufactured by melting and forging processes and optional machining, and shall be allowed to cool prior to reheating. Heat treatment shall consist of normalizing and tempering for Grade 1, Classes A and B, and quenching and tempering for all other grades and classes. Heat and product analyses shall be performed wherein specimens shall conform to required chemical composition of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, copper, and aluminum. Steels shall also undergo tension, impact, and Brinell hardness tests, and shall conform to the following mechanical requirements: tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, reduction of area, Brinell hardness, and Charpy V-notch.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers normalized and tempered, and quenched and tempered, carbon and alloy steel forged or rolled rings for reduction gears.
1.2 Several grades and classes of steel are covered as follows:
1.2.1 Grade 1, Classes A and B, and Grade 2, Classes C and D, are carbon steel.
1.2.2 Grade 3, Classes E and F, Grade 4, Classes G, H, I, J, K and L, Grade 5, Classes M and P, and Grade 6, Class T, are alloy steel.
1.2.3 All grades and classes are considered weldable under proper conditions. Welding techniques are of fundamental importance and it is pre-supposed that welding procedure and inspection will be in accordance with proper methods for the class of material used.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A290/A290M – 05
Standard Specification for
Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Rings for Reduction
1
Gears
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA290/A290M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 4. Ordering Information and General Requirements
1.1 This specification covers normalized and tempered, and 4.1 In addition to the ordering information required by
quenched and tempered, carbon and alloy steel forged or rolled Specification , the purchaser shall specify in the inquiry,
rings for reduction gears. contract, and order the grade and class desired and the
1.2 Several grades and classes of steel are covered as supplementary requirements, if any, which should apply.
follows: 4.2 Material supplied to this specification shall conform to
1.2.1 Grade 1, ClassesAand B, and Grade 2, Classes C and the requirements of Specification , which outlines additional
D, are carbon steel. ordering information, manufacturing requirements, testing and
1.2.2 Grade 3, Classes E and F, Grade 4, Classes G, H, I, J, retesting methods and procedures, marking, certification, prod-
K and L, Grade 5, Classes M and P, and Grade 6, Class T, are uct analysis variations, and additional supplementary require-
alloy steel. ments.
1.2.3 All grades and classes are considered weldable under
5. Materials and Manufacture
proper conditions. Welding techniques are of fundamental
importance and it is pre-supposed that welding procedure and 5.1 Melting Process:
5.1.1 The steel shall be produced by any of the melting
inspection will be in accordance with proper methods for the
class of material used. requirements in Specification , which may be supplemented by
Supplementary Requirement S6, Vacuum Degassing.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in 5.2 Discard—Sufficient discard shall be taken from each
ingot to secure freedom from piping and undue segregation.
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
5.3 Forging Process—The forgings shall receive their hot
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance mechanical work in accordance with the requirements of
Specification .
with the standard.
5.4 Heat Treatment:
2. Referenced Documents
5.4.1 Cooling Prior to Heat Treatment—After forging and
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: before reheating for heat treatment, the forgings shall be
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing allowed to cool in a manner to prevent injury, to accomplish
of Steel Products transformation, and prevent flakes.
A788/A788M Specification for Steel Forgings, General Re- 5.4.2 Heat treatment shall consist of normalizing and tem-
quirements pering for Grade 1 classes A and B and quenching and
tempering for all other grades and classes.
3. Terminology
5.4.2.1 Normalizing—A furnace charge thus treated is
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of the terms used may be termed a normalizing charge.
found in Specification .
5.4.2.2 Quenching—The forgings shall be completely aus-
tenitizedandthenquenchedinasuitablemedium.Agroupthus
treated is termed a quenching charge.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
5.4.2.3 Tempering—Afurnace charge thus treated is termed
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets. a tempering charge. Minimum tempering temperatures shall be
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2005. Published September 2005. Originally
as follows:
approved in 1946. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as A290 – 02. DOI:
10.1520/A0290_A0290M-05.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A290/A290M – 05
7.1.2 Test Method—Full-size tension and Charpy V-notch
Minimum Tempering Temperature
Grade and Class °F [°C]
impact tests shall be conducted in accordance with Test
Grade 1 Classes A and B 1200 [650])
Methods and Definitions .
Grade 2 ClassesC&D,E,F,G,H,M,P 1100 [595])
7.2 Brinell Hardness—Forgings shall be within the hard-
Grade 3 ClassesE&F 1100 [595]
Grade 4 ClassesG&H 1100 [59
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.