ASTM D3859-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Selenium in Water
Standard Test Methods for Selenium in Water
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of dissolved and total recoverable selenium in most waters and wastewaters. Both test methods utilize atomic absorption procedures, as follows: Sections Test Method A---Gaseous Hydride AAS 2 7 to 15 Test Method B---Graphite Furnace AAS 16 to 24 Test Method A 1 to 20 [mu]g/L Test Method B 2 to 100 [mu]g/L
1.2 These test methods are applicable to both inorganic and organic forms of dissolved selenium. They are applicable also to particulate forms of the element, provided that they are solubilized in the appropriate acid digestion step. However, certain selenium-containing heavy metallic sediments may not undergo digestion.
1.3 These test methods are most applicable within the following ranges:
These ranges may be extended (with a corresponding loss in precision) by decreasing the sample size or diluting the original sample, but concentrations much greater than the upper limits are more conveniently determined by flame atomic absorption spectrometry.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Notes 2 and 3.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact
ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 3859 – 98
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Methods for
1
Selenium in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3859; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Con-
3
duits
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of dissolved
D 3919 Practice for Measuring Trace Elements in Water by
and total recoverable selenium in most waters and wastewaters.
3
Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry
Both test methods utilize atomic absorption procedures, as
D 4841 Practice for Estimation of Holding Time for Water
follows:
3
Samples Containing Organic and Inorganic Constituents
Sections
2
Test Method A—Gaseous Hydride AAS 7to15
3. Terminology
Test Method B—Graphite Furnace AAS 16 to 24
3.1 Definitions:
1.2 These test methods are applicable to both inorganic and
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in these test methods,
organic forms of dissolved selenium. They are applicable also
refer to Terminology D 1129.
to particulate forms of the element, provided that they are
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
solubilized in the appropriate acid digestion step. However,
3.2.1 total recoverable selenium—an arbitrary analytical
certain selenium-containing heavy metallic sediments may not
term relating to the recoverable forms of selenium that are
undergo digestion.
determinable by the digestion procedures included in these test
1.3 These test methods are most applicable within the
methods.
following ranges:
Test Method A 1 to 20 μg/L
4. Significance and Use
Test Method B 2 to 100 μg/L
4.1 In most natural waters selenium concentrations seldom
These ranges may be extended (with a corresponding loss in
exceed 10 μg/L. However, the runoff from certain types of
precision) by decreasing the sample size or diluting the original
seleniferous soils at various times of the year can produce
sample, but concentrations much greater than the upper limits
concentrations as high as several hundred micrograms per litre.
are more conveniently determined by flame atomic absorption
Additionally, industrial contamination can be a significant
spectrometry.
source of selenium in rivers and streams.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 High concentrations of selenium in drinking water have
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
been suspected of being toxic to animal life. Selenium is a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priority pollutant and all public water agencies are required to
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
monitor its concentration.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
4.3 These test methods determine the dominant species of
statements, see Note 2 and Note 3.
selenium reportedly found in most natural and wastewaters,
including selenities, selenates, and organo-selenium com-
2. Referenced Documents
pounds.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water 5. Purity of Reagents
3
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
5.1 Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests.
D 2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all reagents shall
3
Applicable Methods of Committee D–19 on Water
conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical
Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such
4
specifications are available. Other grades may be used, pro-
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-19 on
vided it is ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high
Water and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic
Constituents in Water.
4
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 1998. Published December 1998. Originally
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
published as D 3859 – 84. Last previous edition D 3859 – 93.
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
2
Lansford, M., McPherson, E. M., and Fishman, M. J., Atomic Absorption listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
Newsletter, Vol 13(4), 1974, pp. 103–105. Pollack, E. N., and West, S. J., Atomic Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
Absorption Newsletter, Vol 12(1), 1973, pp. 6–8. and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.
...







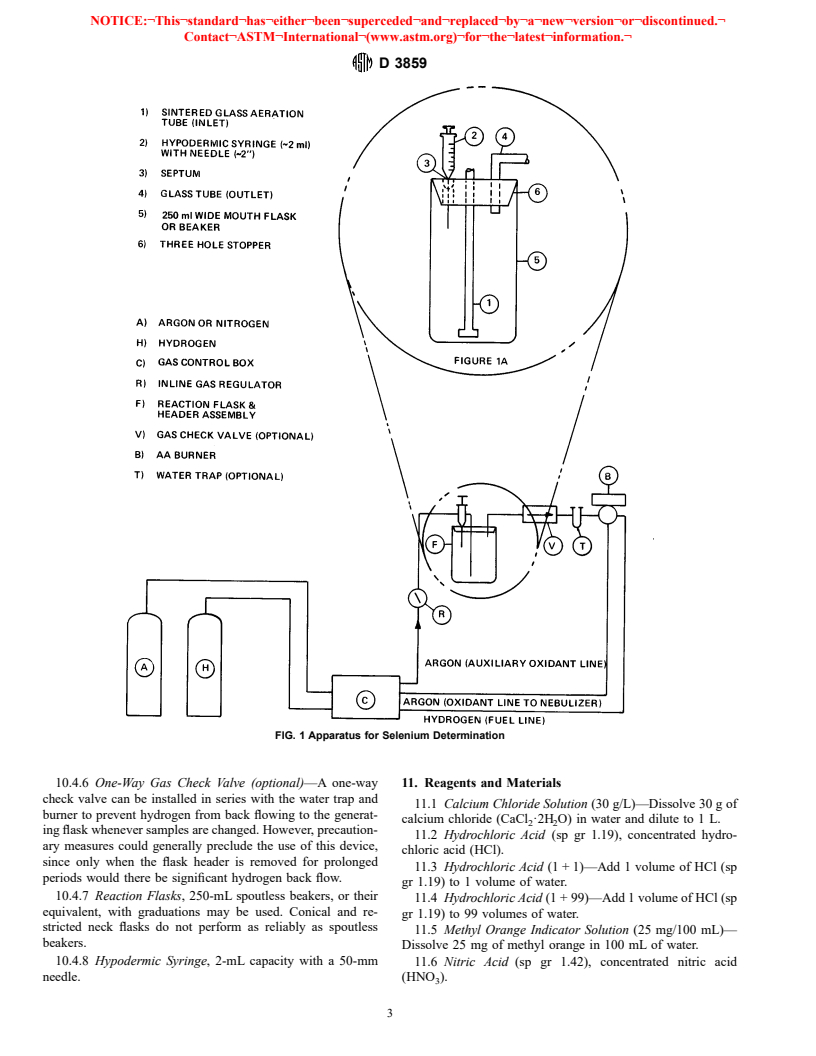
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.