ASTM E1017-88(1994)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Generic Performance Requirements for Exterior Residential Window Assemblies (Withdrawn 2003)
Standard Specification for Generic Performance Requirements for Exterior Residential Window Assemblies (Withdrawn 2003)
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the performance requirements for exterior prime and replacement residential window assemblies, regardless of their method or materials of manufacture. These requirements are limited only to exterior prime window assemblies and does not include requirements for secondary windows or storm windows.
1.2 Although this specification establishes various levels of acceptance criteria for window assemblies, there is no intent to infer that a given window assembly or design meeting any of these levels is acceptable for use in a particular building. The loads and levels of performance to which the test specimen is subjected within this specification are physical quantities to be applied or measured during testing and do not include consideration of safety factors.
1.3 This is a developmental specification representing those parameters that are customarily used to measure the generic performance of windows. The requirements prescribed in this specification shall be supplemented by the writers of individual window specifications to take into account particular material of construction. It is the intent of Subcommittee E06.51 to expand these requirements in future revisions to cover additional parameters as applicable.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. Metric (SI) equivalents of inch-pound units may be approximate.
1.5 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: E 1017 – 88 (Reapproved 1994)
Standard Specification for
Generic Performance Requirements for Exterior Residential
Window Assemblies
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1017; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors
Under Specified Pressure Across the Specimen
1.1 This specification establishes the performance require-
E 330 Test Method for Structural Performance of Exterior
ments for exterior prime and replacement residential window
Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors by Uniform Static Air
assemblies, regardless of their method or materials of manu-
Pressure Difference
facture. These requirements are limited only to exterior prime
E 547 Test Method for Water Penetration of Exterior Win-
window assemblies and does not include requirements for
dows, Curtain Walls, and Doors by Cyclic Static Air
secondary windows or storm windows.
Pressure Differential
1.2 Although this specification establishes various levels of
E 631 Terminology of Building Constructions
acceptance criteria for window assemblies, there is no intent to
F 588 Test Methods for Resistance of Window Assemblies
infer that a given window assembly or design meeting any of
to Forced Entry, Excluding Glazing
these levels is acceptable for use in a particular building. The
2.2 ANSI Standard:
loads and levels of performance to which the test specimen is
A58.1 Building Code Requirements for Minimum Design
subjected within this specification are physical quantities to be
Loads in Buildings and Other Structures
applied or measured during testing and do not include consid-
eration of safety factors.
3. Terminology
1.3 This is a developmental specification representing those
3.1 Definitions: For definitions of terms used in this speci-
parameters that are customarily used to measure the generic
fication, see Terminology E 631 or the appropriate test method.
performance of windows. The requirements prescribed in this
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
specification shall be supplemented by the writers of individual
3.2.1 exterior window—the construction intended to be
window specifications to take into account particular material
installed in the exterior of the building envelope; does not refer
of construction. It is the intent of Subcommittee E06.51 to
to the position of this construction relative to a storm or
expand these requirements in future revisions to cover addi-
secondary window.
tional parameters as applicable.
3.2.2 prime window—the vision area of new building con-
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
struction that protects the building interior from climatic
as the standard. SI equivalents of inch-pound units may be
elements as opposed to a storm or secondary product used
approximate.
mainly for energy conservation.
1.5 The following hazards caveat pertains only to the test
3.2.3 replacement window—the vision area that takes the
method portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard
place of an existing window.
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
4. Classification
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
4.1 Window assemblies are generally divided into types
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
based upon their intended application (for example, residential,
to use.
commercial, industrial, etc.). For the purposes of this specifi-
2. Referenced Documents cation, which deals only with residential-type window assem-
blies, windows are subdivided into the following grades based
2.1 ASTM Standards:
on their performance capabilities with the grade numbers
E 283 Test Method for Determining the Rate of Air Leakage
indicating the design pressure in pounds per square foot.
4.1.1 Grade 15,
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-6 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.51
on Component Performance of Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.11.
Current edition approved July 25, 1988. Published September 1988. Originally Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street,
published as E 1017 – 85. Last previous edition E 1017 – 85. New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
E 1017 – 88 (1994)
TABLE 1 Performance Test Requirements (Inch-Pound Units)
Grade Level
15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Preliminary load (minimum test pressure sus- 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
tained without damage), lbf/ft
Air infiltration for operable windows (maximum
infiltration at each test pressure, ft /min·ft
of operating crack length):
0.57 lbf/ft 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.10 0.10 0.10
1.57 lbf/ft 0.37 0.37 0.37 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.15 0.15 0.15
6.24 lbf/ft 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.30 0.30 0.30
A
Air infiltration for nonoperable windows
(maximum infiltration at each test pressure,
3 2
ft /min·ft of overall window area):
0.57 lbf/ft 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.10 0.10 0.10
1.57 lbf/ft 0.37 0.37 0.37 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.15 0.15 0.15
6.24 lbf/ft 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.60 0.30 0.30 0.30
Water penetration (minimum test pressure sus- 2.86 2.86 2.86 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50 5.00 5.50 6.00
tained without leakage, lbf/ft )
Structural performance (minimum test pressure 22.5 30 37.5 45 52.5 60 67.5 75 82.5 90
sustained without damage, lbf/ft )
B
Forced entry resistance . . . . . . . . . .
A
Nonoperable windows refer to a complete window assembly and do not include any operable portions. To calculate air leakage when windows contain both operable
and nonoperable portions, no consideration shall be made for the nonoperable portion of the window unit.
B
To be determined by the specifying authority.
4.1.2 Grade 20, differential prescribed in Table 1 and Table 2 for the grade of
4.1.3 Grade 30, performance desired, there shall be no glazing material break-
4.1.4 Grade 40, age, permanent damage to fasteners, hardware parts, or any
4.1.5 Grade 50, and other components that would cause the unit to be inoperable,
4.1.6 Grade 60. and there shall be no permanent deformation of any main
frame, sash, or ventilator member in excess of 0.4 % of its
5. Performance Requirements
span.
5.1 Preliminary Loading Requirements—When tested in 5.6 Forced Entry Resistance Requirements—When tested in
accordance with 8.6, the forced entry resistance shall meet or
accordance with 8.1, under the uniform static air pressure
differential prescribed in Table 1 and Table 2 for the grade of exceed Test Methods F 588 requirements set forth by the
specifying authority.
performance desired, there shall be no glazing material break-
age, permanent damage to fasteners, hardware parts, or any
6. Test Specimen
other components that would cause the unit to be inoperable.
6.1 Window assemblies tested for conformance to this
5.2 Operating Force Requirements—When tested in accor-
specification shall be specimens representative of those pro-
dance with 8.2, the operating force shall never exceed 25 lbf
duced by the manufacturer or fabricator. Test specimens shall
(111 N).
be caulked, sealed, painted, or otherwise finished and prepared
5.3 Air Infiltration Requirements—When tested in accor-
only as they would normally be prepared for actual installation
dance with 8.3, the rate of air infiltration measured at each of
and use. Test specimens shall be mounted for testing as
the three uniform static air pressure differentials shall not
required by the appropriate test method, in a manner simulating
exceed the limits established in Table 1 and Table 2 for the
the intended field installation of the unit in accordance with the
grade of performance desired.
manufacturer’s written installation instructions.
5.4 Water Penetration Resistance Requirements—When
6.2 Test specimens submitted for testing for conformance to
tested in accordance with 8.4, under the uniform static air
this specification shall be of the largest frame and sash or
pressure differential prescribed in Table 1 and Table 2 for the
ventilator size for which conformance is desired.
grade of performance desired, no water shall pass beyond the
6.2.1 Casement, awning, projected, nonoperative, and simi-
interior face of the test specimen and overflow into the room or
lar designs submitted for testing shall be of the largest unit
penetrate into the wall cavity area.
frame and sash or ventilator area for which conformance is
5.5 Structural Performance Requirements—When tested in
desired.
accordance with 8.5, under the uniform static air pressure
6.2.2 Double-hung, single-hung, and similar designs sub-
mitted for testing shall be of the greatest width and of the
4 largest unit frame and sash or ventilator area in that width for
Supporting data are available from ASTM Headquarters. Request RR: E06-
1001. which conformance is desired.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
E 1017 – 88 (1994)
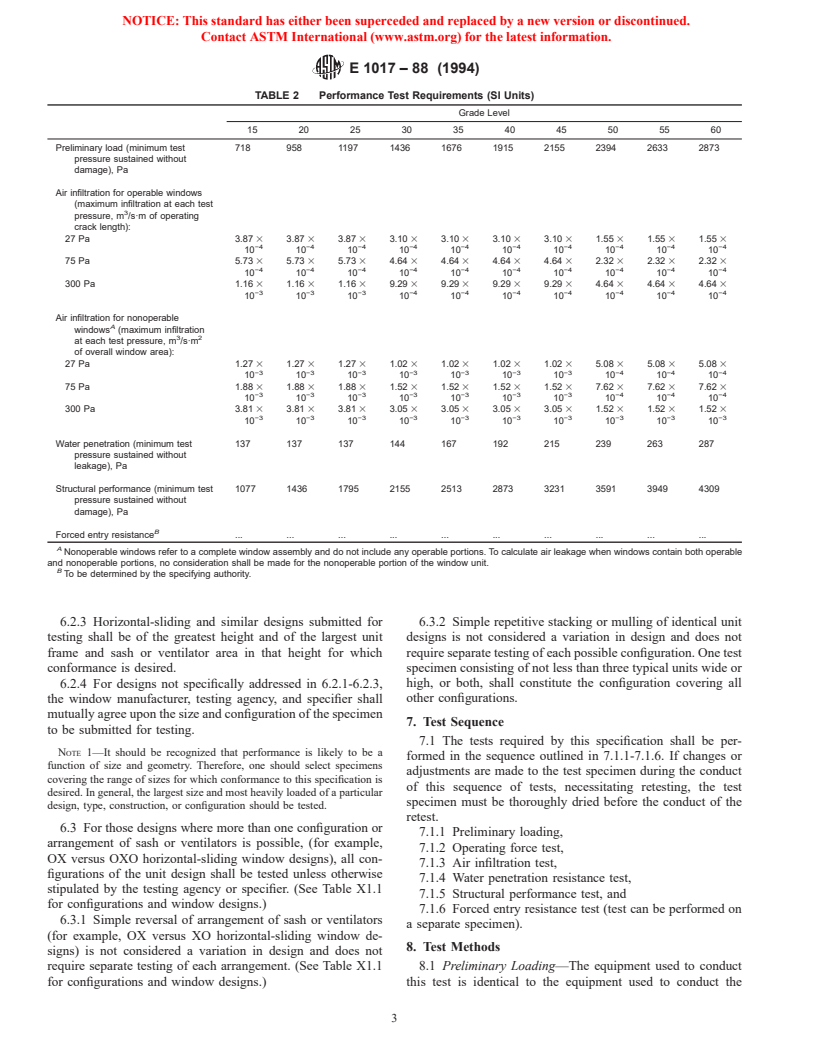
TABLE 2 Performance Test Requirements (SI Units)
Grade Level
15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Preliminary load (minimum test 718 958 1197 1436 1676 1915 2155 2394 2633 2873
pressure sustained without
damage), Pa
Air infiltration for operable windows
(maximum infiltration at each test
pressure, m /s·m of operating
crack length):
27 Pa 3.87 3 3.87 3 3.87 3 3.10 3 3.10 3 3.10 3 3.10 3 1.55 3 1.55 3 1.55 3
−4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
75 Pa 5.73 3 5.73 3 5.73 3 4.64 3 4.64 3 4.64 3 4.64 3 2.32 3 2.32 3 2.32 3
−4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
300 Pa 1.16 3 1.16 3 1.16 3 9.29 3 9.29 3 9.29 3 9.29 3 4.64 3 4.64 3 4.64 3
−3 −3 −3 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4 −4
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
Air infiltration
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.