ASTM D831/D831M-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Gas Content of Cable and Capacitor Oils
Standard Test Method for Gas Content of Cable and Capacitor Oils
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The gas content of cable and capacitor oils is considered to be important, since the evolution of gas in the form of bubbles can have an adverse effect on the insulating properties of these fluids. It is customary to degas these oils prior to use, and this test method provides a means of determining the gas content before and after degassing.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the gas content of electrical insulating oils of low and medium viscosities in the general range up to 190 mm2/s at 104°F [40°C], such as are used in capacitors and paper-insulated electric cables and cable systems of the oil-filled type. The determination of gas content is desirable for any insulating oil having these properties and intended for use in a degassed state.Note 1—For testing insulating oils with viscosities of 19 mm2/s or below at 40°C, see Test Method D2945.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D831/D831M − 12
Standard Test Method for
1
Gas Content of Cable and Capacitor Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D831/D831M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope dissolvedgas.Fromthevolumeofoiladmittedtothechamber,
the temperature, the pressure produced, and volume occupied
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the gas
by the released gas, the gas volume under standard conditions
content of electrical insulating oils of low and medium
2 of pressure and temperature may be calculated as a percentage
viscosities in the general range up to 190 mm /s at 104°F
by volume of oil.
[40°C], such as are used in capacitors and paper-insulated
electric cables and cable systems of the oil-filled type. The
4. Significance and Use
determination of gas content is desirable for any insulating oil
4.1 Thegascontentofcableandcapacitoroilsisconsidered
having these properties and intended for use in a degassed
to be important, since the evolution of gas in the form of
state.
2
NOTE 1—For testing insulating oils with viscosities of 19 mm /s or bubbles can have an adverse effect on the insulating properties
below at 40°C, see Test Method D2945.
of these fluids. It is customary to degas these oils prior to use,
and this test method provides a means of determining the gas
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
content before and after degassing.
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
5. Apparatus (see Fig. 1)
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
5.1 Degassing Chamber—Degassing chamber, A, made of
4
with the standard. heat-resistantglass (withcalibratedoilwellatbottom),having
afixedtotalspacevolumeofabout175to300mL.Theoilwell
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
shall have a maximum capacity of 50 mL and shall be
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
calibrated in 0.2-mL divisions.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.2 Stopcocks—Glass stopcocks, B and C, which shall have
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
large-diameter barrels and a mirror finish to ensure against
5
leakage. Use stopcock grease on all stopcocks and ground-
2. Referenced Documents
glass joints.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.3 Atomizer—Glass pipet, D, placed to drop oil on the side
2
D2945Test Method for Gas Content of Insulating Oils
of the degassing chamber, or
2
(Withdrawn 2012)
5.3.1 FrittedDisk(Alternative)—Capacity30mm,medium-
porosity.
3. Summary of Test Method
NOTE 2—Some experience has shown improvement in the atomization
3.1 This test method consists essentially of feeding the oil
2
process,particularlyforoilsofmediumviscosityabove95mm /sat40°C,
into an evacuated chamber in such a manner that the oil is
if a 30-mm medium-porosity fritted disk is substituted for the pipet.
thoroughlyexposedtothevacuum,allowingfreeescapeofany
5.4 Pressure Gage— Pressure gage, E, of modified McLeod
6
type. Includethevolumeofthisgageintheover-allvolumeof
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D27 on
Electrical Insulating Liquids and Gasesand is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
4
mittee D27.03 on Analytical Tests. Borosilicate glass has been found to be satisfactory for this purpose.
5
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2012. Published November 2012. Originally AstopcockgreaseequivalenttoNo.15521.Areadilyavailablevacuumsealing
approved in 1945. Last previous edition approved in 1994 as D831–94(2004). compound. Dow Corning grease #1597418, has been found to be satisfactory for
DOI: 10.1520/D0831_D0831M-12. this use.
2 6
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or A McLeod gauge Flosdorf modification, available from Sigma-Aldrich
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Company,hasbeenfoundsatisfactoryforthispurpose.Thesolesourceofsupplyof
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the apparatus known to the committee at this time is Sigma-Aldrich Company. If
the ASTM website. you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM
2
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
1
www.astm.org. meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you
...
Designation: D831 − 94 (Reapproved 2004) D831/D831M − 12
Standard Test Method for
1
Gas Content of Cable and Capacitor Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D831;D831/D831M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the gas content of electrical insulating oils of low and medium viscosities in
2
the general range up to 190 cStmm /s at 104°F (40°C),[40°C], such as are used in capacitors and paper-insulated electric cables
and cable systems of the oil-filled type. The determination of gas content is desirable for any insulating oil having these properties
and intended for use in a degassed state.
2
NOTE 1—For testing insulating oils with viscosities of 19 cStmm at 40°C or below,/s or below at 40°C, see Test Method D2945.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2 2
D2945 Test Method for Gas Content of Insulating Oils (Withdrawn 2012)
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 This test method consists essentially of feeding the oil into an evacuated chamber in such a manner that the oil is thoroughly
exposed to the vacuum, allowing free escape of any dissolved gas. From the volume of oil admitted to the chamber, the
temperature, the pressure produced, and volume occupied by the released gas, the gas volume under standard conditions of pressure
and temperature may be calculated as a percentage by volume of oil.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The gas content of cable and capacitor oils is considered to be important, since the evolution of gas in the form of bubbles
can have an adverse effect on the insulating properties of these fluids. It is customary to degas these oils prior to use, and this test
method provides a means of determining the gas content before and after degassing.
5. Apparatus (see Fig. 1)
4
5.1 Degassing Chamber—Degassing chamber, A, made of heat-resistant glass (with calibrated oil well at bottom), having a
fixed total space volume of about 175 to 300 mL. The oil well shall have a maximum capacity of 50 mL and shall be calibrated
in 0.2-mL divisions.
5.2 Stopcocks—Glass stopcocks, B and C, which shall have large-diameter barrels and a mirror finish to ensure against leakage.
5
Use stopcock grease on all stopcocks and ground-glass joints.
5.3 Atomizer—Glass pipet, D, placed to drop oil on the side of the degassing chamber, or
5.3.1 Fritted Disk (Alternative)—Capacity 30 mm, medium-porosity.
2
NOTE 2—Some experience has shown improvement in the atomization process, particularly for oils of medium viscosity above 95 cStmm /s at 40°C,
if a 30-mm medium-porosity fritted disk is substituted for the pipet.
6
5.4 Pressure Gage— Pressure gage, E, of modified McLeod type. Include the volume of this gage in the over-all volume of
the apparatus (Note 3). This is essential and must also include the volume of the gage-connecting tubing.
NOTE 3—The volume of the gage may be obtained from the manufacturer or measured.
5.5 Oil Trap, F, having a capacity of 250 mL.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D831/D831M − 12
FIG. 1 Apparatus for Determination of Gas Content of Cable and Capacitor Oils
5.6 Thermometer, T, room ambient.
5.7 Cold Trap, J, employed to eliminate possible error due to presence of condensable vapors.
5.8 Oven, K, employed to enhance the atomization process. The oven shall enclose the degassing chamber, A, between
stopcocks B and C, and point L. Provide suitable means for reading, maintaining, and regulating temperature in a range from 30
to 150°C. Measure temperature by means of a thermocouple fastened to the oil chamber at the 25-mL mark and suitably shielded
to eliminate radiation errors.
6. Sampling
6.1 When convenient, connect the degassing chamber of the measuring equipment directly to the container from which the oil
is to be sampled. This is usually not convenient and is often impossible. The method of sampling described in 6.2 is recommended
as an alternative.
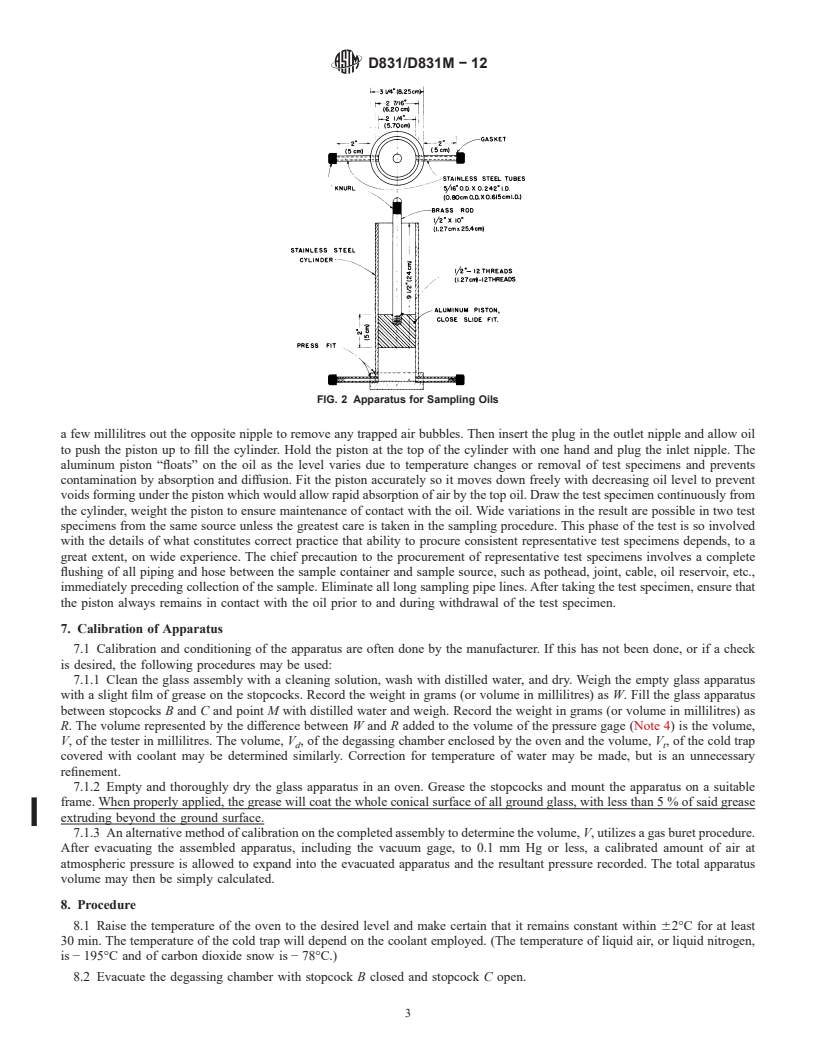
1
6.2 Use the sample container as shown in Fig. 2, which consists of a stainless s
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.