ASTM E3036-15(2021)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Notating Facade Conditions in the Field
Standard Guide for Notating Facade Conditions in the Field
SCOPE
1.1 This guide consists of symbols and notations pertaining to documenting deficient conditions observed during facade inspections.
1.2 The purpose of this guide is to provide a quick shorthand, notation system that will serve as a uniform system for facade inspectors to record their observations on existing elevation drawings or photographs, or both, of existing building facades.
1.3 This guide is not intended to be used to record or document a diagnosis for the particular symptom.
1.4 Notations are listed in alphabetical order. Compound terms appear as per the first word as spoken.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E3036 − 15 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Guide for
1
Notating Facade Conditions in the Field
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E3036; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.1 This guide consists of symbols and notations pertaining
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
to documenting deficient conditions observed during facade
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
inspections.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 The purpose of this guide is to provide a quick
2
shorthand, notation system that will serve as a uniform system
2.1 ASTM Standards:
for facade inspectors to record their observations on existing
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
elevation drawings or photographs, or both, of existing build-
3
3. Symbols
ing facades.
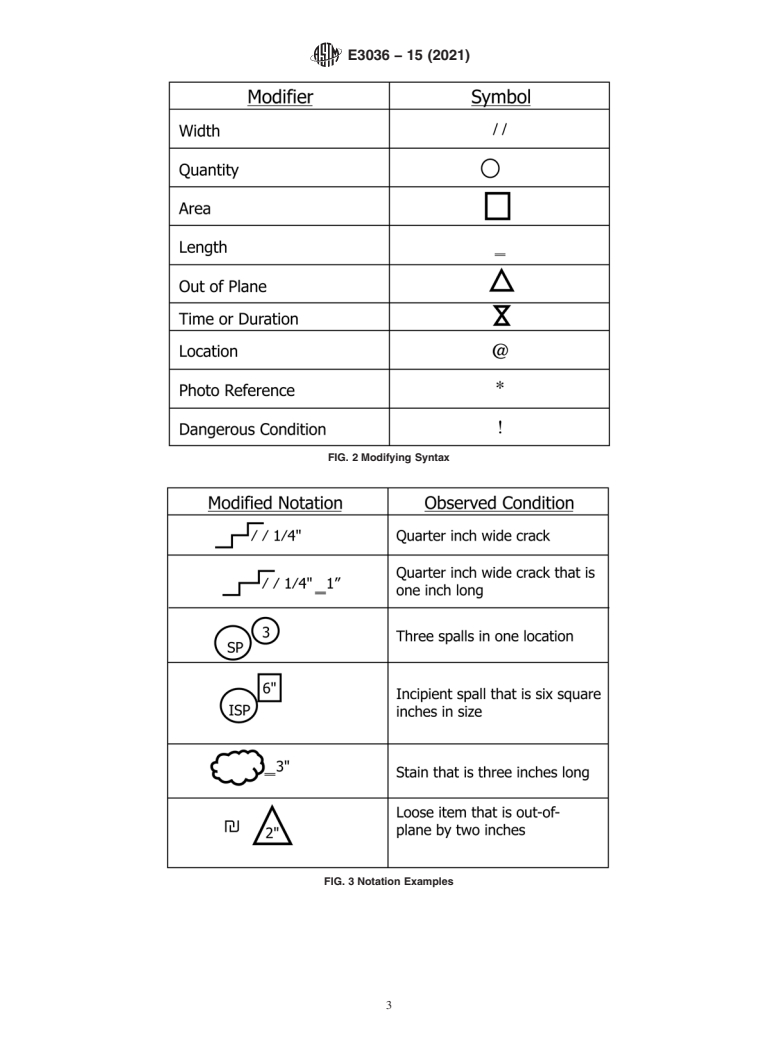
3.1 See Fig. 1.
1.3 This guide is not intended to be used to record or
document a diagnosis for the particular symptom.
4. Modifying Syntax
1.4 Notations are listed in alphabetical order. Compound
4.1 See Fig. 2.
terms appear as per the first word as spoken.
5. Notation Examples
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
5.1 See Fig. 3.
standard.
6. Keywords
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
6.1 condition; facade; notation; survey
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1 2
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Performance For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.55 on Perfor- contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
mance of Bu
...
This May Also Interest You
ABSTRACT
This specification covers exterior windows, glazed curtain walls, doors and impact protective systems used in buildings located in geographic regions that are prone to hurricanes. The test specimens shall be Fenestration assemblies, and impact protective systems; which shall be tested using the large missile test, and small missile test. The air pressure cycling, missiles, and impact location are also detailed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers exterior windows, glazed curtain walls, doors, and impact protective systems used in buildings located in geographic regions that are prone to hurricanes.
1.1.1 Exception—Exterior garage doors and rolling doors are governed by ANSI/DASMA 115 and are beyond the scope of this specification.
1.2 This specification provides the information required to conduct Test Method E1886.
1.3 Qualification under this specification provides a basis for judgment of the ability of applicable elements of the building envelope to remain unbreached during a hurricane; thereby minimizing the damaging effects of hurricanes on the building interior and reducing the magnitude of internal pressurization. While this standard was developed for hurricanes, it may be used for other types of similar windstorms capable of generating windborne debris.
1.4 This specification provides a uniform set of guidelines based upon currently available information and research.2 As new information and research becomes available it will be considered.
1.5 All values are stated in SI units and are to be regarded as standard. Values given in parentheses are for information only. Where certain values contained in reference documents cited and quoted herein are stated in inch-pound units, they must be converted by the user.
1.6 The following precautionary statement pertains only to the test method portion, Section 5, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification15 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification15 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is a standard procedure for determining the resistance to water penetration under uniform static air pressure differences. The air-pressure differences acting across a building envelope vary greatly. These factors should be fully considered prior to specifying the test pressure difference to be used.
Note 1: In applying the results of tests by this test method, note that the performance of a wall or its components, or both, may be a function of proper installation and adjustment. In service, the performance will also depend on the rigidity of supporting construction and on the resistance of components to deterioration by various causes, vibration, thermal expansion and contraction, etc. It is difficult to simulate the identical complex wetting conditions that can be encountered in service, with large wind-blown water drops, increasing water drop impact pressures with increasing wind velocity, and lateral or upward moving air and water. Some designs are more sensitive than others to this upward moving water.
Note 2: This test method does not identify unobservable liquid water which may penetrate into the test specimen.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance of exterior windows, curtain walls, skylights, and doors to water penetration when water is applied to the outdoor face and exposed edges simultaneously with a uniform static air pressure at the outdoor face higher than the pressure at the indoor face.
1.2 This test method is applicable to any curtain-wall area or to windows, skylights, or doors alone.
1.3 This test method addresses water penetration through a manufactured assembly. Water that penetrates the assembly, but does not result in a failure as defined herein, may have adverse effects on the performance of contained materials such as sealants and insulating or laminated glass. This test method does not address these issues.
1.4 The proper use of this test method requires a knowledge of the principles of pressure measurement.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 7.1.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard5 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide is for use by individuals and entities involved with the design and specification of EIFS details for a specific building.
4.2 This guide can be applied to both EIFS-clad barrier wall assembly and EIFS-clad wall with drainage.
4.3 This guide can be applied to new and existing EIFS buildings, prefabricated versus on-site installed EIFS, and residential and commercial EIFS buildings.
4.4 This guide is not meant to replace the types of information normally present in text format in a project’s specifications.
4.5 This guide is not applicable to EIFS materials used in non EIFS applications, such as a topcoat for other base materials like traditional Portland cement plaster (stucco) and concrete.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes the types of project-specific construction conditions that need to be communicated by means of drawings (“details”) for the purpose of constructing Exterior Insulation and Finish System (EIFS)-clad barrier and drainage wall assemblies. EIFS manufacturers provide basic details for the installation of their materials and interface with adjacent materials. These details are generic and, in many cases, do not apply to specific project conditions.
1.2 This guide addresses only the EIFS itself and the interface between the EIFS and the materials immediately adjacent to the EIFS; it does not address all parts of the wall assembly.
1.3 Not all possible construction detail conditions are addressed by this guide. Identify and provide details for all construction conditions that exist on a specific building.
1.4 This guide is intended to supplement but not supersede information from the EIFS manufacturer about how their specific product should be detailed, nor to supersede technical product acceptance reports or the code requirements of regulatory authorities.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Guide3 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SCOPE
1.1 This specification is limited to vapor permeable flexible sheet materials which are intended to be mechanically attached and are generally installed behind the cladding system in exterior walls.
1.2 This specification is limited to the evaluation of materials and does not address installed performance. Although the fastening practices (type of fastener, fastening schedule, etc.) may affect the installed function of these materials, they are not included in this specification.
1.3 This specification does not address integration of the water-resistive barrier with other wall elements. The topic is addressed in more detail in Practice E2112 and Guide E2266.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
8.1 The procedures described are those that will test the behavior of segments of wall construction under conditions representative of those encountered in service. Performance criteria based on data from those procedures can ensure structural adequacy and service life.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the following procedures for determining the structural properties of segments of wall, floor, and roof constructions:
Section
Test Specimens
3
Loading
4
Deformation Measurements
5
Reports
6
Precision and Accuracy
7
TESTING WALLS
Significance and Use
8
Compressive Load
9
Tensile Load
10
Transverse Load—Specimen Horizontal
11
Transverse Load—Specimen Vertical
12
Concentrated Load
13
Impact Load—See Test Methods E695 and E661
Racking Load—Evaluation of Sheathing Materials
on a Standard Wood Frame
14
Racking Load—Evaluation of Sheathing Materials (Wet)
on a Standard Wood Frame
15
TESTING FLOORS
Significance and Use
16
Transverse Load
17
Concentrated Load
18
Impact Load—See Test Methods E695 and E661
TESTING ROOFS
Section
Significance and Use
19
Transverse Load
20
Concentrated Load
21
APPENDIX
Technical Interpretation
Appendix X1
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard14 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard14 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is a standard procedure for determining structural performance under uniform static air pressure difference. This typically is intended to represent the effects of a wind load on exterior building surface elements. The actual loading on building surfaces is quite complex, varying with wind direction, time, height above ground, building shape, terrain, surrounding structures, and other factors. The resistance of many windows, curtain walls, and door assemblies to wind loading is also complex and depends on the complete history of load, magnitude, duration, and repetition. These factors are discussed in ASCE/SEI 7 and in the literature (1-8).5
5.2 Design wind velocities are selected for particular geographic locations and probabilities of occurrence based on data from wind velocity maps such as are provided in ASCE/SEI 7. These wind velocities are translated into uniform static air pressure differences and durations acting inward and outward. Complexities of wind pressures, as related to building design, wind intensity versus duration, frequency of occurrence, and other factors must be considered. Superimposed on sustained winds are gusting winds which, for short periods of time from a fraction of a second to a few seconds, are capable of moving at considerably higher velocities than the sustained winds. The analytical procedures in ASCE/SEI 7, wind tunnel studies, computer simulations, and model analyses are helpful in determining the appropriate design wind loads on exterior surface elements of buildings. Generally, wind load durations obtained from ASCE/SEI 7 are 2 s to 10 s and are dependent upon the specific time reference employed in determining the pressure coefficients.
5.3 Some materials have strength or deflection characteristics that are time dependent. Therefore, the duration of the applied test load may have a significant impact on the performance of materials used in the test specimen. The most common examples of materials with...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the determination of the structural performance of exterior windows, doors, skylights, and curtain walls under uniform static air pressure differences, using a test chamber. This test method is applicable to curtain wall assemblies including, but not limited to, metal, glass, masonry, and stone components.2
1.2 This test method is intended only for evaluating the structural performance associated with the specified test specimen and not the structural performance of adjacent construction.
1.3 The proper use of this test method requires a knowledge of the principles of pressure and deflection measurement.
1.4 This test method describes the apparatus and the procedure to be used for applying uniformly distributed test loads to a specimen.
1.4.1 Procedure A (see 11.2) shall be used when a load-deflection curve is not required.
1.4.2 Procedure B (see 11.3) shall be used when a load-deflection curve is required.
1.5 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory materials. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the standard.
1.6 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with int...
- Standard7 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide may be used by design professionals and others in the building construction industry to provide factual support for professional judgment of materials, products, or systems during the design development of new and remedial building exterior enclosure construction.
4.2 This guide is intended to provide guidance to the user of this standard in the evaluation and qualification of materials, products, or systems with which they do not have substantial, long-term experience or that are intended to be employed in a new or different manner. The standard may be used to investigate and assess the probable performance of such materials, products, or systems in relation to the proposed use on or as part of a building exterior enclosure.
4.3 The procedures outlined in Section 5 will help guide the user in making informed selections based on the materials, products, or systems performance history on constructed projects and provide information on limitations of use, the manufacturer’s performance history, and current status. The use of this guide will reduce, but not eliminate, the risk of in-service performance problems with materials, products, or systems.
4.4 The procedures listed in this guide are intended for use in selecting materials, products, or systems that are critical to the safety, function, or serviceability of a building, or where they constitute substantial components of the work. The recommendations in this guide are not applicable to all materials, products, or systems that can be incorporated in buildings. The user must exercise appropriate judgment and care regarding the need when applying the various procedures included in this guide, including the use of the form included in Appendix X1, with regard to particular materials, products, or systems, and specific buildings. Materials, products, or systems that will be used for a noncritical or incidental use usually do not require an exhaustive evaluation. Materials, products, or systems ...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers guidance to design professionals in the evaluation of materials, products, or systems with which they are not familiar and to help determine that the selected materials, products, or systems are suitable for use on or as a part of a building’s exterior enclosure.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Guide6 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Guide6 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide is intended to provide building professionals with a comprehensive methodology for evaluating water leakage through walls. It addresses the performance expectations and service history of a wall, the various components of a wall, and the interaction between these components and adjacent construction. It is not intended as a construction quality control procedure, nor as a preconstruction qualification procedure. It is intended for evaluating buildings that exhibit water leakage.
4.1.1 Qualifications—This guide requires the evaluator to possess a knowledge of basic physics and of construction and wall design principles and practices.
4.1.2 Application—The sequential activities described herein are intended to produce a complete and comprehensive evaluation program, but all activities may not be applicable or necessary for a particular evaluation program. It is the responsibility of the professional using this guide to determine the activities and sequence necessary to properly perform an appropriate leakage evaluation for a specific building.
4.1.3 Preliminary Assessment—A preliminary assessment may indicate that water leakage problems are limited to a specific element or portion of a wall. The preliminary assessment may also indicate that the wall is not the source of a leak even though it is perceived as such by the building occupant. The presence of water might result from a roofing problem, a condensation problem, a plumbing problem, operable windows or doors left opened or unlatched or some other condition not directly related to water leakage through the building wall and is outside the scope of this guide. The evaluation of causes may likewise be limited in scope, and the procedures recommended herein abridged according to the professional judgement of the evaluator. A statement stipulating the limits of the investigation should be included in the report.
4.1.4 Expectations—Expectations about the overall effectiveness of an evaluatio...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes methods for determining and evaluating causes of water leakage of exterior walls. For this purpose, water penetration is considered leakage, and therefore problematic, if it exceeds the planned resistance or temporary retention and drainage capacity of the wall, is causing or is likely to cause premature deterioration of a building or its contents, or is adversely affecting the performance of other components. A wall is considered a system including its exterior and interior finishes, fenestration, structural components, and components for maintaining the building interior environment.
1.2 Investigative techniques discussed may be intrusive, disruptive, or destructive. It is the responsibility of the investigator to establish the limitations of use, to anticipate and advise of the destructive nature of some procedures, and to plan for patching and selective reconstruction as necessary.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3.1 Exception—Solely inch-pound units are stated in 10.3.1, 10.3.2.1, X1.5.3.7, X2.5.1.3, X3.4.3.3, X5.1.2.2, X5.5.5, X5.6.3, and X8.5.1.3.
1.4 This practice does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. Establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Awareness of safety and familiarity with safe procedures are particularly important for above-ground operations on the exterior of a building and destructive investigative procedures which typically are associated with the work described in this guide.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of Internat...
- Guide39 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Guide39 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This guide is intended to assist the construction team in evaluating the constructability, functionality, sequence of construction, interference, tolerances, component performance, and assembled system performance of the exterior wall systems.
4.2 This guide does not establish specific roles for the parties involved during construction or the contractual obligations of those parties. The role of each party within any specific project should be established and documented before the start of the project.
4.3 This guide is intended for use when specifying construction mockups that are either integrated mockups or off-structure mockups.
4.4 This guide is intended to aid the specifier in the development of a QA mockup program for assessing the performance of exterior walls. It is not intended to provide a comprehensive list of applicable test methods for QA testing available or applicable to a mockup program.
4.5 This guide does not address preconstruction laboratory testing of a wall system.
4.6 This guide is intended to address technical issues with the performance of the wall system and the interconnection of the various components and systems. A mockup may or may not be used as an aesthetic mockup; however, this guide is not intended to address aesthetic issues with the wall system.
4.7 This guide is not intended to provide guidance for construction observation services. However, the mockup may be useful to inform inspectors of the intended construction, sequence, materials, and interface conditions encountered on the project and serve as a standard of quality to which the remainder of construction can be compared.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides information to assist in the specification, design, and performance testing of field-constructed exterior wall assemblies (“mockups”) for construction projects. This includes testing procedures appropriate to evaluate the component and assembly performance for water penetration resistance, air leakage resistance, and other test methods that may be applied as part of the quality assurance (QA) program for the installed systems.
1.2 This guide is intended to be applied to exterior wall mockups that include components, systems, and assemblies including, but not limited to, curtain walls, windows, doors, masonry walls, precast concrete, cast-in-place concrete, exterior insulation and finish system (EIFS), roofing interfaces, stucco, wood siding, metal panels, sealants, appurtenances, penetrations, louvers, and combinations thereof. Such mockups are expected to include the intersection between wall systems.
1.3 This guide is not intended to provide a comprehensive list of potential testing that may be applicable to field-constructed mockups. Additional tests may be applicable to mockups for specific projects.
1.4 This guide is not intended to address all possible project delivery methods and as such the requirements listed herein must be evaluated by the specifier for appropriateness with the delivery method.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical...
- Guide11 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Durable adhesive bonds to aluminum alloys can be obtained reliably only through proper selection and careful control of the materials used and the steps in the bonding process. The preparation of the aluminum alloys to obtain clean, uniform surfaces with appropriate characteristics is a critical step. This practice describes how such surfaces can be obtained.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the preparation of clean uniform surfaces of aluminum alloys suitable for formation of durable adhesive bonds to nonmetallic honeycomb materials in the manufacture of sandwich panels for tactical shelters.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard where only SI units are given or where SI units are given first followed by inch-pound units; where inch-pound units are given first followed by SI units, the inch-pound units are to regarded as standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific warning statement, see 6.2.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard4 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard4 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.