ASTM A263-12(2019)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Stainless Chromium Steel-Clad Plate
Standard Specification for Stainless Chromium Steel-Clad Plate
ABSTRACT
This guide covers standard specification for a carbon steel plate or a low-alloy steel base to which is integrally and continuously bonded on one or both sides of a layer of stainless chromium steel. The steel shall be made by open-hearth, electric-furnace, or basic-oxygen process, or by secondary processes whereby steel made from these primary processes is remelted using, but not limited to electroslag remelting or vacuum-arc remelting processes. The steel plate may be heat-treated after the forming process. Tensile properties shall be determined by a tension test of the composite plate for clad plates that meet the specified values of tensile strength and yield strength. The composite plate shall conform to any desired combination of alloy-cladding metal and base metal. Tests for strength of the bond, when required, shall be performed and shall meet the specified values of shear and bond strengths. The test specimen shall undergo one or more tension tests, as required by the specifications for the base metal and, when specified, one shear test or three bond bend tests shall be made representing each plate as rolled. Product analysis may also be required for the cladding alloy on the finished product.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers plate of a carbon steel or low-alloy steel base to which is integrally and continuously bonded on one or both sides a layer of stainless chromium steel. The material is generally intended for pressure vessel use.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: A263 −12 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Specification for
Stainless Chromium Steel-Clad Plate
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A263; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope A578/A578M Specification for Straight-Beam Ultrasonic
2 Examination of Rolled Steel Plates for Special Applica-
1.1 This specification covers plate of a carbon steel or
tions
low-alloy steel base to which is integrally and continuously
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
bonded on one or both sides a layer of stainless chromium
cal Analysis of Steel Products
steel. The material is generally intended for pressure vessel
2.2 Other Standards:
use.
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. Terminology
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
and are not considered standard.
3.1.1 This material is considered as single-clad or double-
clad stainless chromium-steel plate, depending on whether one
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- or both sides are covered.
3.1.2 alloy cladding, n—the stainless chromium steel com-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- ponent of the composite plate.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.3 base metal (backing steel), n—component to which
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
the alloy cladding is applied, usually the greater percentage of
the composite plate.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.4 integrally and continuously bonded, n—a condition in
2.1 ASTM Standards:
whichthealloycladdingandbasemetalarebroughttogetherto
A6/A6M Specification for General Requirements for Rolled
form a metallurgical bond at essentially the entire interface of
Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Piling
the two metals by means other than those processes that do not
A20/A20M SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforSteel
produce a homogeneous composite plate.
Plates for Pressure Vessels
A240/A240M Specification for Chromium and Chromium- 4. Ordering Information
Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure
4.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
Vessels and for General Applications
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
specification. Such requirements may include, but are not
of Steel Products
limited to, the following:
A480/A480M Specification for General Requirements for
4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces).
Flat-Rolled Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate,
4.1.2 Cladding alloy specification (UNS or ASTM Specifi-
Sheet, and Strip
cation A240/A240M) and whether cladding is for corrosion
allowance only.
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel, 4.1.3 Base metal specification.
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.1.4 Bond integrity Class (1, 3, or 5; see Section 13).
A01.11 for Steel Plates for Boilers and Pressure Vessels.
4.1.5 Dimensions including the minimum or nominal thick-
Current edition approved March 1, 2019. Published April 2019. Originally
nesses of the cladding alloy and the backing steel, or of the
approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as A263 – 12. DOI:
10.1520/A0263-12R19.
total composite and if more or less restrictive thickness
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
tolerances apply.
cation SA-263 in Section II of that Code.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
the ASTM website. www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A263 − 12 (2019)
4.1.6 Product analysis, if required (see Section 10). Specify scribed in 6.2 and 6.3 and as agreed upon between the
whetherapplicabletothecladdingalloy,backingsteel,orboth. purchaser and the manufacturer.
4.1.7 Mechanical properties including shear test if required
6.2 Alloy Cladding Metal—The alloy-cladding metal speci-
(see Sections 7, 8, and 9).
fied shall conform to the requirements as to chemical compo-
4.1.8 Finish (see Section 12).
sition prescribed for the respective chromium steel in Specifi-
4.1.9 Restrictions, if required, on repair by welding (see
cation A240/A240M.
Section 14).
6.3 Base Metal—The base metal shall be carbon steel or
4.1.10 Additionstothespecificationorspecialrequirements
low-alloy steel conforming to the ASTM specifications for
such as any applicable construction code rules.
steels for pressure vessels or other as agreed by the purchaser
4.1.11 Notification when the cladding alloy is to be used for
and the manufacturer. The base metal shall conform to the
inclusion in the design strength calculations for an applicable
chemical requirements of the specification to which it is
construction code.
ordered.
NOTE 1—Construction codes may dictate certain fabrication require-
ments when the cladding is used in the design calculations that may be
7. Mechanical Properties
different than if the cladding is used for corrosion resistance only. This
may be particularly important when the alloy cladding involves the use of 7.1 Tensile Requirements:
welded components in the explosion bonded clad manufacturing process.
7.1.1 The tensile properties shall be determined by a tension
It is incumbent on the purchaser to make the clad manufacturer aware of
test of the composite plate for clad plates that meet all of the
any such restrictions or applications at time of order.
following conditions.
4.2 Inadditiontothebasicrequirementsofthisspecification
(1) The nominal composite gage is less than or equal to
and the backing steel specification, certain supplementary 1
1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm).
requirements are available when additional control, testing, or
(2) The specified minimum tensile strength of the base
examination is required to meet end use requirements. The
steel is less than or equal to 70 000 psi (485 MPa).
purchaser is referred to the listed supplementary requirements
(3) The specified minimum yield strength of the base steel
in this specification and to the detailed requirements in
is less than or equal to 40 000 psi (275 MPa).
Specification A20/A20M.
The tensile properties thus determined shall be not less than
the minimum and not more than 5000 psi (35 MPa) over the
4.3 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict
maximum prescribed in the specification for the base steel
with the requirements of SpecificationA20/A20M, the require-
used.All other tensile test requirements of the specification for
ments of this specification shall prevail.
the base steel shall be met.
7.1.2 The tensile properties shall be determined by a tension
5. Materials and Manufacture
test of the base steel only for clad plates that meet one of the
5.1 Process:
following conditions. The properties thus determined shall
5.1.1 The steel shall be made by the open-hearth, electric-
meet all of the tensile test requirements for the base steel.
furnace, or basic-oxygen processes, or by secondary processes
(1) The composite gage is greater than 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm).
whereby steel made from these primary processes is remelted
(2) The specified minimum tensile strength of the base
using, but not limited to electroslag remelting or vacuum-arc
steel is greater than 70 000 psi (485 MPa).
remelting processes.
(3) The specified minimum yield strength of the base steel
5.1.2 The alloy-cladding metal may be metallurgically
is greater than 40 000 psi (275 MPa).
bonded to the base metal by any method that will produce a
7.1.3 If the cladding is for corrosion allowance only, the
clad steel that will conform to the requirements of this
cladding need not be included in the tensile test. The tensile
specification.
properties thus determined shall meet the base steel require-
5.1.3 For explosively bonded products, the alloy cladding
ments.
metal may be comprised of two or more separate alloy plates
7.2 Tests for strength of the bond, when required, must be
or sheets completely welded together to form a single fabri-
specified by the purchaser and shall consist of one of the
cated component.
following.
5.2 Heat Treatment—Unless otherwise specified or agreed
7.2.1 Shear Strength—When required by the purchaser, the
upon between the purchaser and the manufacturer, all plates
minimum shear strength of the alloy cladding and base metals
shall be furnished in the normalized, tempered, normalized and
shall be 20 000 psi (140 MPa). The shear test, when specified,
tempered, or quenched and tempered condition as permitted by
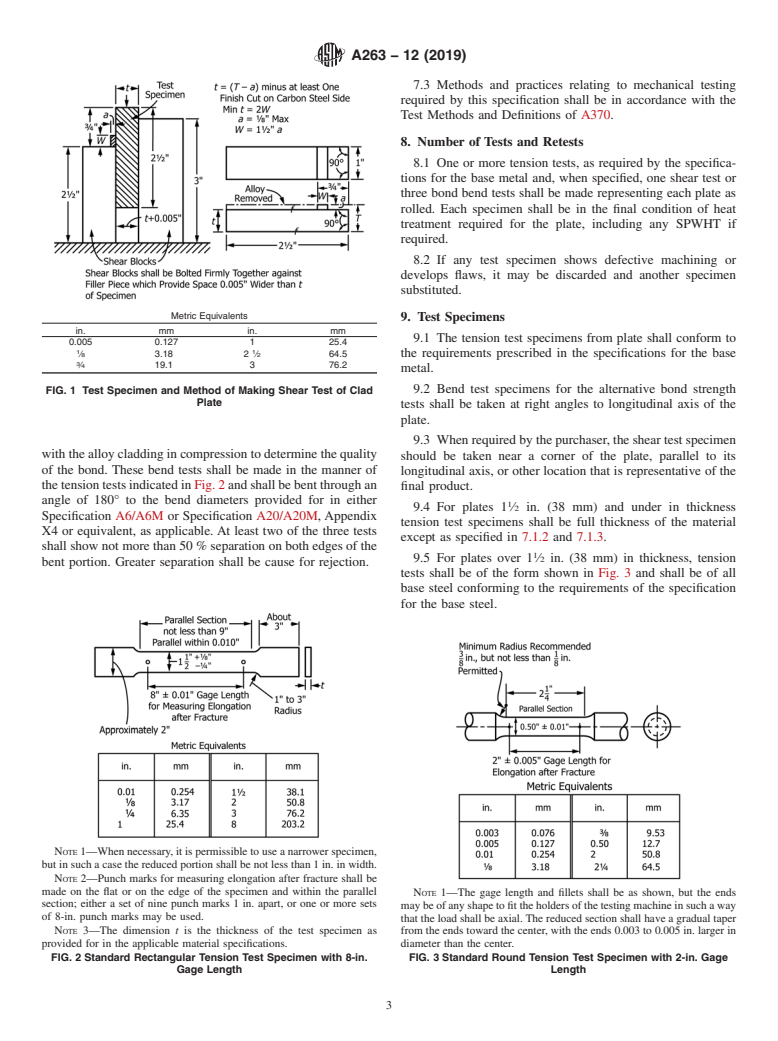
shall be made in the manner indicated in Fig. 1. The minimum
the backing steel specification. Stress relieving of the compos-
cladding thickness for shear testing shall be 0.075 in. (1.9 mm)
ite plate by heating subcritically is permitted, provided the
exclusive as ordered. Testing for shear strength for clad plates
temperature is 75°F (40°C) or more below the minimum
with minimum cladding thickness of 0.075 in. (1.9 mm) or less
tempering temperature (when tempered).
shall be permitted upon agreement between the purchaser and
the manufacturer.
6. Chemical Composition
7.2.2 Bond Strength—As an alternative to the shear strength
6.1 The composite plate shall conform to any desired test provided in 7.2.1, or when agreed upon by the purchaser
combination of alloy-cladding metal and base metal as de- and the manufacturer, or both, three bend tests shall be made
A263 − 12 (2019)
7.3 Methods and practices relating to mechanical testing
required by this specification shall be in accordance with the
Test Methods and Definitions of A370.
8. Number of Tests and Retests
8.1 One or more tension tests, as required by the specifica-
tions for the base metal and, when specified, one shear test or
three bond bend tests shall be made representing each plate as
rolled. Each specimen shall be in the final condition of heat
treatment required for the plate, including any SPWHT if
required.
8.2 If any test specimen shows defective machining or
develops flaws, it may be discarded and another specimen
substituted.
Metric Equivalents
9. Test Specimens
in. mm in. mm
9.1 The tension test specimens from plate shall conform to
0.005 0.127 1 25.4
1 1
⁄8 3.18 2 ⁄2 64.5 the requirements prescribed in the specifications for the base
⁄4 19.1 3 76.2
metal.
FIG. 1 Test Specimen and Method of Making Shear Test of Clad 9.2 Bend test specimens for the alternative bond strength
Plate
tests shall be taken at right angles to longitudinal axis of the
plate.
9.3 When required by the purchaser, the shear test specimen
withthealloycladdingincompressiontodeterminethequality
should be taken near a corner of the plate, parallel to its
of the bond. These bend tests shall be made in the manner of
longitudinal axis, or other location that is representative of the
thetensiontestsindicatedinFig.2andshallbebentthroughan
final product.
angle of 180° to the bend diameters provided for in either
9.4 For plates 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) and under in thickness
Specification A6/A6M or Specification A20/A20M, Appendix
tension test specimens shall be full thickness of the material
X4 or equivalent, as applicable. At least two of the three tests
except as specified in 7.1.2 and 7.1.3.
shall show not more than 50 % separation on both edges of the
9.5 For plates over 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) in thickness, tension
bent portion. Greater separation shall be cause for rejection.
tests shall be of the form shown in Fig. 3 and shall be of all
base steel conforming to the requirements of the specification
for the base steel.
NOTE 1—When necessary, it is permissible to use a narrower specimen,
but in such a case the reduced portion shall be not less than 1 in. in width.
NOTE 2—Punch marks for measuring elongation after fracture shall be
made on the flat or on the edge of the specimen and within the parallel
NOTE 1—The gage length and fillets shall be as shown, but the ends
section; either a set of nine punch marks 1 in. apart, or one or more sets
maybeofanyshapetofittheholdersofthetestingmachineinsuchaway
of 8-in. punch marks may be used.
that the load shall be axial. The reduced section shall have a gradual taper
NOTE 3—The dimension t is the thickness of the test specimen as from the ends toward the center, with the ends 0.003 to 0.005 in. larger in
provided for in the applicable material specifications. diameter than the center.
FIG. 2 Standard Rectangular Tension Test Specimen with 8-in. FIG. 3 Standard Round Tension Test Specimen with 2-in. Gage
Gage Length Length
A263 − 12 (2019)
9.6 The bend test specimen used for bond strength determi- backing steel or total composite, and 0.03 in. (0.8 mm) under
1 3
nation shall be 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) wide by not more than ⁄4 in. for the alloy cladding.
(19 mm) in thickness and shall be machined to the form and
11.4 Permissible variations for excess thickness of the total
dimensions shown in Fig. 2, or may be machined with both
composite shall be the greater of 0.125 in. (3 mm) or 10 % of
edges parallel. In reducing the thickness of the specimen, both
the total composite thickness ordered and may occur in either
the alloy cladding and the base steel shall be machined so as to
backing steel, cladding, or both, provided the minimum for
maintain the same ratio of clad metal to base steel as is
each is met.
maintained in the plate, except that the thickness of the clad
11.5 More restrictive or less restrictive permissible varia-
metal need not be reduced below ⁄8 in. (3.1 mm). The sides of
tions may be agreed upon by the purchaser and the manufac-
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.