ASTM B951-10
(Practice)Standard Practice for Codification of Unalloyed Magnesium and Magnesium-Alloys, Cast and Wrought
Standard Practice for Codification of Unalloyed Magnesium and Magnesium-Alloys, Cast and Wrought
ABSTRACT
This practice provides a system for the codification of unalloyed magnesium and magnesium alloys in the cast and wrought forms. Code designations shall be based on their chemical composition limits. For alloys, designations shall consist of not more than two letters representing the alloying elements specified in the greatest amount, followed by the respective percentages and a serial letter. The letters that represent the alloying elements are: A for aluminum; C for copper; E for rare earths; J for strontium; K for zirconium; L for lithium; M for manganese; Q for silver; S for silicon; T for tin; V for gadolinium; W for yttrium; and Z for zinc. For unalloyed metals, designations shall consist of the specified minimum purity, followed by a serial letter. For both cases, the full name of the base metal precedes the designation, but is omitted for brevity when the base metal being referred to is obvious.
SCOPE
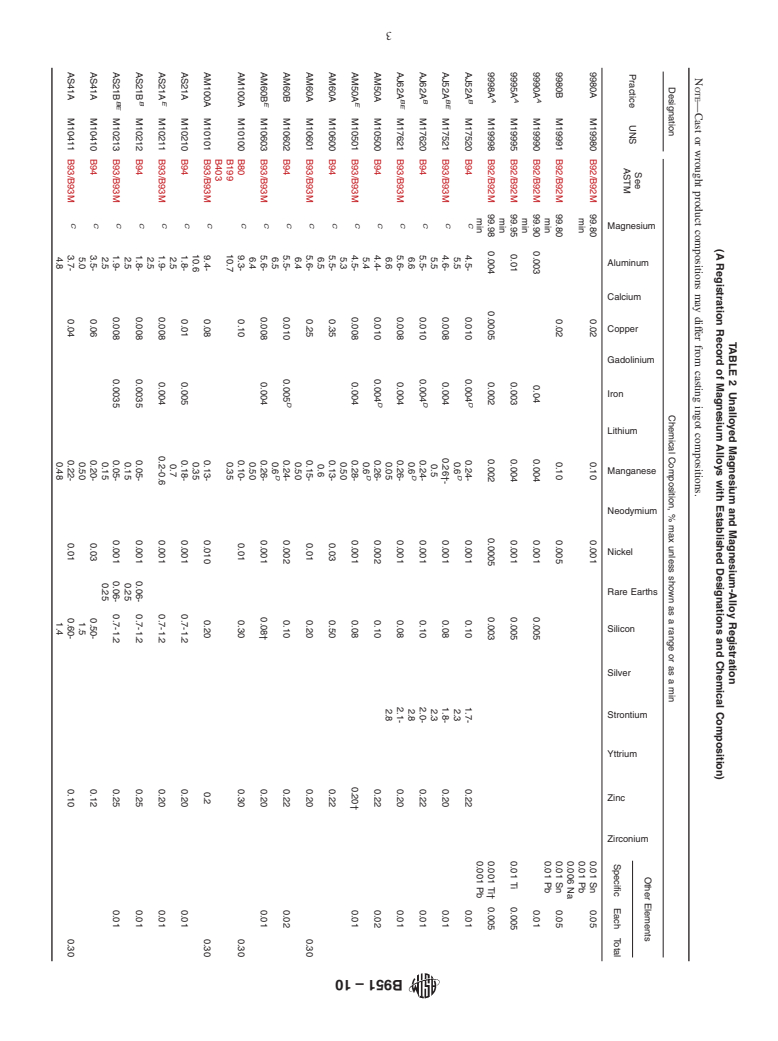
1.1 This practice provides a system for designating unalloyed magnesium and magnesium-alloys that have been used commercially since 1952, and thus is intended to be the registration source for unalloyed magnesium and magnesium-alloys. A record of designations along with the established compositions is given in Table 2.
1.2 The equivalent Unified Numbering System (UNS) alloy designations shown in the appendixes are in accordance with Practice E527.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B951 – 10
Standard Practice for
Codification of Unalloyed Magnesium and Magnesium-
1
Alloys, Cast and Wrought
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B951; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
Note—Table 2 and section 4.2 were corrected editorially and the year date changed on Jan. 29, 2010.
1. Scope* B199 Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Permanent Mold
Castings
1.1 This practice provides a system for designating unal-
B403 Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Investment Cast-
loyed magnesium and magnesium-alloys that have been used
ings
commercially since 1952, and thus is intended to be the
B843 Specification for Magnesium Alloy Anodes for Ca-
registration source for unalloyed magnesium and magnesium-
thodic Protection
alloys. A record of designations along with the established
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
compositions is given in Table 2.
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1.2 The equivalent Unified Numbering System (UNS) alloy
designations shown in the appendixes are in accordance with
3. Basis of Codification
Practice E527.
3.1 The designations for alloys and unalloyed metals are
2. Referenced Documents based on their chemical composition limits.
2.1 The following documents form a part of this practice to
NOTE 1—For unalloyed magnesium, magnesium-alloys, cast and
the extent referenced herein:
wrought, standard limits for alloying elements and impurities are ex-
2
pressed to the following places:
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B80 Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Sand Castings Less than 0.0001 % (used only for magnesium alloys) 0.0000X
0.0001 to 0.001 % 0.000X
B90/B90M Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Sheet and
0.001 to 0.01 % 0.00X
Plate
0.01 to 0.10 %
Unalloyed aluminum made by a refining process 0.0XX
B91 Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Forgings
Alloys and unalloyed aluminum or magnesium 0.0X
B92/B92M Specification for Unalloyed Magnesium Ingot
not made by a refining process
and Stick For Remelting
0.10 through 0.55 % 0.XX
Over 0.55 % 0.X,X.X,XX.X
B93/B93M Specification for Magnesium Alloys in Ingot
Form for Sand Castings, Permanent Mold Castings, and
3.2 Designations shall be assigned, revised, and cancelled
Die Castings
by Subcommittee B07.04 of ASTM Committee B07 on Light
B94 Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Die Castings
Metals and Alloys on written requests to its chairman. Com-
B107/B107M Specification for Magnesium-Alloy Extruded
plete chemical composition limits shall be submitted with
Bars, Rods, Profiles, Tubes, and Wire
request for assignment or revision of designations. Arbitrary
assignments by other subcommittees or committees will not be
recognized.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B07 on Light
Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B07.04 on 4. Alloys
Magnesium Alloy Cast and Wrought Products.
4.1 Designationforalloysshallconsistofnotmorethantwo
Current edition approved Jan. 29, 2010. Published March 2010. Originally
letters representing the alloying elements (Note 2) specified in
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as B951 – 09. DOI:
10.1520/B0951-10.
the greatest amount, arranged in order of decreasing percent-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
ages, or in alphabetical order if of equal percentages, followed
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
by the respective percentages rounded off to whole numbers
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. and a serial letter (Note 3). The full name of the base metal
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B951 – 10
precedes the designation, but it is omitted for brevity when the 4.3 In rounding percentages, the nearest whole number shall
base metal being referred to is obvious. be used. If two choices are possible as when the decimal is
followed by a 5 only, or a 5 followed only by zeros, the nearest
NOTE 2—For codification, an alloying element is defined as an element
even whole number shall be used.
(other than the base metal) having a minimum content greater than zero
4.4 When a range is specified for the alloying element, the
either directly specified or computed in accordance with the percentages
specified. rounded mean shall be used in the designation.
NOTE 3—The serial letter is arbitrarily assigned i
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.