ASTM D6973-14(2019)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristics of petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical industrial or mobile hydraulic applications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume high-pressure vane pump test procedure for indicating the wear characteristics of petroleum hydraulic fluids. See Annex A1 for recommended testing conditions for water-based synthetic fluids.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: D6973 − 14 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic
Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6973; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
ε NOTE—Editorial updates made throughout in September 2022.
1. Scope ISO 4406 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Fluids—Method for
Coding the Level of Contamination by Solids Particles
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume high-
ISO 7745 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Fire-Resistant (FR)
pressure vane pump test procedure for indicating the wear
Fluids—Guidelines for Use
characteristicsofpetroleumhydraulicfluids.SeeAnnexA1for
ISO 11171 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Calibration of Auto-
recommended testing conditions for water-based synthetic
matic Particle Counters for Liquids
fluids.
ISO 11500 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Determination of Par-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
ticulate Contamination by Automatic Counting Using the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
Light Extinction Principle
only.
2.3 Other Documents:
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4
SAE 100R13–20 Hydraulic Hose Specification
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ANSI/(NFPA) T2.13.1 R3-1998 Recommended Practice—
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Hydraulic Fluid Power—Use of Fire-Resistant Fluids in
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- 5
Industrial Systems
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3. Terminology
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.1 flushing, v—the process of cleaning the test system
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
before testing to prevent cross-contamination.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Summary of Test Method
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 Hydraulic fluid in the amount of 190 L 6 4 L(50 gal 6
2.1 ASTM Standards: 1 gal) is circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 50 h
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
at a pump speed of 2400 r⁄min 6 20 r/min and a pump outlet
Determine the Precision of a Test Method pressure of 20.7 MPa 6 0.2 MPa (3000 psig 6 20 psig). Fluid
2.2 ISO Standards: temperatureatthepumpinletis95 °C 63 °C(203 °F 65 °F).
ISO 4021 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Particulate Contamina- An ISO Grade 32 or 10W viscosity is required.
tionAnalysis—Extraction of Fluid Samples from Lines of
4.2 The mass of the cam ring and all ten vanes should be
an Operating System
individuallydeterminedbeforeandafterthetest.Themassloss
ofthecamringshouldbereportedwiththecombinedmassloss
of all ten vanes. The intra-vanes (inserts) are not part of the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
required mass loss measurements and should be separately
Subcommittee D02.N0 on Hydraulic Fluids.
measured if desired. Other reported values are fluid cleanliness
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. Originally
before and after the test, initial flow rate, and final flow rate.
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D6973 – 14. DOI:
10.1520/D6973-14R19E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr.,Warrendale,
the ASTM website. PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
3 5
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
D6973 − 14 (2019)
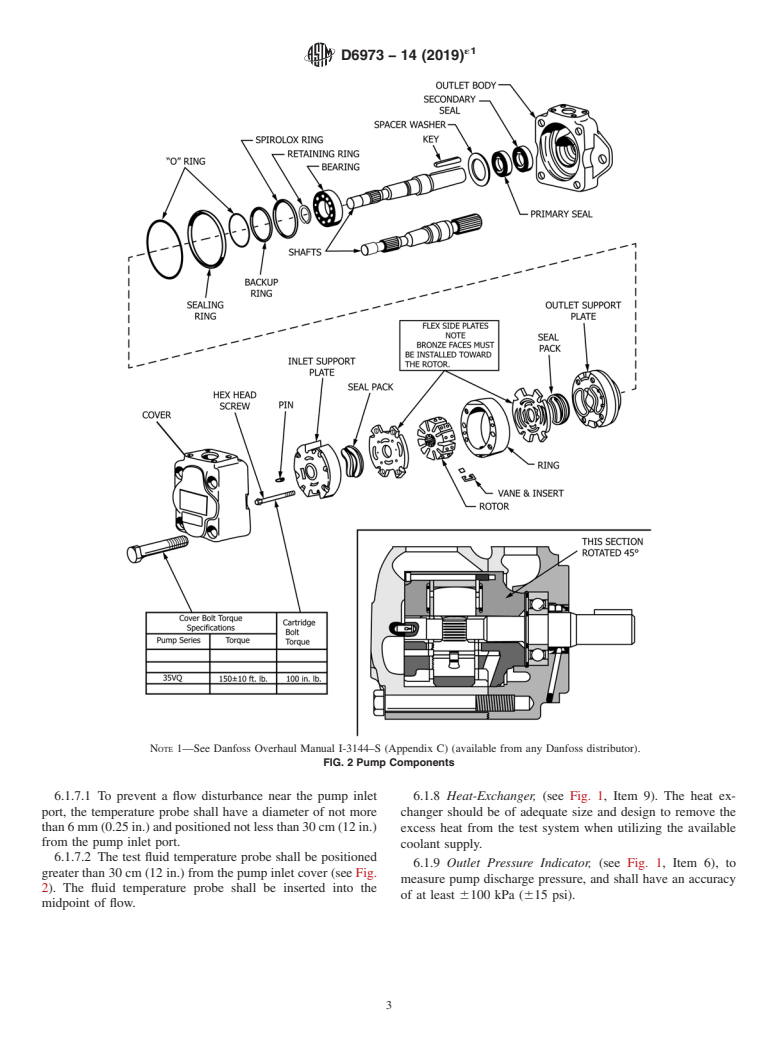
Description of Components:
1 Reservoir, 190 L (50 gal) of oil; elevated above pump centerline to provide gravity feed
2 Temperature gage or thermocouple
3 Inlet pressure gage
4 Pump: 35VQ25A-11*20 (Cartridge kit P/N 4998040–002)
5 Electric motor, 93 kW (125 hp)
6 Outlet pressure gage
7 Pressure relief valve
8 Filter
9 Cooler
10 Flowmeter
NOTE 1—See Danfoss Overhaul Manual I-3144–S (Appendix B) (available from any Danfoss distributor).
FIG. 1 System Schematic
4.3 Prior to installing the hydraulic test fluid into the rig, a 6.1.3.1 There are to be no modifications to the pump
stand flush is required to remove any contaminants. A mini- housing.
mum quantity of 190 L 6 4 L (50 gal 6 1 gal) of fluid (see 6.1.4 Reservoir, equipped with a baffle and lid, all of
Note 1) made of the same chemical formulation as the test stainless steel construction.
fluid,isrequiredforthestandflush.Thereforethetotalquantity 6.1.4.1 Additional fluid ports may be added to the reservoir
of oil required for the test is 380 L (100 gal). as required by the user to assist in measuring fluid level,
reservoir temperature, and so forth.
5. Significance and Use
6.1.4.2 If the reservoir is positioned so that the contents
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear character- cannotbevisuallycheckedforairentrainmentbyremovingthe
lid, a fluid-sight glass viewing port may be located in the side
istics of petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant
of the reservoir.
volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead
to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical industrial or 6.1.5 Pump Outlet Pressure Control Valve, with either
manual or remote control (see Fig. 1, Item 7).
mobile hydraulic applications.
6.1.6 Temperature-control Device, suitable for controlling
6. Apparatus
coolant flow to the heat exchanger to maintain test fluid at the
specified temperature (see Fig. 1, Item 9).
6.1 The basic system consists of the following (see Fig. 1):
6.1.7 Temperature Indicator, (see Fig. 1, Item 2) shall have
6.1.1 Electric Motor, or other suitable drive, capable of a
a minimum accuracy of 61 °C and shall have an appropriate
rotational speed of 2400 r/min with 93 kW (125 hp) as
sensor to monitor pump inlet temperature.
suggested minimum power requirement (see Fig. 1, Item 5).
6.1.2 Test Stand Base, with appropriate, rigid mounting for
the motor, pump, reservoir, and other components. 7
The individual cartridge parts can be purchased separately, if desired. The
6,7
Danfoss part numbers for these items are cartridge screws: P/N 410609, alignment
6.1.3 Rotary Intra-Vane Pump,replaceablecartridgetype,
pins:P/N418108,inletsupportplate:P/N430806,outletsupportplate:P/N412003,
Vickers 35VQ25A-11*20 (Cartridge Kit P/N 4998040-002)
flexsideplatekit:P/N923953,sealpack:P/N433766,rotor:P/N262154,camring:
3 3
rated at 81 cm /rev (4.98 in. /rev) flow at 1200 r/min. A
P/N 4999594-001, vane kit (includes ten intra-vanes and ten vanes): 922700.
protective shield around the pump is recommended.
Available from any Danfoss distributor.
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
is Danfoss, 14615 Lone Oak Rd., Eden Prairie, MN 55344, http://
www.danfoss.com. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this
information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive
6 1
The replaceable cartridge consists of the inlet support plate, outlet support careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which
plate, flex side plates, seal pack, rotor, cam ring, intra-vane, and vanes. you may attend.
´1
D6973 − 14 (2019)
NOTE 1—See Danfoss Overhaul Manual I-3144–S (Appendix C) (available from any Danfoss distributor).
FIG. 2 Pump Components
6.1.7.1 To prevent a flow disturbance near the pump inlet 6.1.8 Heat-Exchanger, (see Fig. 1, Item 9). The heat ex-
port, the temperature probe shall have a diameter of not more changer should be of adequate size and design to remove the
than6mm(0.25in.)andpositionednotlessthan30cm(12in.)
excess heat from the test system when utilizing the available
from the pump inlet port.
coolant supply.
6.1.7.2 The test fluid temperature probe shall be positioned
6.1.9 Outlet Pressure Indicator, (see Fig. 1, Item 6), to
greater than 30 cm (12 in.) from the pump inlet cover (see Fig.
measure pump discharge pressure, and shall have an accuracy
2). The fluid temperature probe shall be inserted into the
of at least 6100 kPa (615 psi).
midpoint of flow.
´1
D6973 − 14 (2019)
6.1.10 Inlet Pressure Indicator, (see Fig. 1, Item 3), to 6.2.8 Thehighpressuredischargeline(fromthepumptothe
measure pump inlet pressure, and shall have an accuracy of at pressure control valve) shall have a minimum inside diameter
least 67 kPa (61 psi). of 31.75 mm (1 ⁄4 in.) with a maximum allowable working
pressure rating greater than 20.7 MPa (3000 psi). A seamless
6.1.11 FilterUnit,(seeFig.1,Item8),tolimitsystemdebris
steel pipe with a 60 mm outside diameter and 11.1 mm wall
from causing wear to the test pump. The filter performance
thickness (2 in. double extra strong pipe–XXS) or equivalent
should be β ≥ 100.
high-pressure hose (SAE 100R13–20) are recommended for
6.1.11.1 The filter housing shall be installed with dual
the discharge line.
pressure gages (see Fig. 1, Item 13) or a differential pressure
6.2.9 The fluid return line and fittings (from the pressure
transducer to monitor pressure across the filter to warn of
control valve to the filter, flowmeter, heat exchanger, and
impending collapse of the element.
reservoir) should have a minimum inside diameter of 2.54 cm
6.1.11.2 If dual pressure gages are used to monitor filter
(1 in.).Aseamless steel pipe with 33 mm outside diameter and
pressure,theratedcollapsepressureofthefilterelementshould
3.4 mm wall thickness (1 in. Schedule 40) is recommended for
be known.
the fluid return line.
6.1.12 Flow-Measuring Device, (see Fig. 1, Item 12), with
6.2.10 A shut-off valve may be located in the plumbing
an accuracy of at least 61 L/min (60.25 gpm).
between the reservoir and the inlet to the pump. The full flow
6.1.12.1 It is suggested that the test circuit be equipped with
valve shall have a minimum orifice diameter of 5.08 cm (2 in.)
some automated shutdown capabilities for safety reasons.
and shall be positioned no closer than 30 cm (12 in.) from the
Safety relays could be any of the following: low-level, high
pump inlet port.
pressure, high temperature, and low flow safety switches
NOTE 3—Some users find the addition of a shut-off valve on the return
incorporated into the system.
line to be a useful addition to the piping since it allows filter changes and
6.1.12.2 Acheckshouldbemadetoensurethattheflushand
other system maintenance to be performed without draining the reservoir.
testfluidarecompatiblewithsealsoranyothermaterialsinthe
(Warning—If a shut-off valve is installed in the fluid return line, the user
system.
shalltakeproceduralstepstoensurethatthisvalvehasbeenopenedbefore
the pump is started. If the valve is not opened, low pressure system
6.1.13 Flexible Motor Coupling, to connect the motor drive
components may rupture.)
and the pump.
6.1.14 Fluid Sampling Port, in accordance with ISO 4021.
7. Reagents and Materials
6.2 The various components of the test system shall be
7.1 (Warning—Use adequate safety provisions with all
placed in the system as indicated in Fig. 1.
solvents.)
6.2.1 The test system shall be arranged and provided with
7.2 Aliphatic Naphtha, Stoddard solvent or equivalent is
necessary drain valves so that complete draining is possible
satisfactory. (Warning—Combustible. Vapor harmful.)
with no fluid trap areas.
7.3 Precipitation Naphtha. (Warning—Extremely flam-
6.2.2 Goodhydraulicspipingpracticesshouldbeusedwhen
mable. Harmful if inhaled. Vapors can cause flash fire.)
constructingthetestsystemtoavoidairentrainmentpointsand
7.4 Isopropanol. (Warning—Flammable, vapor harmful in
flow restrictions.
large amounts, eye irritant, extremely combustible when hot.)
6.2.3 The pump should be mounted so that its internal
(Warning—In instances when the solvents listed in Section 7
surfaces can easily be inspected and cleaned, alignment can be
are not effective, alternative solvents may be used. It is the
checked, and the operator has comfortable access when torqu-
responsibility of the user to determine the suitability of
ing the head.
alternative solvents and any hazards associated with their use.)
6.2.4 Apressure transducer, to measure inlet pressure, shall
be placed within 30.5 cm (12 in.) of the opening of the pump
8. Test Stand Maintenance
cover.
8.1 Temperature, pressure, flow sensors and shut-off
6.2.5 The inlet pressure of the pump shall be 13.8 kPa 6
switches shall be checked periodically for proper calibration
7 kPa (2 psig 6 1 psig) once the break-in procedure is
and operation in accordance with good engineering practice, as
complete and test conditions have been met (see 12.2).
determined by the user.
NOTE 1—See Annex A1 for recommended testing conditions for
NOTE 4—If an axial turbine flowmeter is used, calibrate with 0.876
water-based synthetic fluids.
specific gravity, ISO Grade 32 hydraulic oil. Perform a 10-point calibra-
6.2.6 The reservoir should be mounted so that it can be
tion over a ranges of 0 L⁄min to 227 L⁄min (0 gpm to 50 gpm). This
calibration shall be performed by the flowmeter manufacturer or other
cleaned and filled with ease and the contents may be readily
qualified personnel.
inspected by removal of the reservoir lid or inspection cover.
8.2 It is recommended that the pump shaft (P\N 242287),
6.2.7 The inlet line (from the reservoir to the pump intake)
shaft seal (P\N 394973), and shaft bearings (P\N 38441 or
shall have an internal diameter of at least 5.08 cm (2 in.) and
equivalent) (seeFig.2)bereplacedaftereverytentestruns(or
shall have a straight run of at least 61 cm (24 in.) to the pump
sooner if high mass loss, vibration, cavitation, or visual
inlet port.
deterioration is encountered).
NOT
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.