ASTM D2765-95
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Determination of Gel Content and Swell Ratio of Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
Standard Test Methods for Determination of Gel Content and Swell Ratio of Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
SCOPE
1.1 The gel content (insoluble fraction) produced in ethylene plastics by crosslinking can be determined by extracting with solvents such as decahydronaphthalene or xylene. Such extraction test methods are described herein. They are applicable to crosslinked ethylene plastics of all densities, including those containing fillers, and all provide corrections for the inert fillers present in some of those compounds.
1.2 Test Method A, which permits most complete extraction in least time, is to be used for referee tests, but two alternative nonreferee Test Methods B and C are also described. The first of these differs from the referee test method only in sample preparation; that is, it requires use of shavings taken at selected points in cable insulation, for example, rather than the ground sample required by the referee test method. Because the shaved particles are larger, less total surface per sample is exposed to the extractant, so this test method ordinarily yields extraction values about 1 to 2% lower than the referee method. The second of the alternative test methods requires that a specimen in one piece be extracted in xylene at a constant temperature of 110°C. At this temperature and with a one-piece specimen, even less extraction occurs (from 3 to 9% less than the referee test method) but swell ratio (a measure of the degree of crosslinking in the gel phase) can be determined.
1.3 Extraction tests can be made on articles of any shape. They have been particularly useful for electrical insulations since specimens may be selected from those portions of the insulation most susceptible to insufficient crosslinking.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only. Note 1-ISO 10147 is similar to this test, but is not equivalent.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Sections 6, 10, and 25.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D2765–95
Standard Test Methods for
Determination of Gel Content and Swell Ratio of
Crosslinked Ethylene Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2765; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
1.1 The gel content (insoluble fraction) produced in ethyl-
tionary statements are given in Sections 6, 10, and 25.
ene plastics by crosslinking can be determined by extracting
with solvents such as decahydronaphthalene or xylene. Such
2. Referenced Documents
extraction test methods are described herein. They are appli-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cabletocrosslinkedethyleneplasticsofalldensities,including
D 297 Test Methods for Rubber Products—Chemical
thosecontainingfillers,andallprovidecorrectionsfortheinert
Analysis
fillers present in some of those compounds.
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
1.2 TestMethodA,whichpermitsmostcompleteextraction
Insulating Materials for Testing
in least time, is to be used for referee tests, but two alternative
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
nonreferee Test Methods B and C are also described. The first
D1603 Test Method for Carbon Black in Olefin Plastics
of these differs from the referee test method only in sample
D 1998 Specification for Polyethylene Upright Storage
preparation;thatis,itrequiresuseofshavingstakenatselected
Tank
points in cable insulation, for example, rather than the ground
D3351 Test Method for Gel Count of Plastic Film
samplerequiredbytherefereetestmethod.Becausetheshaved
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
particles are larger, less total surface per sample is exposed to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
the extractant, so this test method ordinarily yields extraction
values about 1 to 2% lower than the referee method. The
3. Terminology
second of the alternative test methods requires that a specimen
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
inonepiecebeextractedinxyleneataconstanttemperatureof
3.1.1 gel content—the percentage by mass of polymer
110°C. At this temperature and with a one-piece specimen,
insoluble in a specified solvent after extraction under the
even less extraction occurs (from 3 to 9% less than the referee
specified conditions.
test method) but swell ratio (a measure of the degree of
3.1.2 soluble—capable of being loosened or dissolved, sus-
crosslinking in the gel phase) can be determined.
ceptible of being dissolved in or as if in a fluid. (SeeWebster’s
1.3 Extraction tests can be made on articles of any shape.
Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary, 1988.)
They have been particularly useful for electrical insulations
3.1.3 swell ratio—the ratio of the gel volume in the swollen
since specimens may be selected from those portions of the
state to its volume in the unswollen state.
insulation most susceptible to insufficient crosslinking.
3.2 Terms as shown inTerminology D883 are applicable to
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
this test method.
standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for informa-
tion only.
4. Summary of Test Methods
NOTE 1—There is no equivalent ISO Method.
4.1 Specimens of the crosslinked ethylene plastic are
weighed and then immersed in the extracting solvent at the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
temperature specified by the procedure selected and for the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
time designated by that procedure. After extraction, the speci-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
mens are removed, dried, and reweighed as directed. The
1 2
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01.
PlasticsandarethedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD20.12onOlefinPlastics. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1995. Published January 1996. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
published as D2765–68. Last previous edition D2765–90. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D2765–95
amountofmaterialextractediscalculatedand,ifdesired,swell 8.1.1 Round-Bottom Flask, with large-mouth ground-glass
ratio also may be determined by the means described in or cork joint. For one or two determinations at one time, a
alternative Test Method C. 500-mLflask is appropriate. For several determinations at one
time, but not exceeding six, a 2000-mL flask is suitable.
5. Significance and Use
8.1.2 Heating Mantle to fit the flask and with sufficient
5.1 Many important properties of crosslinked ethylene plas-
heating capacity to boil decahydronaphthalene (boiling point
tics vary with the gel content. Hence, determination of the gel
190 to 193°C) or xylene (boiling point 138 to 141°C).
content provides a means of both controlling the process and
8.1.3 Reflux Condenser with ground-glass or cork joint to
rating the quality of finished products.
fit into flask.
5.2 Extraction tests permit verification of the proper gel
8.1.4 Ring Stand and Appropriate Clamps.
content of any given crosslinked ethylene plastic and they also
8.1.5 Grinding Equipment, suitable for reducing the sample
permit comparison between different crosslinked ethylene
to a fineness between 30 and 60 mesh.Abench-top laboratory
plastics, including those containing fillers, provided that, for
mill is satisfactory, although any procedure which will pro-
the latter, the following conditions are met:
duce a sample of the required fineness without generating
5.2.1 The filler is not soluble in either decahydronaphtha-
excessive heat may be used.
lene or xylene at the extraction temperature.
8.1.6 U.S. No. 30 and U.S. No. 60 Sieves.
5.2.2 The amount of filler present in the compound either is
8.1.7 U.S. No. 120 Stainless Steel Wire Cloth.
known or can be determined.
8.1.8 VacuumOven,withvacuumsourcecapableofcreating
5.2.3 Sufficient crosslinking has been achieved to prevent
a vacuum of at least 710 mm (28 in.) Hg and equipped with a
migration of filler during the extraction. Usually it has been
thermometer capable of measuring 150°C.
found that, at extraction levels up to 50%, the extractant
NOTE 2—If a slightly higher degree of accuracy is desired (about 1 to
remains clear and free of filler.
2%) a modified Soxhlet Extractor; Kontes Catalog No. 58610, Size C,
5.3 Since some oxidative degradation of the material can
Kontes Glass Co., Vineland, NJ or equivalent may be employed wherein
occur at the reflux temperature of the extractants, a suitable
thespecimenisheldinanextractionthimble.Theextractionthimble,with
antioxidant is added to the extractant to inhibit such degrada-
extra-coarsefrittedglassdisksealedin;CorningGlassCatalogNo.33950,
tion. 45-mm body diameter, 130-mm height or equivalent (height must subse-
quentlybecutto75mm).Thefritteddiskisextra-coarsewithfusededge;
5.4 Before proceeding with this test method, reference
Corning Glass Catalog No. 31000, 40-mm diameter or equivalent. Glass
shouldbemadetothespecificationofthematerialbeingtested.
1 3
wool 13 to 19 mm thick ( ⁄2 to ⁄4 in.) placed on the bottom of the
Any test specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions, or
extraction thimble to support one gram 30–60 mesh ground sample which
testing parameters, or a combination thereof, covered in the
is covered with 13 to 19 mm thick layer of glass wool, a fritted glass disk
materials specification shall take precedence over those men-
and a small glass weight. The extraction thimble assembly rests upon the
tioned in this test method. If there are no material specifica-
55-mmportionofthethimblepreviouslycutoff,thelatterinsertedintothe
modified Soxhlet.
tions, then the default conditions apply.
9. Reagents
6. Precautions
6.1 This test method measures a much larger threedimen- 9.1 Decahydronaphthalene, practical, boiling point 190 to
sional polymer network than that measured by Test Method 193°C.
D3351 and should not be confused with it. 9.2 Xylene,ACS reagent grade, boiling point 138 to 141°C.
6.2 It has been reported that crosslinked ultra-high molecu- 9.3 2,28-methylene-bis (4-methyl-6-tertiary butyl phenol).
lar weight polyethylene fails to completely dissolve in this
10. Safety Precautions
procedure at times.
10.1 Xylene and decahydronaphthalene are toxic and flam-
7. Conditioning
mable solvents and as such should be handled carefully. Use
7.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 23 6
only in a ventilated hood. Check the effectiveness of the hood
2°C(73.4 63.6°F)and50 65%relativehumidityfornotless
before starting the tests. Do not inhale the vapors. Excessive
than 40 h prior to test in accordance with Procedure A of
inhalation of the vapors may cause dizziness or headache, or
Practice D618, for those tests where conditioning is required.
both. In the event of excessive inhalation, seek fresh clean air.
In cases of disagreement, the tolerances shall be6 1°C
(61.8°F) and 62% relative humidity.
11. Test Specimens
7.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the standard labora-
11.1 At least two specimens each containing 0.300 6 0.015
tory atmosphere of 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 65%
g of ground polymer weighed to the nearest 0.001 g shall be
relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test meth-
tested.
ods. In cases of disagreement, the tolerances shall be 61°C
(61.8°F) and 62% relative humidity.
A Wiley Cutting Mill, Intermediate Model, or equivalent, Catalog No. 8-338,
TEST METHOD A (REFEREE TEST METHOD)
available from Fisher Scientific Co., 711 Forbes Ave., Pittsburgh, PA 15219, has
been found satisfactory for this purpose.
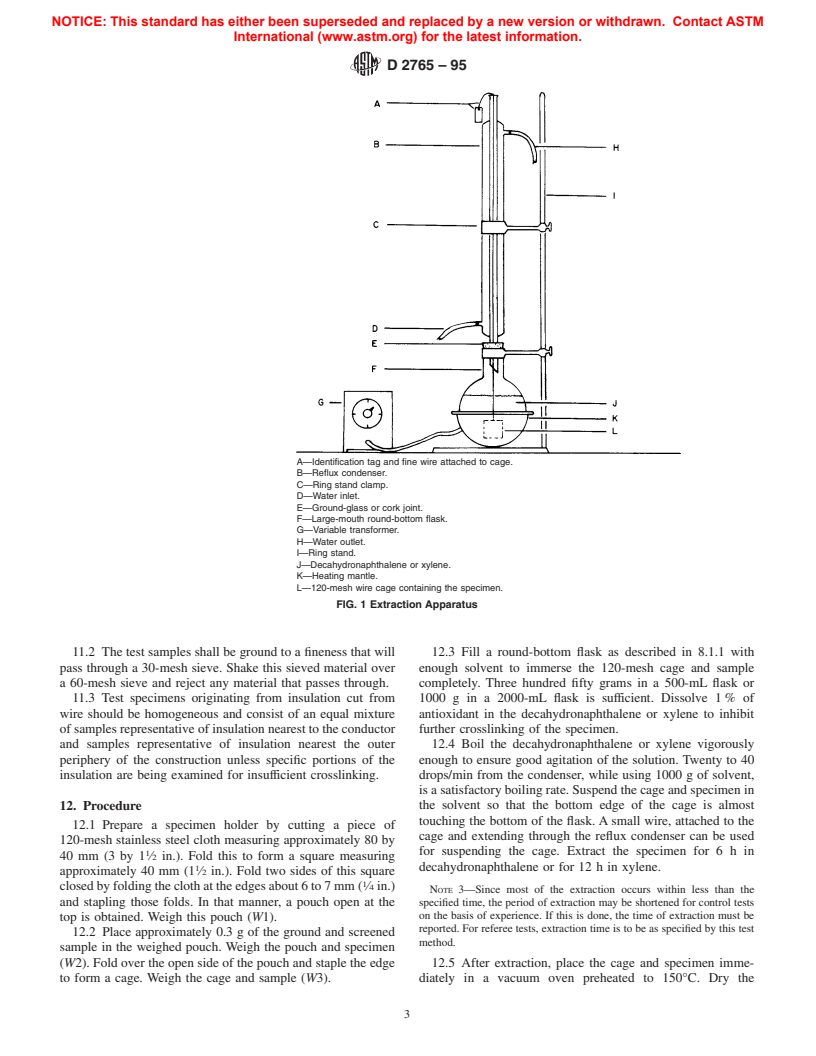
8. Apparatus
Antioxidant,availablefromCytecunderthetradenameCyanox2246,hasbeen
8.1 The extraction apparatus shall be of the following
found satisfactory for this purpose. Cytec Industries, PolymerAdditive Department,
general type, as illustrated in Fig. 1: 5 Garret Mountain Plaza, West Paterson, NJ 07424.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D2765–95
A—Identification tag and fine wire attached to cage.
B—Reflux condenser.
C—Ring stand clamp.
D—Water inlet.
E—Ground-glass or cork joint.
F—Large-mouth round-bottom flask.
G—Variable transformer.
H—Water outlet.
I—Ring stand.
J—Decahydronaphthalene or xylene.
K—Heating mantle.
L—120-mesh wire cage containing the specimen.
FIG. 1 Extraction Apparatus
11.2 The test samples shall be ground to a fineness that will 12.3 Fill a round-bottom flask as described in 8.1.1 with
pass through a 30-mesh sieve. Shake this sieved material over enough solvent to immerse the 120-mesh cage and sample
a 60-mesh sieve and reject any material that passes through. completely. Three hundred fifty grams in a 500-mL flask or
11.3 Test specimens originating from insulation cut from 1000 g in a 2000-mL flask is sufficient. Dissolve 1% of
wire should be homogeneous and consist of an equal mixture antioxidant in the decahydronaphthalene or xylene to inhibit
ofsamplesrepresentativeofinsulationnearesttotheconductor further crosslinking of the specimen.
and samples representative of insulation nearest the outer 12.4 Boil the decahydronaphthalene or xylene vigorously
periphery of the construction unless specific portions of the enough to ensure good agitation of the solution. Twenty to 40
insulation are being examined for insufficient crosslinking. drops/min from the condenser, while using 1000 g of solvent,
isasatisfactoryboilingrate.Suspendthecageandspecimenin
12. Procedure the solvent so that the bottom edge of the cage is almost
touching the bottom of the flask.Asmall wire, attached to the
12.1 Prepare a specimen holder by cutting a piece of
cage and extending through the reflux condenser can be used
120-mesh stainless steel cloth measuring approximately 80 by
for suspending the cage. Extract the specimen for6hin
40 mm (3 by 1 ⁄2 in.). Fold this to form a square measuring
decahydronaphthalene or for 12 h in xylene.
approximately 40 mm (1 ⁄2 in.). Fold two sides of this square
closedbyfoldingtheclothattheedgesabout6to7mm( ⁄4in.)
NOTE 3—Since most of the extraction occurs within less than the
and stapling those folds. In that manner, a pouch open at the specified time, the period of extraction may be shortened for control tests
on the basis of experience. If this is done, the time of extraction must be
top is obtained. Weigh this pouch (W1).
reported. For referee tests, extraction time is to be as specified by this test
12.2 Place approximately 0.3 g of the ground and screened
method.
sample in the weighed pouch. Weigh the pouch and specimen
(W2). Fold over the open side of the pouch and staple the edge 12.5 After extraction, place the cage and specimen imme-
to form a cage. Weigh the cage and sample (W3). diately in a vacuum oven preheated to 150°C. Dry the
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D2765–95
specimentoconstantweightunderatleast710mm(28in.)Hg TEST METHOD B (NONREFEREE TEST METHOD)
vacuum. Cool and weigh (W4). If the compound absorbs
15. Scope
moisture, cool the specimen in a desiccator before weighing.
15.1 This modification of the referee test method was
NOTE 4—It has been reported that drying time sometimes can be
developed particularly for wire and cable insulations and
materiallyshortenedifthecageandsamplearecooledfor15minandthen
differs from the referee test method only in specimen prepara-
are placed either on a suspended screen or on lint-free absorbent material
tion.
to remove excess solvent before being put into the vacuum drying oven.
15.2 In using this alternative test method, it should be
12.6 If extraction tests are regularly made, the apparatus
recognized that the values obtained may be lower than those
may be left assembled and the extracting solvent (containing
obtained by referee Test MethodAfor the reason given in 1.2.
inhibitor as directed) may be reused until it darkens. How
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.