ASTM D2197-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion of Organic Coatings by Scrape Adhesion
Standard Test Method for Adhesion of Organic Coatings by Scrape Adhesion
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Coatings to perform satisfactorily must adhere to the substrates on which they are applied. This test method has been found useful in differentiating the degree of adhesion of coatings to substrates. It is most useful in providing relative ratings for a series of coated panels exhibiting significant differences in adhesion.
4.2 Studies performed in a laboratory using the loop stylus specified in the previous edition showed meaningful adhesion data were impossible when loads of 10 to 20 kg were required to break the surface of a solvent based coating. The chrome plated loop stylus chattered and skipped across the coating surface when loads of this magnitude were required. Similar meaningless data were obtained when powder coatings were tested that required more than 10 kg to break the surface. Therefore, testing under these conditions is not applicable.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the adhesion of organic coatings such as paint, varnish, and lacquer when applied to smooth, flat (planar) panel surfaces.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2197 − 16
Standard Test Method for
1
Adhesion of Organic Coatings by Scrape Adhesion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2197; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Thematerialsundertestareappliedatuniformthickness
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the adhe-
to flat panels, usually sheet metal of uniform surface texture.
sion of organic coatings such as paint, varnish, and lacquer
After drying, the adhesion is determined by pushing the panels
when applied to smooth, flat (planar) panel surfaces.
beneath a rounded stylus or loop that is loaded in increasing
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
amounts until the coating is removed from the substrate
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
surface.
only.
4. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 4.1 Coatings to perform satisfactorily must adhere to the
substratesonwhichtheyareapplied.Thistestmethodhasbeen
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- found useful in differentiating the degree of adhesion of
coatings to substrates. It is most useful in providing relative
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ratings for a series of coated panels exhibiting significant
differences in adhesion.
2. Referenced Documents
2
4.2 Studies performed in a laboratory using the loop stylus
2.1 ASTM Standards:
specified in the previous edition showed meaningful adhesion
D609 Practice for Preparation of Cold-Rolled Steel Panels
data were impossible when loads of 10 to 20 kg were required
for Testing Paint, Varnish, Conversion Coatings, and
to break the surface of a solvent based coating. The chrome
Related Coating Products
plated loop stylus chattered and skipped across the coating
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness
surface when loads of this magnitude were required. Similar
of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels
meaningless data were obtained when powder coatings were
D1005 Test Method for Measurement of Dry-Film Thick-
tested that required more than 10 kg to break the surface.
ness of Organic Coatings Using Micrometers
Therefore, testing under these conditions is not applicable.
D7091 Practice for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry
Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to
5. Apparatus
Ferrous Metals and Nonmagnetic, Nonconductive Coat-
5.1 Application Equipment, as described in Practices D823.
ings Applied to Non-Ferrous Metals
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
5.2 Film-Thickness Measuring Apparatus, as described in
ASTM Test Methods
Test Method D1005 or Practice D7091.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
5.3 Balanced Beam, ScrapeAdhesion Tester (Figs. 1 and 2),
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
consisting of a balanced beam to which is secured a platform
for supporting weights, and a rod at an angle of 45° that holds
the scraping loop.The rod shall be set so that the scraping loop
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
contacts test surfaces directly below the weights. The loop
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
1
shall be 1.6-mm ( ⁄16-in.) diameter rod, bent into a “U” shape
Subcommittee D01.23 on Physical Properties of Applied Paint Films.
with an outside radius of 3.25 6 0.05 mm (0.128 6 0.002 in.)
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2016. Published January 2017. Originally
andhardenedtoRockwellHRC56to58,andshallbeasmooth
approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D2197 – 13. DOI:
10.1520/D2197-16.
finish. The loop can be either chromium plated, nickel plated,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
or heat treated polished steel, as agreed upon between the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
purchaser and the supplier. These testers are adjustable to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. accommodate flat, metallic, and nonmetallic specimens to
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2197 − 16
FIG. 1 Bal
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2197 − 13 D2197 − 16
Standard Test Method for
1
Adhesion of Organic Coatings by Scrape Adhesion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2197; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the adhesion of organic coatings such as paint, varnish, and lacquer when
applied to smooth, flat (planar) panel surfaces.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D609 Practice for Preparation of Cold-Rolled Steel Panels for Testing Paint, Varnish, Conversion Coatings, and Related Coating
Products
D823 Practices for Producing Films of Uniform Thickness of Paint, Varnish, and Related Products on Test Panels
D1005 Test Method for Measurement of Dry-Film Thickness of Organic Coatings Using Micrometers
D7091 Practice for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to Ferrous Metals
and Nonmagnetic, Nonconductive Coatings Applied to Non-Ferrous Metals
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The materials under test are applied at uniform thickness to flat panels, usually sheet metal of uniform surface texture. After
drying, the adhesion is determined by pushing the panels beneath a rounded stylus or loop that is loaded in increasing amounts
until the coating is removed from the substrate surface.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Coatings to perform satisfactorily must adhere to the substrates on which they are applied. This test method has been found
useful in differentiating the degree of adhesion of coatings to substrates. It is most useful in providing relative ratings for a series
of coated panels exhibiting significant differences in adhesion.
4.2 Studies performed in a laboratory using the loop stylus specified in the previous edition showed meaningful adhesion data
were impossible when loads of 10 to 20 kg were required to break the surface of a solvent based coating. The chrome plated loop
stylus chattered and skipped across the coating surface when loads of this magnitude were required. Similar meaningless data were
obtained when powder coatings were tested that required more than 10 kg to break the surface. Therefore, testing under these
conditions is not applicable.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Application Equipment, as described in Practices D823.
5.2 Film-Thickness Measuring Apparatus, as described in Test Method D1005 or Practice D7091.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.23 on Physical Properties of Applied Paint Films.
Current edition approved May 15, 2013Dec. 1, 2016. Published May 2013January 2017. Originally approved in 1963. Last previous edition approved in 20102013 as
D2197 – 10.D2197 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/D2197-13.10.1520/D2197-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2197 − 16
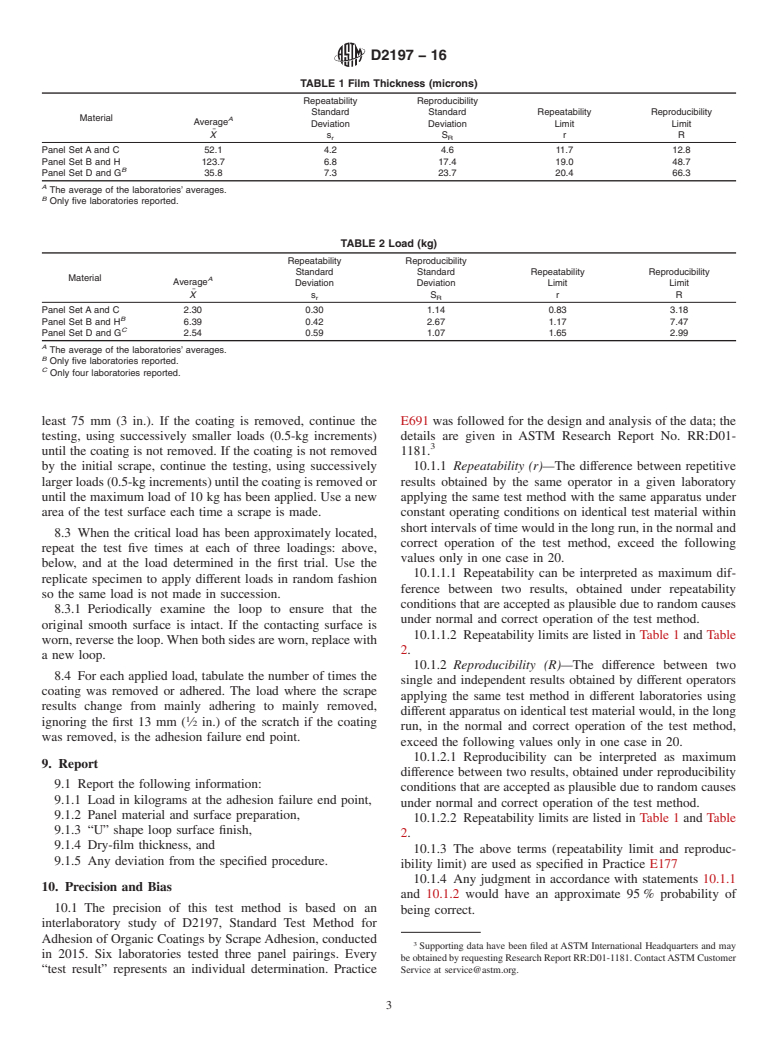
5.3 Balanced Beam, Scrape Adhesion Tester (Figs. 1 and 2), consisting of a balanced beam to which is secured a platform for
supporting weights, and a rod at an angle of 45° that holds the scraping loop. The rod shall be set so that the scraping loop contacts
1
test surfaces directly below the weights. The loop shall be 1.6-mm ( ⁄16-in.) diameter rod, bent into a “U”
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.