ASTM A542/A542M-99(2004)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Quenched-and-Tempered, Chromium-Molybdenum, and Chromium-Molybdenum-Vanadium
Standard Specification for Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Quenched-and-Tempered, Chromium-Molybdenum, and Chromium-Molybdenum-Vanadium
ABSTRACT
This specification covers pressure vessel plates, alloy steel, quenched-and-tempered, chromium-molybdenum, and chromium-molybdenum-vanadium. As a steel making practice, the steel shall be killed and shall conform to specified fine austenitic grain size requirements. Plate types A, B, C, D, and E shall be heat treated by heating to a suitable austenitizing temperature, holding for a sufficient period of time to attain uniform temperature throughout the thickness, and quenching in a suitable liquid medium by spraying or immersion. The steel shall conform to the required chemical compositions. The required mechanical properties that include tension test requirements and notch toughness requirements are presented in details.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers two types of 21/4 Cr-1 Mo and three types of Cr-Mo-V alloy steel plates for use in the quenched-and-tempered condition, intended for the fabrication of welded pressure vessels and components.
1.2 Material under this specification is available in five types, designated "A," "B," "C,"" D," and "E." Type B is identical to Type A except for restrictive limits for carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, and nickel. The material is also available in five classes having the following strength levels. Type E is available only as Class 4 and 4a. ClassMinimum Tensile Strength, ksi [MPa] 1 105 [725] 2 115 [795] 3 95 [655] 4 and 4a 85 [585]
1.3 The maximum thickness of plates is limited only by the capacity of the chemical composition to meet the specified mechanical property requirements.
1.4 The minimum thickness of plates is limited to 3/16 in. [5 mm].
1.5 The material is intended to be suitable for fusion welding. Welding technique is of fundamental importance and it is presupposed that welding procedures will be in accordance with approved methods.
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents, therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
´1
Designation: A542/A542M – 99 (Reapproved 2004)
Standard Specification for
Pressure Vessel Plates, Alloy Steel, Quenched-and-
Tempered, Chromium-Molybdenum, and Chromium-
Molybdenum-Vanadium
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA542/A542M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—Supplementary Requirement S14, Bend Test, was editorially removed in September 2004.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2 3
1.1 Thisspecification coverstwotypesof2 ⁄4 Cr-1Moand 2.1 ASTM Standards:
three types of Cr-Mo-V alloy steel plates for use in the A20/A20M Specification for General Requirements for
quenched-and-tempered condition, intended for the fabrication Steel Plates for Pressure Vessels
of welded pressure vessels and components. A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
1.2 Material under this specification is available in five of Steel Products
types, designated “A,” “B,” “C,” “D,” and “E.” Type B is A435/A435M Specification for Straight-Beam Ultrasonic
identical to Type A except for restrictive limits for carbon, Examination of Steel Plates
phosphorus,sulfur,andnickel.Thematerialisalsoavailablein A577/A577M Specification for UltrasonicAngle-Beam Ex-
five classes having the following strength levels. Type E is amination of Steel Plates
available only as Class 4 and 4a. A578/A578M Specification for Straight-Beam Ultrasonic
Examination of Rolled Steel Plates for Special Applica-
Class Minimum Tensile Strength, ksi [MPa]
tions
1 105 [725]
2 115 [795]
3. General Requirements and Ordering Information
3 95 [655]
4 and 4a 85 [585]
3.1 Material supplied to this material specification shall
conform to SpecificationA20/A20M. These requirements out-
1.3 The maximum thickness of plates is limited only by the
line the testing and retesting methods and procedures, permis-
capacity of the chemical composition to meet the specified
sible variations in dimensions, and mass, quality and repair of
mechanical property requirements.
3 defects, marking, loading, etc.
1.4 The minimum thickness of plates is limited to ⁄16 in. [5
3.2 Specification A20/A20M also establishes the rules for
mm].
the ordering information which should be complied with when
1.5 The material is intended to be suitable for fusion
purchasing material to this specification.
welding. Welding technique is of fundamental importance and
3.3 In addition to the basic requirements of this specifica-
itispresupposedthatweldingprocedureswillbeinaccordance
tion, certain supplementary requirements are available when
with approved methods.
additional control, testing, or examination is required to meet
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
end use requirements. These include:
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
3.3.1 Vacuum treatment,
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
3.3.2 Additional or special tension testing,
system are not exact equivalents, therefore, each system must
3.3.3 Impact testing, and
beusedindependentlyoftheother.Combiningvaluesfromthe
3.3.4 Nondestructive examination.
two systems may result in nonconformance with this specifi-
3.4 The purchaser is referred to the supplementary require-
cation.
ments listed in this specification and to the detailed require-
ments in Specification A20/A20M.
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA01 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and RelatedAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
A01.11 on Steel Plates for Boilers and Pressure Vessels.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2004. Published September 2004. Originally
´1 3
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 1999 asA542/A542M–99 . For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/A0542_A0542M-99R04E01. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
cation SA-542 in Section II of that Code. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
´1
A542/A542M – 99 (2004)
3.5 If the requirements of this specification are in conflict to1010°C]forTypesA,B,C,andDand1850to2050°F[1010
withtherequirementsofSpecificationA20/A20M,therequire- to 1120°C] for Type E before the heat treatment specified in
5.1.
ments of this specification shall prevail.
5.4 When the purchaser elects to perform the heat treatment
required above, the material manufacturer shall temper the
4. Manufacture
platespriortoshipmentatatemperaturenotlowerthan1050°F
4.1 Steelmaking Practice—The steel shall be killed and
[565°C] for Types A, B, C, and D and not lower than 1200°F
shall conform to the fine austenitic grain size requirement of
[650°C] for Type E.
Specification A20/A20M.
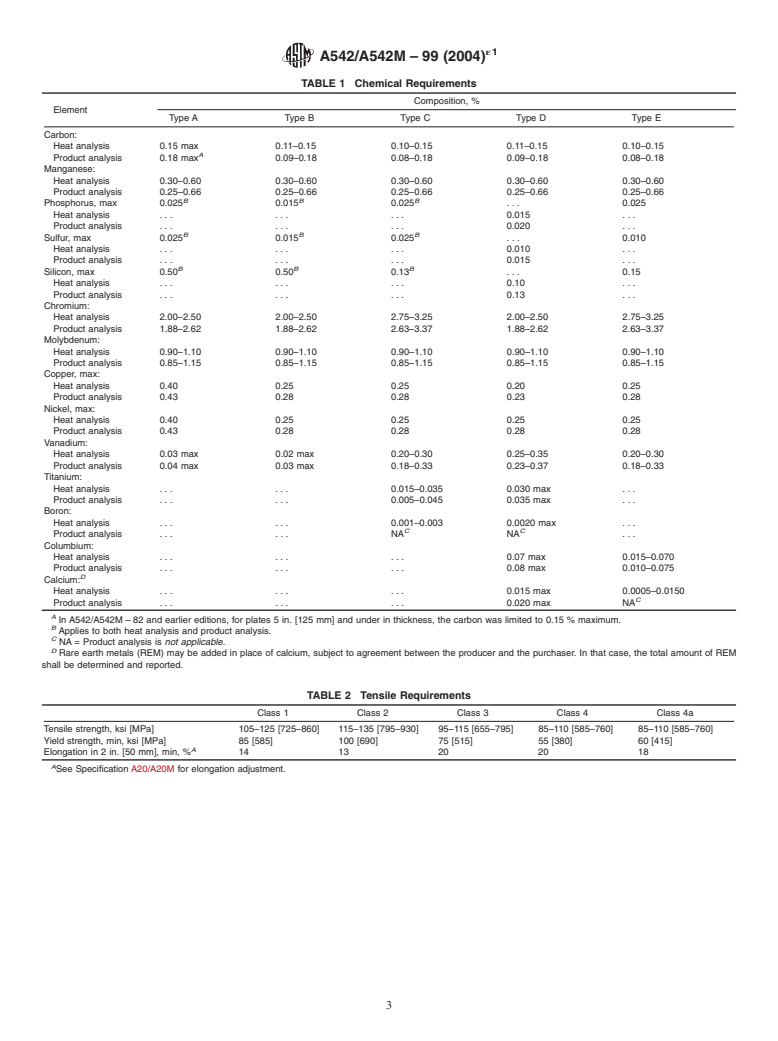
6. Chemical Composition
5. Heat Treatment 6.1 The steel shall conform to the chemical requirements
shown in Table 1.
5.1 All plates shall be heat treated by heating to a suitable
austenitizing temperature, holding for a sufficient period of 7. Mechanical Properties
time to attain uniform temperature throughout the thickness,
7.1 Tension Test Requirements:
and quenching in a suitable liquid medium by spraying or
7.1.1 The material as represented by the tension-test speci-
immersion. For Type D material, the minimum austenitizing
mens shall conform to the requirements shown in Table 2.
temperature shall be 1650°F [900°C]. ForType E material, the 7.1.2 For nominal plate thicknesses of ⁄4 in. [20 mm] and
minimum austenitizing temperature shall be 1850°F [1010°C].
under, the 1 ⁄2-in. [40-mm] wide rectangular specimen may be
usedforthetensiontest,andtheelongationmaybedetermined
5.2 Afterquenching,theplatesshallbetemperedtoproduce
in a 2-in. [50-mm] gage length that includes the fracture and
the specified tensile requirements by heating to a suitable
that shows the greatest elongation.
temperatureandholdingforaperiodoftimeofnotlessthat30
7.2 Notch Toughness Requirements—Classes 4 and 4a:
min/in. [1.2 min/mm] of thickness but not less than ⁄2 h. The
7.2.1 A transverse Charpy V-notch test from each plate-as-
minimum tempering temperature shall be as follows:
heat-treated shall have a minimum energy absorption value of
Type Class Temperature, °F [°C]
40 ft·lbf [54 J] average of three specimens and 35 ft·lbf [48 J]
A, B, C 1, 2, 3 1050 [565]
for one specimen only in the set.
A, B, C 4 1200 [650]
7.2.2 For Class 4, the impact test temperature shall be as
A, B, C, D 4a 1250 [675]
specified on the order.
5.3 Plates over 4 in. [100 mm] in thickness shall receive a
7.2.3 For Class 4a, the impact test temperature shall be 0°F
prior heat treatment of normalizing at, or water quenching [−18°C].
from,atemperaturewithintherangefrom1650to1850°F[900
´1
A542/A542M – 99 (2004)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Element
Type A Type B Type C Type D Type E
Carbon:
Heat analysis 0.15 max 0.11–0.15 0.10–0.15 0.11–0.15 0.10–0.15
A
Product analysis 0.18 max 0.09–0.18 0.08–0.18 0.09–0.18 0.08–0.18
Manganese:
Heat analysis 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60 0.30–0.60
Product
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.