ASTM E2830-11(2020)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Mobility Capabilities of Emergency Response Robots Using Towing Tasks: Grasped Sleds
Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Mobility Capabilities of Emergency Response Robots Using Towing Tasks: Grasped Sleds
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
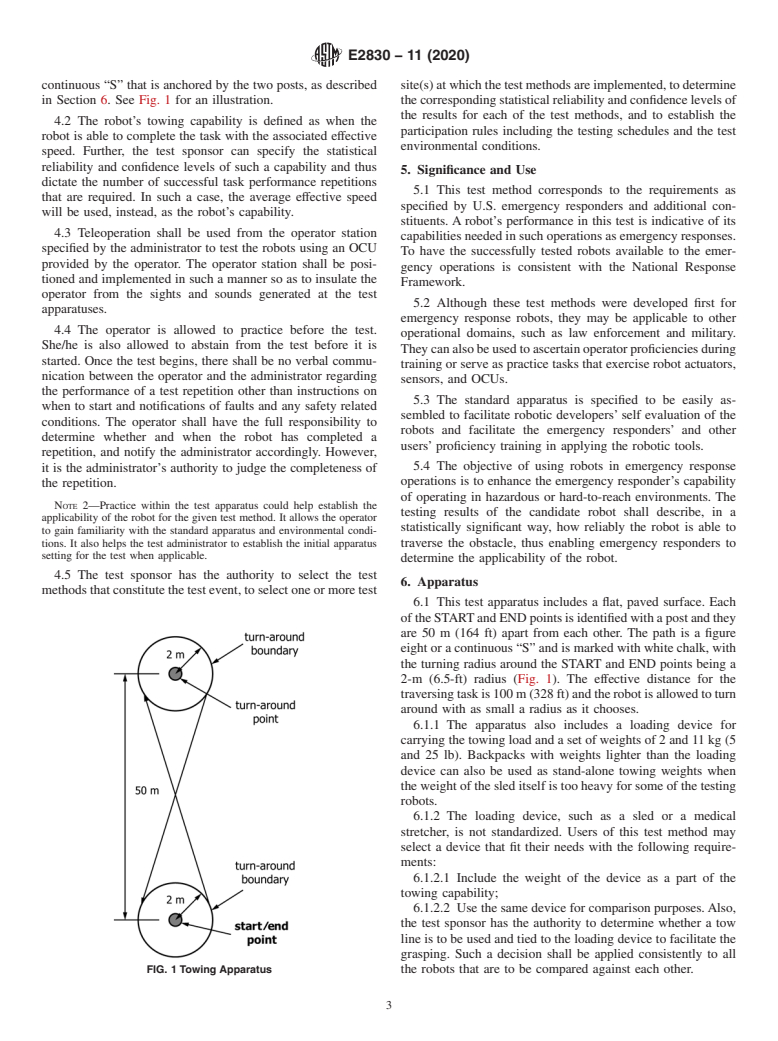
5.1 This test method corresponds to the requirements as specified by U.S. emergency responders and additional constituents. A robot’s performance in this test is indicative of its capabilities needed in such operations as emergency responses. To have the successfully tested robots available to the emergency operations is consistent with the National Response Framework.
5.2 Although these test methods were developed first for emergency response robots, they may be applicable to other operational domains, such as law enforcement and military. They can also be used to ascertain operator proficiencies during training or serve as practice tasks that exercise robot actuators, sensors, and OCUs.
5.3 The standard apparatus is specified to be easily assembled to facilitate robotic developers’ self evaluation of the robots and facilitate the emergency responders’ and other users’ proficiency training in applying the robotic tools.
5.4 The objective of using robots in emergency response operations is to enhance the emergency responder’s capability of operating in hazardous or hard-to-reach environments. The testing results of the candidate robot shall describe, in a statistically significant way, how reliably the robot is able to traverse the obstacle, thus enabling emergency responders to determine the applicability of the robot.
SCOPE
1.1 Purpose:
1.1.1 The purpose of this test method, as a part of a suite of mobility test methods, is to quantitatively evaluate a teleoperated ground robot’s towing capability with the task of grasping loads and traversing a specified route on a flat and paved surface.
1.1.2 Robots shall possess a certain set of mobility capabilities, including towing, to suit critical operations such as emergency responses. This capability would be required to perform such emergency response-related tasks as delivering critical supplies, moving victims to safe locations, or transporting suspected packages away from humans.
1.1.3 Emergency response ground robots shall be able to handle many types of obstacles and terrains. The required mobility capabilities include traversing gaps, hurdles, stairs, slopes, various types of floor surfaces or terrains, and confined passageways. Yet additional mobility requirements include sustained speeds and towing capabilities. Standard test methods are required to evaluate whether candidate robots meet these requirements.
1.1.4 ASTM Task Group E54.08.01 specifies a mobility test suite, which consists of a set of test methods for evaluating these mobility capability requirements. This towing-by-grasping test method is a part of the mobility test suite. The apparatuses associated with the test methods challenge specific robot capabilities in repeatable ways to facilitate comparison of different robot models as well as particular configurations of similar robot models.
1.1.5 The test methods quantify elemental mobility capabilities necessary for ground robot emergency response applications. As such, the test suite should be used collectively to represent a ground robot’s overall mobility performance.
Note 1: Additional test methods within the suite are anticipated to be developed to address additional or advanced robotic mobility capability requirements, including newly identified requirements and even for new application domains.
1.2 Performing Location—This test method shall be performed in a testing laboratory or the field where the specified apparatus and environmental conditions are implemented.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, hea...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2830 − 11 (Reapproved 2020)
Standard Test Method for
Evaluating the Mobility Capabilities of Emergency Response
1
Robots Using Towing Tasks: Grasped Sleds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2830; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
requirements, including newly identified requirements and even for new
1. Scope
application domains.
1.1 Purpose:
1.2 Performing Location—This test method shall be per-
1.1.1 The purpose of this test method, as a part of a suite of
formed in a testing laboratory or the field where the specified
mobility test methods, is to quantitatively evaluate a teleoper-
apparatus and environmental conditions are implemented.
ated ground robot’s towing capability with the task of grasping
loads and traversing a specified route on a flat and paved 1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
surface. asthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesaremathemati-
1.1.2 Robots shall possess a certain set of mobility cal conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for
capabilities,includingtowing,tosuitcriticaloperationssuchas information only and are not considered standard.
emergency responses. This capability would be required to
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
perform such emergency response-related tasks as delivering
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
critical supplies, moving victims to safe locations, or transport-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ing suspected packages away from humans.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1.3 Emergency response ground robots shall be able to
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
handle many types of obstacles and terrains. The required
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
mobility capabilities include traversing gaps, hurdles, stairs,
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
slopes, various types of floor surfaces or terrains, and confined
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
passageways. Yet additional mobility requirements include
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
sustained speeds and towing capabilities. Standard test meth-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
ods are required to evaluate whether candidate robots meet
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
these requirements.
1.1.4 ASTMTask Group E54.08.01 specifies a mobility test
2. Referenced Documents
suite, which consists of a set of test methods for evaluating 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
these mobility capability requirements. This towing-by-
E2521 Terminology for Evaluating Response Robot Capa-
grasping test method is a part of the mobility test suite. The
bilities
apparatuses associated with the test methods challenge specific
E2592 Practice for Evaluating Response Robot Capabilities:
robotcapabilitiesinrepeatablewaystofacilitatecomparisonof
Logistics: Packaging for Urban Search and Rescue Task
different robot models as well as particular configurations of
Force Equipment Caches
similar robot models.
2.2 Other Standards:
1.1.5 The test methods quantify elemental mobility capa-
National Response Framework U.S. Department of Home-
bilities necessary for ground robot emergency response appli-
3
land Security
cations. As such, the test suite should be used collectively to
represent a ground robot’s overall mobility performance.
3. Terminology
NOTE 1—Additional test methods within the suite are anticipated to be
3.1 Terminology E2521 lists additional definitions relevant
developed to address additional or advanced robotic mobility capability
to this test method.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E54 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Homeland Security Applications and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
E54.09 on Response Robots. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2020. Published January 2020. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as E2830 – 11. DOI: Available from Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), P.O. Box
10.1520/E2830-11R20. 10055, Hyattsville, MD 20782-8055, http://www.fema
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.