ASTM D1770-94(2006)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Neps, Vegetable Matter, and Colored Fiber in Wool Top
Standard Test Method for Neps, Vegetable Matter, and Colored Fiber in Wool Top
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Test Method D 1770 for the determination of neps, vegetable matter, and colored fiber may be used for the acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wool top but caution is advised because the between-laboratory precision is known to be poor. Comparative tests as directed in 5.1.1 may be advisable.
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in reported test results when using Test Method D 1770 for acceptance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the supplier should conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias. As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are from a lot of material of the type in question. The test specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. The average results from the two laboratories should be compared using Student’t-test for unpaired data and an acceptable probability level chosen by the two parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the supplier must agree to interpret future test results in the light of the known bias.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the number of neps and pieces of vegetable matter by size classes, and the number of colored fibers, in 15 g samples of wool top.
1.2 This test method is applicable to wool top in any form. Note 1 - For the determination of number of neps per specified mass of cotton samples, refer to Test Method D 1446.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1770 – 94 (Reapproved 2006)
Standard Test Method for
Neps, Vegetable Matter, and Colored Fiber in Wool Top
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1770; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.2 laboratory sample, n—a portion of material taken to
represent the lot sample, or the original material, and used in
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofthenumber
the laboratory as a source of test specimens.
of neps and pieces of vegetable matter by size classes, and the
2 3.1.3 lot, n—in acceptance sampling, that part of a consign-
number of colored fibers, in 15 g samples of wool top.
ment or shipment consisting of material from one production
1.2 This test method is applicable to wool top in any form.
lot.
NOTE 1—Forthedeterminationofnumberofnepsperspecifiedmassof
3.1.4 nep, n—one or more fibers occurring in a tangled and
cotton samples, refer to Test Method D1446.
unorganized mass.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.4.1 Discussion—For the purpose of this test method, the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mass of unorganized fibers retains its identity upon removal
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
from a fibrous strand.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.5 test specimen, n— for wool top, a length of specified
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
mass taken at random from a length of wool top selected as a
laboratory sample.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.6 top, n—in wool, a continuous untwisted strand of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
wool fibers from which the shorter fibers or noils have been
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
removed by combing.
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
3.1.7 vegetable matter, n— in wool top, the pieces of burrs,
D1446 Discontinued 1978; Method of Test for Number of
seeds, shive, leaves, twigs, and grasses which have escaped
Neps in Cotton Samples
removal in processing, also foreign vegetable fibers such as
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
hemp, sisal, etc., if present.
Nep Scale Standard (1 Photo), Vegetable Matter Standard (1
3.1.8 For definitions of other textile terms used in this test
Photo)
method, refer to Terminology D123.
3. Terminology
4. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Definitions:
4.1 Four test specimens are taken and examined in accor-
3.1.1 colored fiber, n— in wool top, any fiber the color or
dancewithspecifiedprocedures.Eachobservedneporpieceof
shade of which differs from the normal color or shade of the
vegetable matter is classified by size, by visual comparison
fiber mass of the sample.
with a specified standard size chart. The numbers of each class
of neps and class of vegetable matter pieces, and the number of
coloredfibers,arerecordedforeachspecimen.Fromthesedata
1 the average counts per specimen of 15 g are calculated.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 onTextiles
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.13 on Wool and Felt.
5. Significance and Use
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2006. Published October 2006. Originally
´1
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D1770 – 88 (2000) .
5.1 Test Method D1770 for the determination of neps,
DOI: 10.1520/D1770-94R06.
vegetable matter, and colored fiber may be used for the
Foradditionalinformation,referencemaybemadeto“NepsinWorstedSliver,”
Wool Science Review, Vol 22, March 1963, pp. 28–38. acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wool top but
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
caution is advised because the between-laboratory precision is
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
known to be poor. Comparative tests as directed in 5.1.1 may
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
be advisable.
the ASTM website.
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in
on www.astm.org.
reported test results when using Test Method D1770 for
Original prints of these illustrations are available from ASTM International
acceptance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and
Headquarters. OrderAdjunct No.ADJD1770 for Nep Scale Standard and Vegetable
Matter Standard. the supplier should conduct comparative tests to determine if
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1770 – 94 (2006)
NOTE 1—Figs. 1 and 2 should preferably not be used as substitutes for the original prints obtainable from ASTM.
FIG. 1 Visual Standard
there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent 6.4 Tweezers, with pointed ground ends.
statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of
6.5 Balance or Scale,capacityatleast25gwithasensitivity
bias.As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test
of 0.01 g.
specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are
from a lot of material of the type in question. The test
7. Sampling
specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers
7.1 Lot Sample—As a lot sample for acceptance testing,
to each laboratory for testing.The average results from the two
take at random the number of shipping containers directed in
laboratories should be compared using Student’s t-test for
an applicable material specification or other agreement be-
unpaireddataandanacceptableprobabilitylevelchosenbythe
tween the purchaser and the supplier. Consider shipping
two parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either
containers to be the primary sampling units.
its cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the
supplier must agree to interpret future test results in the light of
NOTE 2—An adequate specification or other agreement between the
the known bias.
purchaser and the supplier requires taking into account the variability
between shipping containers, between laboratory samples within a ship-
6. Apparatus ping container, and between test specimens within a laboratory sample to
provide a sampling plan with a meaningful producer’s risk, consumer’s
6.1 Nep Scale Standard, see Fig. 1 and ADJD1770.
risk, acceptable quality level, and limiting quality level.
6.2 Vegetable Matter Standard, see Fig. 2 and ADJD1770.
6.3 Examination Surfaces, consisting of a dark surface 7.2 Laboratory Sample—As a laboratory sample for accep-
illuminated from above for nep test and a white surface tance testing, take from each shipping container in the lot
illuminated from above for vegetable matter and colored fiber sample the first 3 yd (3 m) of material from the lead end of the
tests. Alternatively, a white translucent surface with under- strand that has a clean, uniform appearance. If the shipping
lighting may be used for all tests. When a translucent surface containers in the lot sample contain multiple packages, take a
is used, colored fibers must be reexamined on an over-lighted laboratory sample from one package drawn at random from
white surface to avoid inclusion of medullated fibers. each shipping container.
D1770 – 94 (2006)
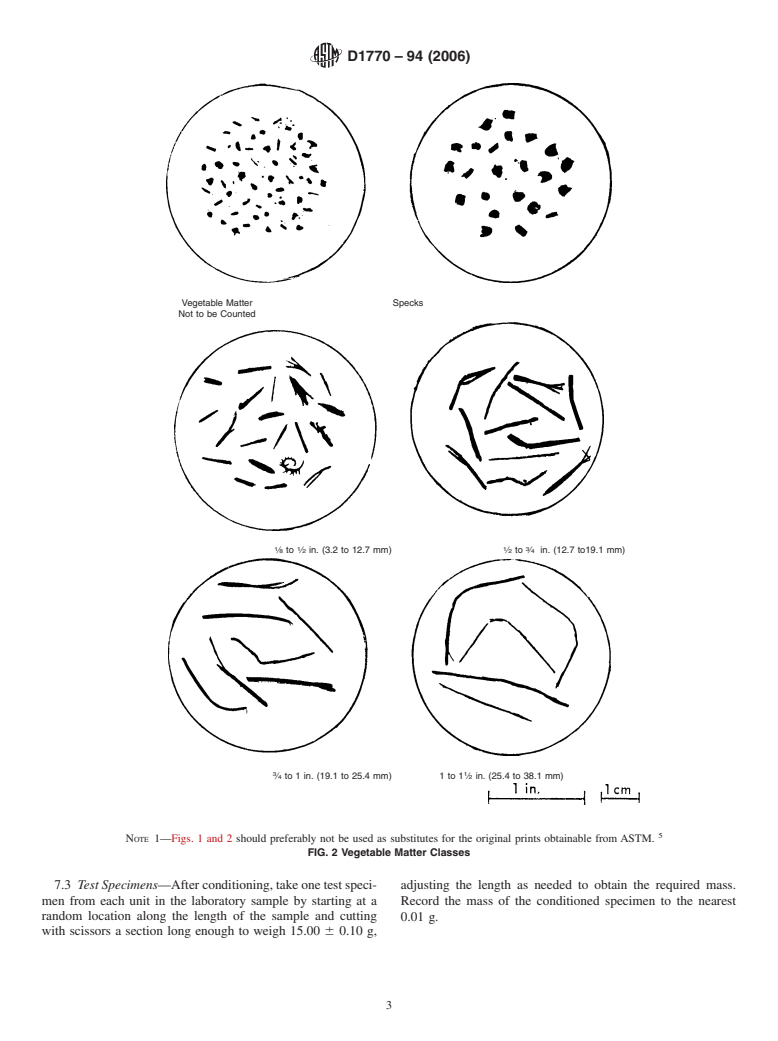
Vegetable Matter Specks
Not to be Counted
1 1 1 3
⁄8 to ⁄2 in. (3.2 to 12.7 mm) ⁄2 to ⁄4 in. (12.7 to19.1 mm)
3 1
⁄4 to 1 in. (19.1 to 25.4 mm) 1 to 1 ⁄2 in. (25.4 to 38.1 mm)
NOTE 1—Figs. 1 and 2 should preferably not be used as substitutes for the original prints obtainable from ASTM.
FIG. 2 Vegetable Matter Classes
7.3 Test Specimens—Afterconditioning,takeonetestspeci- adjusting the length as needed to obtain the required mass.
men from each unit in the laboratory sample by starting at a Record the mass of the conditioned specimen to the nearest
random location along the length of the sample and cutting
0.01 g.
with scissors a section long enough to weigh 15.00 6 0.10 g,
D1770 – 94 (2006)
8. Conditioning
N = average number of neps of nep size class i per 15 g of
i
wool top,
8.1 Bringthelaboratorysamplestomoistureequilibriumfor
n = total number of neps of nep size class i in the four
obtaining test specimens in the standard atmosphere for testing
i
specimens, and
textiles as directed in Practice D1776. Preconditioning is not
w = combined mass of the four specimens, in grams.
necessary.
10.5 Vegetable Matter—Calculate to the nearest 0.1 unit-
9. Procedure
the average number of vegetable matter pieces of each size
class per 15 g of wool top, using Eq 3:
9.1 Test each weighed specimen, in the prevailing atmo-
sphere if preferred, as follows:
V 5 v 3 15/w (3)
j j
9.1.1 Draw a portion not exceeding one-tenth of the speci-
where:
men and spread it over the prescribed examination surface.
V = average number of vegetable matter pieces of size
j
9.1.2 Remove with tweezers each colored fiber and reserve
class j per 15 g of wool top,
for counting.
v = total number of vegetable matter pieces of size class
j
9.1.3 Also remove with tweezers each nep (except those
j in the four specimens, and
obviouslysmallerthansize1onthenepscale,Fig.1),andeach
w = combined mass of four specimens, in grams.
piece of vegetable matter (except those ob
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.