ASTM D3348-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Rapid Field Test for Trace Lead In Unleaded Gasoline (Colorimetric Method)
Standard Test Method for Rapid Field Test for Trace Lead In Unleaded Gasoline (Colorimetric Method)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended for use in the field by nontechnical people for the quantitative measurement of lead in unleaded gasoline in the range from 0.01 to 0.10 g Pb/U.S. gal (2.64 to 26.4 mg Pb/L). This method applies to all commercial gasolines and responds to all types of lead alkyls as well as to other organic and inorganic forms of lead. Note 1-This test method is a screening test and is not to be used as a replacement for Test Method D3116, Test Method D3229, or Test Method D3237.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see Notes 3 and 4 and Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: D 3348 – 98
Standard Test Method for
Rapid Field Test for Trace Lead In Unleaded Gasoline
(Colorimetric Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3348; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope filtered into a solution of 4-(2-pyridylazo)-resorcinol disodium
salt (PAR) and ammonium hydroxide. The lead is determined
1.1 This test method is intended for use in the field by
by measuring its PAR complex colorimetrically at 490 nm
nontechnical people for the quantitative measurement of lead
using a previously prepared calibration curve.
in unleaded gasoline in the range from 0.01 to 0.10 g Pb/U.S.
gal (2.64 to 26.4 mg Pb/L). This method applies to all
4. Significance and Use
commercial gasolines and responds to all types of lead alkyls
4.1 This test is used to determine trace quantities of lead in
as well as to other organic and inorganic forms of lead.
unleaded gasoline. Unwarranted amounts of lead may cause
NOTE 1—This test method is a screening test and is not to be used as a
deposits in automotive pollution control equipment and poi-
replacement for Test Method D 3116, Test Method D 3229, or Test
soning of catalytic mufflers.
Method D 3237.
5. Interferences
1.2 The values stated in SI units shall be regarded as
standard.
5.1 PAR also reacts with many other metals forming highly
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
colored complexes. However, none of these are normally found
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
present in a soluble form in gasoline. The following metals
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
were found to form colors with PAR and if present may
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
interfere to give high results: Fe II, Fe III, Co II, Ni II, Cu II,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
Zn II, Cd II, Mn II, Sn II, V IV, Pb II, U VI, Ti IV, and the rare
precautionary statements, see Note 3 and Note 4 and Section 7.
earths.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Apparatus
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.1 Ultraviolet Lamp, long wavelength, 3660 Å, placed in
D 3116 Test Method for Trace Amounts of Lead in Gaso-
a standard 4-W fluorescent fixture.
line
NOTE 2—A 3-min electric timer is connected to the fixture in the
D 3229 Test Method for Low Levels of Lead in Gasoline by
prototype kit.
X-Ray Spectrometry
6.2 Measuring Block, aluminum, drilled to hold an 18 by
D 3237 Test Method for Lead in Gasoline by Atomic
150-mm test tube, with a mark at a level equal to 5.0 mL of
Absorption Spectrometry
liquid in the test tube.
3. Summary of Test Method
6.3 Colorimeter, Portable, capable of operating at 490 mm.
Any equivalent instrument capable of measurement near 514
3.1 The gasoline is treated with iodine and tetraethyl am-
nm (the optimum Pb-PAR complex wavelength) may be used.
monium chloride in chloroform and subjected to ultraviolet
6.4 Test Tubes, borosilicate, 18 by 150 mm.
light. The lead alkyls form water-soluble lead alkyl iodides,
6.5 Pipets, glass, dropping, capable of delivering 2.0 mL
which are removed from the gasoline by shaking it with an
with a 2-mL bulb.
aqueous ammonium nitrate solution. The aqueous extract is
NOTE 3—Caution: Gasoline or any of the reagents must not come in
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis. Lamp F4T5.BL, available from the General Electric Co., or equivalent, has
Current edition approved Feb. 10, 1998. Published June 1998. been found satisfactory for this purpose.
. Originally published as D 3348 – 74. Last previous edition D 3348 – 92 Three-minute timer, available from H. M. Rhodes, Avon, CT 06001, Catalog
This test method is based on the use of the Mobil Lead Test Kit (Fig. X1.1). No. 90021, has been found satisfactory for this purpose.
3 8
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01. Disposable culture tubes, available from the Sargent Welch Co., 35 Stern Ave.,
Discontinued—See 1992 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02. Springfield, NJ 07081, Catalog No. S-79523K, have been found satisfactory for this
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02. purpose.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D 3348
contact with rubber. If this happens, discard the bulb and pipet and start
7.9 Iodine/TEAC/CHCl Solution (Reagent A)—Dissolve
again.
1.000 g 6 1 mg of iodine in 75 mL of chloroform (CHCl )in
a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 1.000 g 6 1 mg of tetraethy-
6.6 Funnel, plastic, 2 in. in inside diameter.
lammonium chloride (TEAC) and mix until dissolved. Dilute
6.7 Filter Paper, ashless, hardened, smooth, very fast, 11.0
to the mark with CHCl .
cm in diameter.
6.8 Graduated Cylinder, plastic, 10-mL.
NOTE 6—Solutions described in 7.4, 7.6, and 7.9 have been found to be
6.9 Glass Vials, with caps, disposable, 1-oz capacity.
stable for at least 2 months.
7.10 Lead Standards—This method was developed using
7. Reagents
lead standards prepared by addition of known amounts of
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
various lead alkyls to blended unleaded gasoline to cover the
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
range of this method.
all reagents conform to the specifications of the Committee on
7.11 Tetraethylammonium Chloride Monohydrate (TEAC).
Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where
7.12 Quality Control (QC) Sample(s),— preferably are
such specifications are available. Other grades may be used,
portions of one or more gasoline materials or product standards
provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently
of known lead content that were not used in the generation of
high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of
the instrument calibration curve. These (QC) samples are to be
the determination.
used to check the validity of the testing process as described in
7.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, reference
Section 10. An ample supply of QC sample material shall be
to water shall be understood to mean distilled water or water of
available for the intended period of use, and must be homoge-
equal purity.
neous and stable under the anticipated storage conditions.
7.3 Ammonium Hydroxide (sp gr 0.90)—Concentrated am-
monium hydroxide (NH OH).
8. Calibration
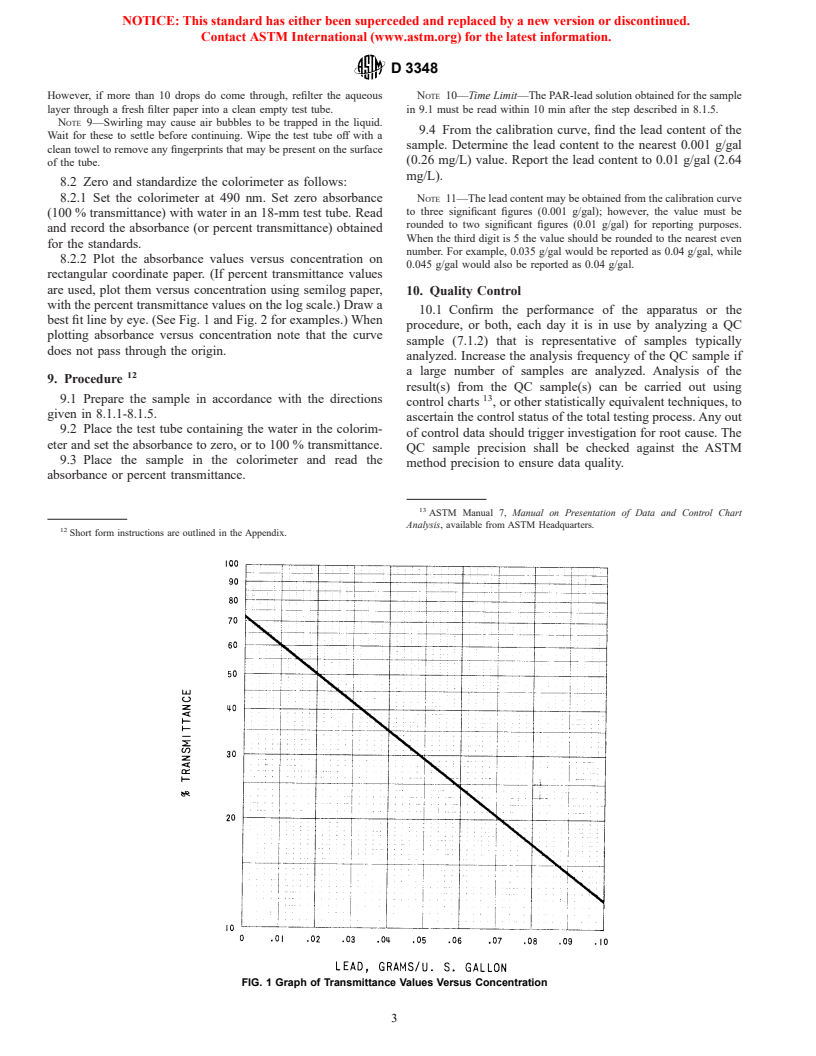
7.4 Ammonium Nitrate Solution (Reagent B)—Dissolve
8.1 Prepare a calibration curve as follows, using at least four
15.0 6 0.1 g of ammonium nitrate (NH NO ) in 750 mL of
4 3
gasoline standards of known lead content that cover the range
water in a 1-L volumetric flask. Dilute to the mark with water.
from 0.01 to 0.10 g Pb/gal (2.64 to 26.4 mg Pb/L).
7.5 Chloroform (CHCl )—(Danger: May be fatal if swal-
8.1.1 Rinse the 2-mL graduated pipet three times with the
lowed. Harmful if inhaled. May produce toxic vapors if
gasoline sample. Add 2.0 mL of the sample to a 1-oz glass vial.
burned. Chronic or repeated exposure can cause liver or kidney
Add 2.0 mL of iodine/TEAC/CHCl solution (Reagent A) from
damage. See Annex A1.1.)
another pipet, to the vial containing the gasoline. Tightly cap
NOTE 4—Warning: Harmful if inhaled or swallowed. Carcinogen (ani-
the vial.
mal positive). Skin and eye irritant. May produce toxic vapors if burned.
8.1.2 Place the vial on the ultraviolet light and set the timer
to give the sample a 3-min exposure.
7.6 Disodium Salt of 4-(2-pyridylazo)-Resorcinol Dihydrate
(PAR·2H O) (Reagent C) —Dissolve 25.0 6 0.1 mg of PAR in 8.1.2.1 Caution—Ultraviolet light can be harmful to the
eyes. A protective shield has been provided in the prototype kit.
750 mL of water in a 1-L volumetric flask. Add 10.0 6 0.1 mL
of concentrated NH OH. Dilute to the mark with water. Store DO NOT remove it or otherwise defeat its purpose. DO NOT
stare at the light.
this in brown bottles out of direct sunlight or in the dark.
8.1.3 After exposure, remove and uncap the vial. Measure
NOTE 5—Caution: Low results are obtained if the monosodium or
10.0 mL of ammonium nitrate solution (Reagent B) into the
unsalted PAR is used in this test. Field experience has shown that the PAR
10-mL graduated cylinder. Add this to the vial containing the
reagent can deteriorate within two to six months. The PAR reagent should
sample. Recap and shake the vial vigorously for 1 min. (The
be tested by adding the reagent to a test tube and determining the percent
transmittance. If the percent transmittance is less than 80 %, the reagent
timer in the kit may be used.)
should be discarded.
8.1.4 Place a clean 18-mm test tube in the aluminum
measuring block. Add 5.0 mL of PAR solution (Reagent C) to
7.7 Gasoline, Lead-Free—Gasoline containing less than
the test tube using the mark on the block such that the upper
0.05 g Pb/gal (13.0 mg Pb/L). (Danger: Extremely flammable.
level of liquid in the tube is equal to the mark on the block.
Harmful if inhaled. Vapors may cause flash fire. See Annex
Place the plastic funnel in the test tube. Fol
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.