ASTM C1326-08e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of Advanced Ceramics
Standard Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of Advanced Ceramics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
For advanced ceramics, Knoop indenters are used to create indentations. The surface projection of the long diagonal is measured with optical microscopes.
The Knoop indentation hardness is one of many properties that is used to characterize advanced ceramics. Attempts have been made to relate Knoop indentation hardness to other hardness scales, but no generally accepted methods are available. Such conversions are limited in scope and should be used with caution, except for special cases where a reliable basis for the conversion has been obtained by comparison tests.
For advanced ceramics, the Knoop indentation is often preferred to the Vickers indentation since the Knoop long diagonal length is 2.8 times longer than the Vickers diagonal for the same load, and cracking is much less of a problem (1). On the other hand, the long slender tip of the Knoop indentation is more difficult to precisely discern, especially in materials with low contrast. The indentation loads chosen in this test method are designed to produce indentations as large as may be possible with conventional microhardness equipment, yet not so large as to cause cracking.
The Knoop indentation is shallower than Vickers indentations made at the same load. Knoop indents may be useful in evaluating coating hardnesses.
Knoop hardness is calculated from the ratio of the applied load divided by the projected indentation area on the specimen surface. It is assumed that the elastic springback of the narrow diagonal is negligible. (Vickers indenters are also used to measure hardness, but Vickers hardness is calculated from the ratio of applied load to the area of contact of the four faces of the undeformed indenter.)
A full hardness characterization includes measurements over a broad range of indentation loads. Knoop hardness of ceramics usually decreases with increasing indentation size or indentation force (load). The trend is known as the indentation size effect (ISE). Hardness approaches a pla...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Knoop indentation hardness of advanced ceramics.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: C1326 − 08
StandardTest Method for
1
Knoop Indentation Hardness of Advanced Ceramics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1326; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Added research report footnote to Section 14.6.1 editorially in September 2008.
1. Scope 2.2 European Standard:
CENENV843-4AdvancedTechnicalCeramics,Monolithic
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Knoop
Ceramics, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature,
indentation hardness of advanced ceramics.
Part 4: Vickers, Knoop, and Rockwell Superficial Hard-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 3
ness Tests
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
2.3 ISO Standard:
standard.
ISO9385 Glass and Glass Ceramics—Knoop Hardness
4
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Test
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3. Terminology
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1 Definitions:
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
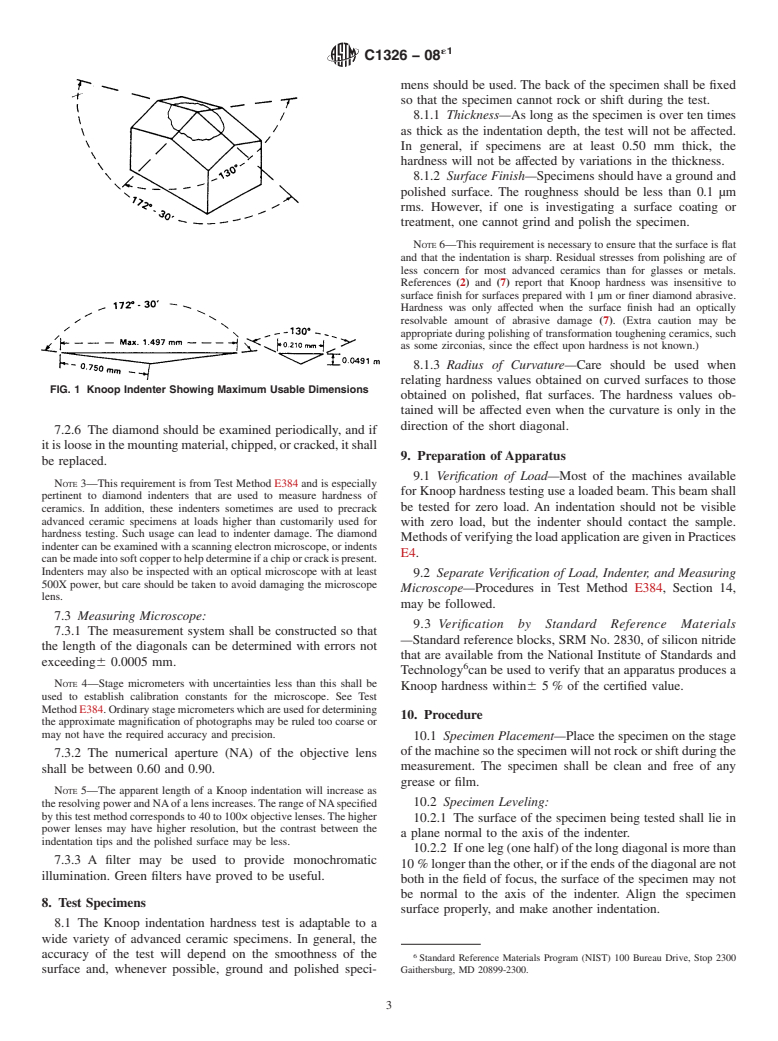
3.1.1 Knoop hardness number (HK), n—an expression of
hardness obtained by dividing the force applied to the Knoop
2. Referenced Documents
indenter by the projected area of the permanent impression
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
made by the indenter.
C730Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of Glass
3.1.2 Knoop indenter, n—a rhombic-based pyramidal-
C849Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of Ce-
shaped diamond indenter with edge angles of 172° 30' and
ramic Whitewares
130° 00'.
E4Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
4. Summary of Test Method
ASTM Test Methods
4.1 This test method describes an indentation hardness test
E384Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of
using a calibrated machine to force a pointed, rhombic base,
Materials
pyramidal diamond indenter having specified face angles,
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
under a predetermined load, into the surface of the material
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
under test and measures the surface projection of the long
IEEE/ASTMSI10Standard for Use of the International
diagonal of the resulting impression after removal of the load.
System of Units (SI) (The Modern Metric System)
NOTE 1—Ageneral description of the Knoop indentation hardness test
is given in Test Method E384. The present test method differs from this
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C28 on
description only in areas required by the special nature of advanced
Advanced Ceramics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C28.01 on
ceramics.
Mechanical Properties and Performance.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as C1326–03. DOI:
3
10.1520/C1326-08E01. Available from European Committee for Standardization (CEN), 36 rue de
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Stassart, B-1050, Brussels, Belgium, http://www.cenorm.be.
4
contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://
the ASTM website. www.iso.ch.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
C1326 − 08
NOTE 2—This test method is similar to Test Methods C730 and C849,
occurs,willcausetiny,rathertightcracksattheindentationtips
but differs primarily in the choice of load and the rate of loading. In
in advanced ceramics. Such cracks will have a negligible
addition, the length correction factor for the resolution limits of optical
interference on measurements of the long diagonal length (2)
microscopes is not utilized.
(unlike Vickers indentations in ceramics).
5. Significance and Use
6.2 Cracking or spalling from the sides of the Knoop
5.1 For advanced ceramics, Knoop indenters are used to impression may also occur, possibly in a time-dependent
createindentations.Thesurfaceprojectionofthelongdiagonal
manner (minutes or hours) after the impression is made. Small
is measured with optical microscopes. amounts of such lateral cracking have little or no influence
upon measured hardness, provided t
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:C 1326–03 Designation:C 1326–08
Standard Test Method for
1
Knoop Indentation Hardness of Advanced Ceramics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1326; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Added research report footnote to Section 14.6.1 editorially in September 2008.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Knoop indentation hardness of advanced ceramics.
1.2This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C 730 Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of Glass
C 849 Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of Ceramic Whitewares
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E 177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods E380Practice for Use of the International
System of Units (SI) (the Modernized Met-
ric System)
E 384 Test Method for Microhindentation Hardness of Materials
E 691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method Practice for Conducting
an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI) (The Modern Metric System)
2.2 European Standard:
CEN ENV 843-4 Advanced Technical Ceramics, Monolithic Ceramics, Mechanical Properties at Room Temperature, Part 4:
3
Vickers, Knoop, and Rockwell Superficial Hardness Tests
2.3 ISO Standard:
4
ISO 9385 Glass and Glass Ceramics—Knoop Hardness Test
3. Terminology
3.1 Definition:
3.1.1 Knoop hardness number (HK), n—an expression of hardness obtained by dividing the force applied to the Knoop indenter
by the projected area of the permanent impression made by the indenter.
3.1.2 Knoop indenter, n—a rhombic-based pyramidal-shaped diamond indenter with edge angles of 172° 308 and 130° 008.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C28 on Advanced Ceramics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C28.01 on Mechanical
Properties and Performance.
Current edition approved Oct.Aug. 1, 2003.2008. Published November 2003.September 2008. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 19992003
as C1326–99.C 1326 – 03.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from European Committee for Standardization, Brussels, Belgium.
3
Available from European Committee for Standardization (CEN), 36 rue de Stassart, B-1050, Brussels, Belgium, http://www.cenorm.be.
4
Available from International Standards Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
4
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.ch.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
C 1326–08
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This test method describes an indentation hardness test using a calibrated machine to force a pointed, rhombic base,
pyramidal diamond indenter having specified face angles, under a predetermined load, into the surface of the material under test
and measures the surface projection of the long diagonal of the resulting impression after removal of the load.
NOTE 1—A general description of the Knoop indentation hardness test is given in Test Method E 384. The present test method differs from this
description only in areas required by the spe
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.