ASTM F812/F812M-97
(Specification)Standard Specification for Surface Discontinuities of Nuts, Inch and Metric Series
Standard Specification for Surface Discontinuities of Nuts, Inch and Metric Series
SCOPE
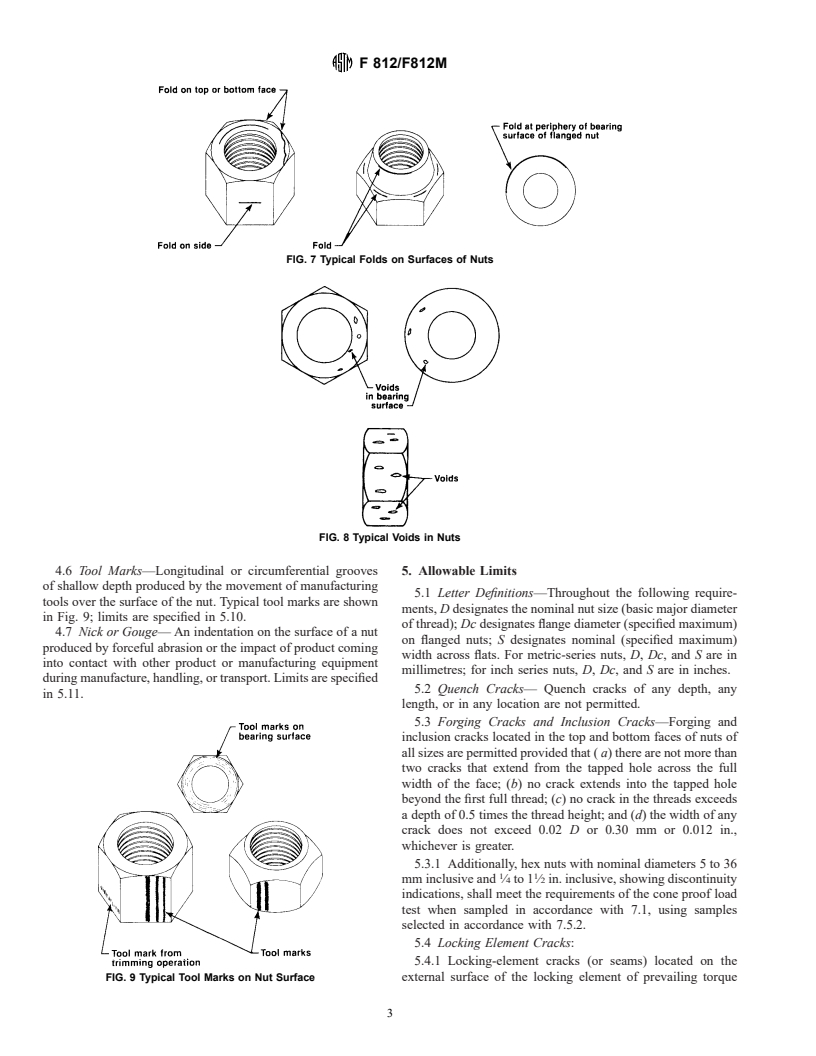
1.1 This specification establishes allowable limits for the various types of surface discontinuities that may occur during the manufacture and processing of metric-series nuts with nominal diameters 5 mm and larger and inch-series nuts with nominal diameters 1/4 in. and larger.
1.2 The values stated in either SI (metric) or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 When the engineering requirements of the application necessitate control of surface discontinuities on nuts, the purchaser shall specify conformance to this ASTM specification in the original inquiry and purchase order.
1.3.1 When the engineering requirements of the application necessitate that surface discontinuities on nuts be controlled within limits closer than those specified in this specification, the purchaser shall specify the applicable limits in the original inquiry and purchase order.
1.4 The allowable limits established in this specification for metric nuts, with nominal diameters 5 to 24 mm inclusive, are essentially identical with requirements given in ISO/DIS 6157/II. There are no ISO standards for surface discontinuities on metric-series nuts with nominal diameters larger than 24 mm or on any inch-series nuts.
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 6, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 812/F812M – 97
Standard Specification for
1
Surface Discontinuities of Nuts, Inch and Metric Series
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 812/F812M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
2
1. Scope Washers, and Rivets
2.2 ISO Standard:
1.1 This specification establishes allowable limits for the
ISO/DIS 6157/II Fasteners, Surface Discontinuities on
various types of surface discontinuities that may occur during
3
Nuts
the manufacture and processing of metric-series nuts with
nominal diameters 5 mm and larger and inch-series nuts with
3. Ordering Information
1
nominal diameters ⁄4 in. and larger.
3.1 Orders for nuts requiring surface discontinuity control
1.2 The values stated in either SI (metric) or inch-pound
shall include:
units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values
3.1.1 ASTM designation and date of issue of this specifica-
stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each
tion.
system must be used independently of the other. Combining
3.1.2 Special requirements, for example, closer discontinu-
values from the two systems may result in nonconformance
ity limits (1.3.1) and inspection sampling plan (6.2).
with the specification.
1.3 When the engineering requirements of the application
4. Types of Surface Discontinuities
necessitate control of surface discontinuities on nuts, the
4.1 Crack—A clean (crystalline) fracture passing through or
purchaser shall specify conformance to this ASTM specifica-
across the grain boundaries and may possibly follow inclusions
tion in the original inquiry and purchase order.
of foreign elements. Cracks are normally caused by overstress-
1.3.1 When the engineering requirements of the application
ing the metal during forging or other forming operations, or
necessitate that surface discontinuities on nuts be controlled
during heat treatment. Where parts are subjected to significant
within limits closer than those specified in this specification,
reheating, cracks usually are discolored by scale.
the purchaser shall specify the applicable limits in the original
4.1.1 Quench Cracks— May occur due to excessively high
inquiry and purchase order.
thermal and transformation stresses during heat treatment.
1.4 The allowable limits established in this specification for
Quench cracks usually traverse an irregular and erratic course
metric nuts, with nominal diameters 5 to 24 mm inclusive, are
on the surface of the nut. Typical quench cracks are shown in
essentially identical with requirements given in ISO/DIS 6157/
Fig. 1; limits are specified in 5.2.
II. There are no ISO standards for surface discontinuities on
4.1.2 Forging Cracks— May occur during the cut-off or
metric-series nuts with nominal diameters larger than 24 mm or
forging operations and are located on the top and bottom face
on any inch-series nuts.
of the nut and at the intersection of the face and flat. Typical
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
forging cracks are shown in Fig. 2; limits are specified in 5.3.
test method portion, Section 6, of this specification: This
4.1.3 Inclusion Cracks— Normally caused by nonmetallic
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
inclusions or stringers inherent in the raw material. Typical
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
inclusion cracks are shown in Fig. 2; limits are specified in 5.3.
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
4.1.4 Locking-Element Cracks—Occur due to application of
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
pressure when forming the locking element of prevailing
tions prior to use.
torque-type nuts. Such cracks are usually located in the vicinity
2. Referenced Documents of the locking element and may be either on the internal or
external surface. Typical locking element cracks are shown in
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Fig. 3; limits are specified in 5.4.
F 606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Prop-
4.1.5 Washer-Retainer Cracks—Openings in the lip or hub
erties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners,
of metal used to retain a washer on a nut. Washer-retainer
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-16 on
Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.02 on Steel Bolts,
2
Nuts, Rivets, and Washers. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.08.
3
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1997. Published June 1998. Originally Available from American National Sta
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.