ASTM B467-09
(Specification)Standard Specification for Welded Copper-Nickel Pipe
Standard Specification for Welded Copper-Nickel Pipe
ABSTRACT
This specification covers welded copper-nickel alloy pipes produced from Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C70600 and C71500 for general engineering applications. Pipes may be produced in any one of the following tempers: as-welded from annealed sheets, strips, or plates (WM50); as-welded from cold-worked sheets, strips, or plates (WM00, WM01, WM02, and so forth); welded and annealed (WO50); welded, light cold drawn (WR00) or hard cold drawn (WR04), and stress relieved; or fully finished as annealed, light drawn (WH00) or hard drawn (WH04), and stress relieved. Products shall be sampled and prepared, then tested accordingly to examine their conformance to dimensional (outside diameter, specific and stock lengths, wall thickness, squareness of cut, and roundness), mechanical (tensile and yield strengths, and elongation), and chemical composition requirements. Specimens shall also undergo nondestructive tests such as radiographic examination, eddy-current test, and hydrostatic test.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
For purposes of determining compliance with the specified limits for requirements of the properties listed in the following table, and observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded as indicated in accordance with the rounding method of Practice E29.
PropertyRounded Unit for Observed or Calculated Value Chemical compositionnearest unit in the last right-hand place of figures of the specified limit Tensile strength
Yield strengthnearest ksi [nearest MPa up to 10 ksi, incl, nearest 5 MPa over 10 ksi] Elongationnearest 1 %
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for welded copper-nickel alloy pipe for general engineering purposes. The following alloys are covered:
Copper Alloy
UNS No. Type of Metal C7060090-10 copper-nickel C7062090-10 copper-nickel (Modified for Welding) C7150070-30 copper-nickel C7152070-30 copper-nickel (Modified for Welding)
1.2 Units—The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems could result in nonconformance with the specification.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B467 −09
StandardSpecification for
1
Welded Copper-Nickel Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B467; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
4
1. Scope* and Bronzes (Withdrawn 2002)
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for
4
CopperAlloys(PhotometricMethods)(Withdrawn2010)
welded copper-nickel alloy pipe for general engineering pur-
2 E243 PracticeforElectromagnetic(Eddy-Current)Examina-
poses. The following alloys are covered:
tion of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes
Copper Alloy Type of Metal
E478 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of CopperAlloys
2
UNS No.
2.2 Other Documents:
5
C70600 90-10 copper-nickel
American Welding Society Specification A5.6
C70620 90-10 copper-nickel
5
American Welding Society Specification A5.7
(Modified for Welding)
C71500 70-30 copper-nickel
C71520 70-30 copper-nickel
3. Terminology
(Modified for Welding)
3.1 For the definitions of terms related to copper and copper
1.2 Units—The values stated in either inch-pound units or
alloys, refer to Terminology B846.
SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the
text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in
4. Types of Welded Pipe
each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system
4.1 As-Welded—Pipe that has been welded with no further
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
workperformedotherthanstraighteningorcuttingtolength,or
from the two systems could result in nonconformance with the
both.
specification.
4.2 Welded and Annealed—Welded pipe that has been
2. Referenced Documents annealed to produce a uniform grain size appropriate to the
3 specified annealed temper.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and 4.3 Welded and Cold Drawn—Welded pipe with internal
Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing flash removed by scarfing, and subsequently cold drawn to
B601 ClassificationforTemperDesignationsforCopperand conform to the specified temper.
Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
4.4 Fully Finished—Welded pipe with internal and external
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
flash removed by scarfing and the pipe or tube subsequently
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
cold drawn over a mandrel and annealed as necessary to
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
conform to the specified temper.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
E54 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Special Brasses
5. Ordering Information
5.1 Include the following information when placing orders
for product under this specification, as applicable.
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
5.1.1 ASTM designation and year of issue,
and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe
5.1.2 Copper Alloy UNS No. (Section 1 and Table 1),
and Tube.
5.1.3 Temper (Section 8),
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009. Published November 2009. Originally
approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as B467 – 88 (2003).
5.1.4 Dimensions: diameter and wall thickness (12.2 and
DOI: 10.1520/B0467-09.
12.3),
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys is a simple expansion of the
5.1.5 Lengths: whether specific or stock (12.4),
former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of a prefix “C”
and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of
the base alloy.
3 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnual Book ofASTM www.astm.org.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd.,
the ASTM website. Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B467−09
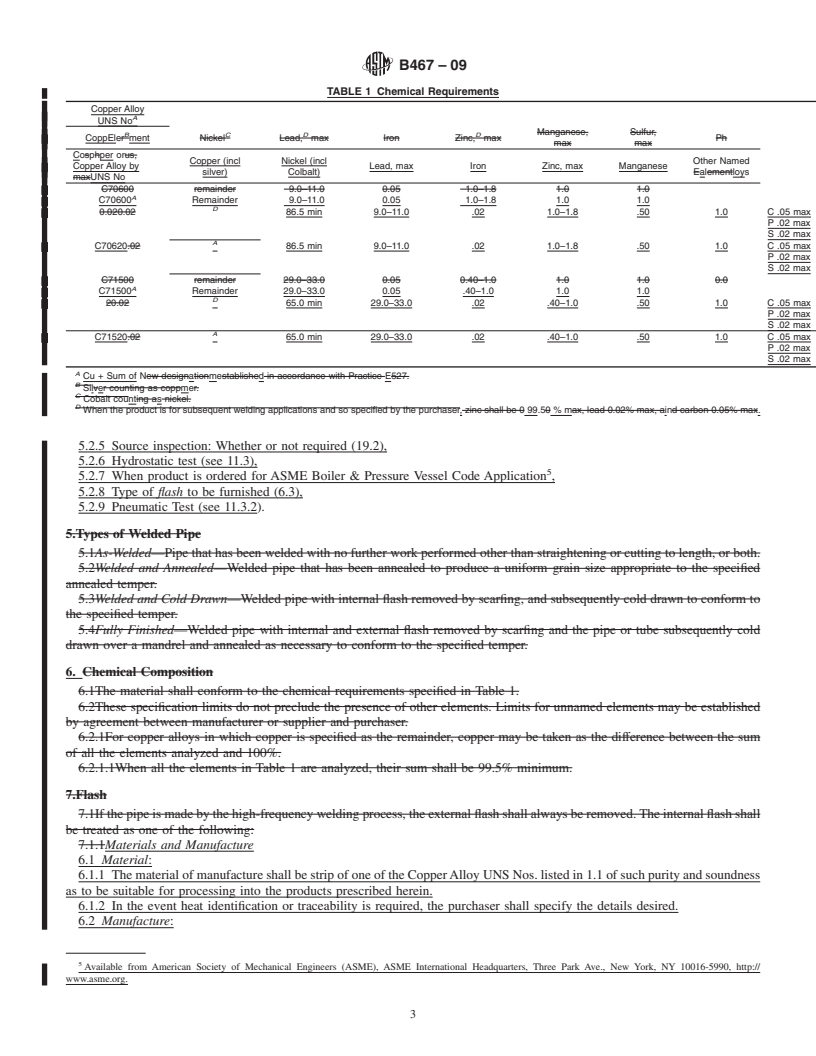
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Element
Copper or Copper
Copper (incl Nickel (incl Other Named
Alloy by Lead, max Iron Zinc, max Manganese
silver) Colbalt) alloys
UNS No
A
C70600 Remainder 9.0–11.0 0.05 1.0–1.8 1.0 1.0
A
C70620 86.5 min 9.0–11.0 .02 1.0–1.8 .50 1.0 C .05 max
P .02 max
S .02 max
A
C71500 Remainder 29.0–33.0 0.05 .40–1.0 1.0 1.0
A
C71520 65.0 min 29.0–33.0 .02 .40–1.0 .50 1.0 C .05 max
P .02 max
S .
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B467–88(Reapproved 2003) Designation: B467 – 09
Standard Specification for
1
Welded Copper-Nickel Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B467; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1This specification covers welded copper-nickel alloy pipe for general engineering purposes. The following alloys are
covered:*
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for welded copper-nickel alloy pipe for general engineering purposes. The
2
following alloys are covered:
Copper Alloy Nominal Composition, %
2
UNS No. Previously Copper
Used
Designation
Copper Type of Metal
C70600 706
C70620 90-10 copper-nickel
(Modified for Weld-
ing)
C71500 715
C71520 70-30 copper-nickel
(Modified for Weld-
ing)
1.2The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text,
the SI units are shown in brackets.The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems could result in nonconformance with the specification.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1The following documents of the issue in effect on date of material purchase form a part of this specification to the extent
referenced herein:
2.2
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B153 Test Method for Expansion (Pin Test) of Copper and Copper-Alloy Pipe and Tubing
B601
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper AlloysWrought and Cast
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.04 on Pipe and
Tube.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2003.2009. Published November 2003.2009. Originally approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved in 19972003 as B467 – 88
(1997).(2003). DOI: 10.1520/B0467-88R03.10.1520/B0467-09.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of a
prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B467 – 09
E75Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys 54 Test Methods for Chemical
Analysis of Special Brasses and Bronzes
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
E243 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy-Current) Examination of Copper and Copper-Alloy Tubes
E255Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for the Determination of Chemical Composition
E527Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
2.3 478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
2.2 Other Documents:
4
American Welding Society Specification A5.6
4
American Welding Society Specification A5.7
3. Terminology
3.1Definitions:
3.1.1welded pipe—product made from sheet, strip, or plate with a seam made by welding.
3.1.2flash or bead—weld metal that protrudes beyond the normal wall, both inside and outside.
3.1.3scarfing—the removing of flash or bead by a cutting operation.
3.2Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1capable of—as used in this specification, the test is not mandatory under the terms of this specification unless definitely
specifiedinthepurchaseorder;however,shouldsubsequenttestingbythepurchaserestablishthatthematerialdoesnotmeetthese
requirements, the material may be rejected.
3.1 For the definitions of terms related to c
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.