ASTM C1128-15
(Guide)Standard Guide for Preparation of Working Reference Materials for Use in Analysis of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Materials
Standard Guide for Preparation of Working Reference Materials for Use in Analysis of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
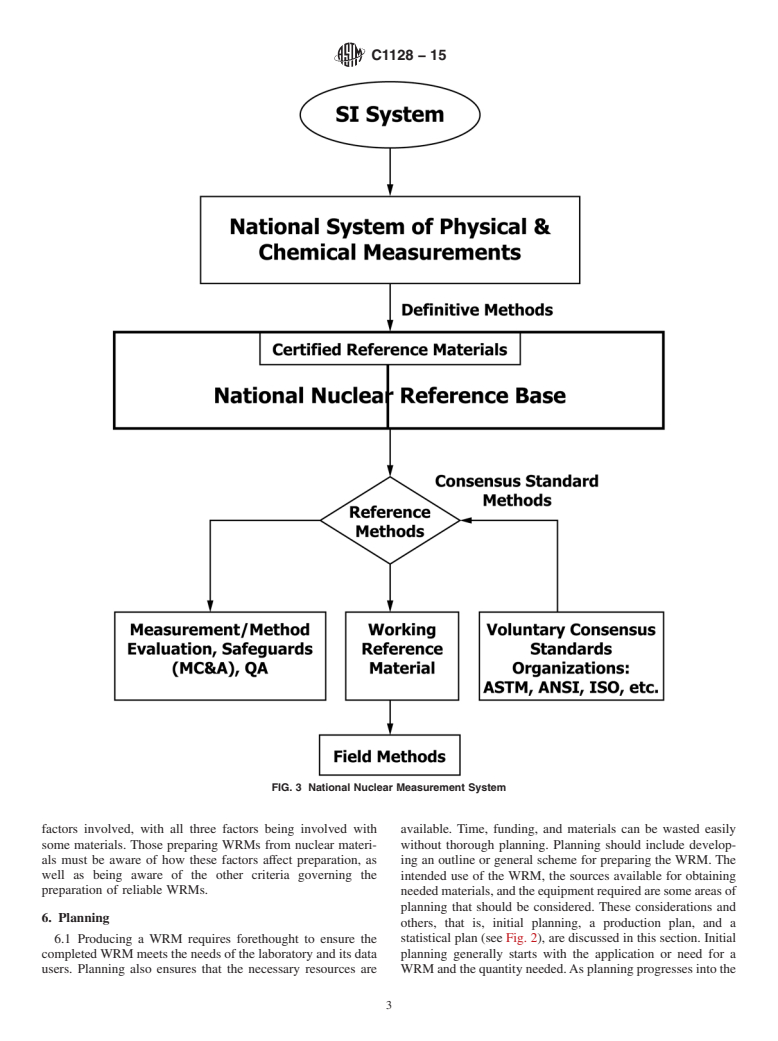
5.1 Certified reference materials (CRMs) prepared from nuclear materials are generally of high purity, possessing chemical stability or reproducible stoichiometry. Usually they are certified using the most unbiased and precise measurement methods available, often with more than one laboratory being involved in making certification measurements. CRMs are generally used on a national or international level, and they are at the top of the metrological hierarchy of reference materials. A graphical representation of a national nuclear measurement system is shown in Fig. 3.
5.2 Working reference materials (WRMs) need to have quality characteristics that are similar to CRMs, although the rigor used to achieve those characteristics is not usually as stringent as for CRMs. Similarly, producers of WRMs should comply with applicable requirements of ISO Guide 34, which are less stringent for WRMs than the requirements for producers of CRMs. Where possible, CRMs are often used to calibrate the methods used for establishing the concentration values (reference values) assigned to WRMs, thus providing traceability to CRMs as required by ISO/IEC 17025. A WRM is normally prepared for a specific application.
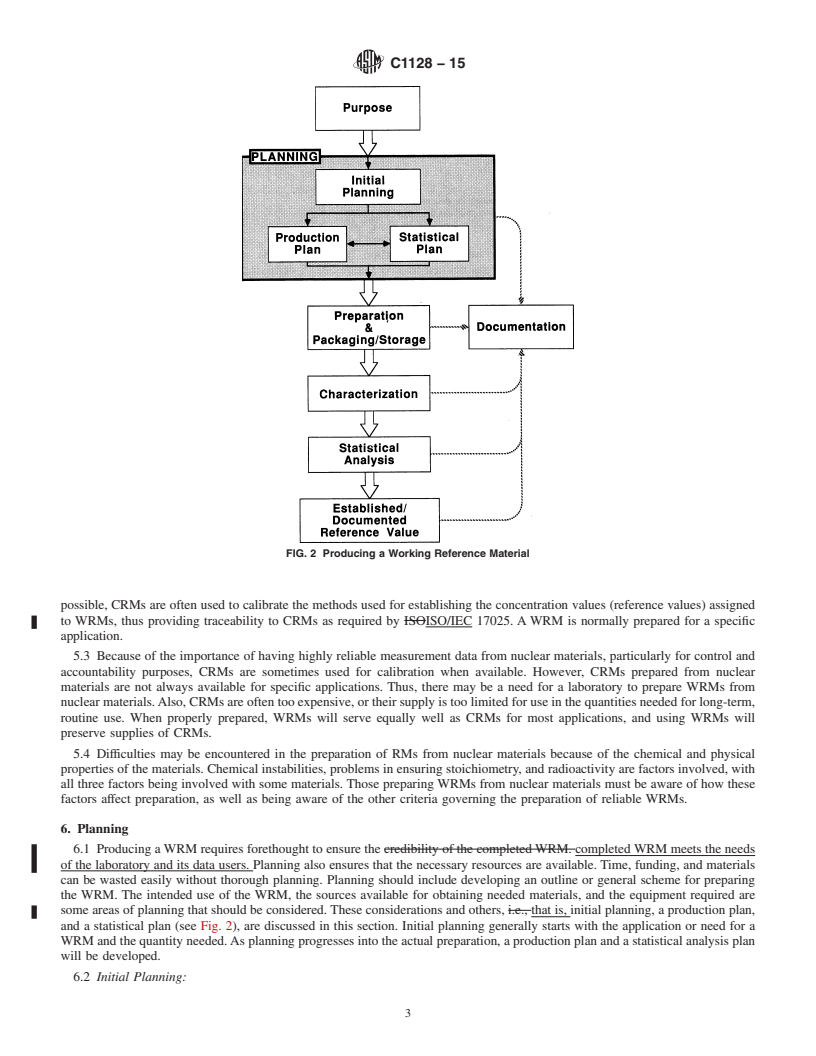
5.3 Because of the importance of having highly reliable measurement data from nuclear materials, particularly for control and accountability purposes, CRMs are sometimes used for calibration when available. However, CRMs prepared from nuclear materials are not always available for specific applications. Thus, there may be a need for a laboratory to prepare WRMs from nuclear materials. Also, CRMs are often too expensive, or their supply is too limited for use in the quantities needed for long-term, routine use. When properly prepared, WRMs will serve equally well as CRMs for most applications, and using WRMs will preserve supplies of CRMs.
5.4 Difficulties may be encountered in the preparation of RMs from nuclear materials because of the chemical and physical properties o...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers the preparation and characterization of working reference materials (WRM) that are produced by a laboratory for its own use in the analysis of nuclear fuel cycle materials. Guidance is provided for establishing traceability of WRMs to certified reference materials by a defined characterization process. The guidance provided is generic; it is not specific for a given material.
1.2 The information provided by this guide is found in the following sections:
Section
Planning
6
Preparation
7
Packaging and Storage
8
Characterization
9
Statistical Analysis
10
Documentation
11
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1128 − 15
Standard Guide for
Preparation of Working Reference Materials for Use in
1
Analysis of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1128; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope a Laboratory Within the Nuclear Industry
C1215Guide for Preparing and Interpreting Precision and
1.1 This guide covers the preparation and characterization
Bias Statements in Test Method Standards Used in the
of working reference materials (WRM) that are produced by a
Nuclear Industry
laboratoryforitsownuseinthedestructiveanalysisofnuclear
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
fuel cycle materials. Guidance is provided for establishing
ISO/IEC17025General Requirements for the Competence
traceability of WRMs to certified reference materials by a
3
of Calibration and Testing Laboratories
defined characterization process. The guidance provided is
ISO Guide30Terms and Definitions Used in Connection
generic; it is not specific for a given material.
3
with Reference Materials
1.2 The information provided by this guide is found in the
ISO Guide 34General Requirements for the Competence of
following sections:
Reference Material Producers
4
Section
2.3 Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology:
Planning 6
JCGM 100:2008Evaluation of Measurement Data—Guide
Preparation 7
Packaging and Storage 8
to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (ISO
Characterization 9
GUM 1995 with Minor Corrections (2008))
Statistical Analysis 10
JCGM 200:2008International Vocabulary of Metrology—
Documentation 11
Basic and General Concepts andAssociatedTerms (VIM)
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
(ISO/IEC Guide 99)
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
5
3. Terminology
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
6
3.1.1 certified reference material (CRM) —a reference ma-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
terial with one or more property values that are certified by a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
technically valid procedure, accompanied by or traceable to a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
certificate or other documentation that is issued by a certifying
body (as defined by ISO Guide30). A certifying body is a
2. Referenced Documents
technically competent body (organization or firm, public or
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
private) that issues a reference material certificate (as defined
C859Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
by ISO Guide30). A reference material certificate is a docu-
C1009Guide for Establishing and Maintaining a Quality
ment certifying one or more property values for a certified
AssuranceProgramforAnalyticalLaboratoriesWithinthe
reference material, stating that the necessary procedures have
Nuclear Industry
been carried out to establish their validity (as defined by ISO
C1068Guide for Qualification of Measurement Methods by
Guide30).
6
3.1.2 reference material (RM) —amaterialorsubstanceone
or more properties of which are sufficiently well established to
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel
Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.08 on Quality
Assurance, Statistical Applications, and Reference Materials.
3
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2015. Published February 2015. Originally Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as C1128–01 (2008). 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
DOI: 10.1520/C1128-15. AvailablefromBureauInternationaldesPoidsetMesures,PavillondeBreteuil,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or F-92312 Sèvres Cedex, France, www.bipm.org.
5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM See C859 for other terms specific to the nuclear fuel cycle.
6
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on It is important that a well defined uncertainty in the stated value(s) be given in
the ASTM website. the certificate.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1128 − 15
be used for the calibration of an apparatus, the assessment of a
measurement method, or assigning values to materials (as
defined by ISO Guide30). A reference material may be
referred to in this
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1128 − 01 (Reapproved 2008) C1128 − 15
Standard Guide for
Preparation of Working Reference Materials for Use in
1
Analysis of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1128; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide covers the preparation and characterization of working reference materials (WRM) that are produced by a
laboratory for its own use in the destructive analysis of nuclear fuel cycle materials. Guidance is provided for establishing
traceability of WRMs to certified reference materials by a defined characterization process. The guidance provided is generic; it
is not specific for a given material.
1.2 The information provided by this guide is found in the following sections:
Section
Planning 6
Preparation 7
Packaging and Storage 8
Characterization 9
Statistical Analysis 10
Documentation 11
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C859 Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
C1009 Guide for Establishing and Maintaining a Quality Assurance Program for Analytical Laboratories Within the Nuclear
Industry
C1068 Guide for Qualification of Measurement Methods by a Laboratory Within the Nuclear Industry
C1215 Guide for Preparing and Interpreting Precision and Bias Statements in Test Method Standards Used in the Nuclear
Industry
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement
3
ISO 17025ISO/IEC 17025 General Requirements for the Competence of Calibration and Testing Laboratories
3
ISO Guide 30 Terms and Definitions Used in Connection with Reference Materials
ISO Guide 34 General Requirements for the Competence of Reference Material Producers
4
2.3 Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology:
JCGM 100:2008 Evaluation of Measurement Data—Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (ISO GUM 1995
with Minor Corrections (2008))
JCGM 200:2008 International Vocabulary of Metrology—Basic and General Concepts and Associated Terms (VIM) (ISO/IEC
Guide 99)
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.08 on Quality Assurance,
Statistical Applications, and Reference Materials.
Current edition approved June 1, 2008Feb. 1, 2015. Published July 2008February 2015. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 20012008 as
C1128 – 01.C1128 – 01 (2008). DOI: 10.1520/C1128-01R08.10.1520/C1128-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
Available from Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, Pavillon de Breteuil, F-92312 Sèvres Cedex, France, www.bipm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1128 − 15
5
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
6
3.1.1 certified reference material (CRM) —a reference material with one or more property values that are certified by a
technically valid procedure, accompanied by or traceable to a certificate or other documentation that is issued by a certifying body
(as defined by ISO Guide 30). A certifying body is a technically competent body (organization or firm, public or private) that issues
a reference material certificate (as defined by ISO Guide 30). A reference material certificate is a document certifying one or more
property values for a certified reference material, stating that the necessary procedures have been carried out to establish their
validity (as defined by ISO Guide 30).
6
3.1.
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.