ASTM D1693-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Environmental Stress-Cracking of Ethylene Plastics
Standard Test Method for Environmental Stress-Cracking of Ethylene Plastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method may be used for routine inspection purposes by subjecting a required number of specimens to the test conditions for a specified time and noting the number that fail. The cracking obtained with the test reagent is indicative of what may be expected from a wide variety of surface-active agents, soaps, and organic substances that are not absorbed appreciably by the polymer.
Environmental stress-cracking is a property that is highly dependent upon the nature and level of the stresses applied and on the thermal history of the specimen (1). Under the conditions of the test method, high local multiaxial stresses are developed through the introduction of a controlled imperfection (2, 3). Environmental stress-cracking has been found to occur most readily under such conditions.
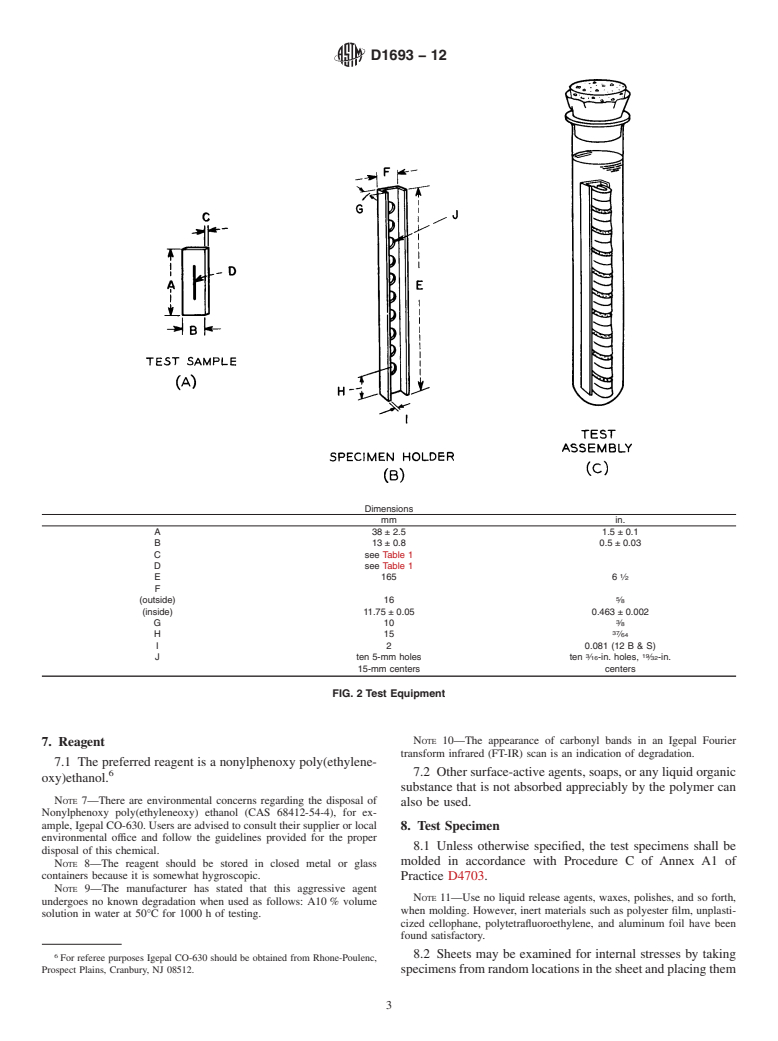
Note 2—Different types of polyethylene plastics as defined in Specification D1248 are generally tested under different levels of strain and stress. When it is expressly desired to compare the types at equal levels of strain, the specimens for all types should be tested under Condition B, Table 1 (4).
Information from this test method is not intended to be used for direct application to engineering problems.
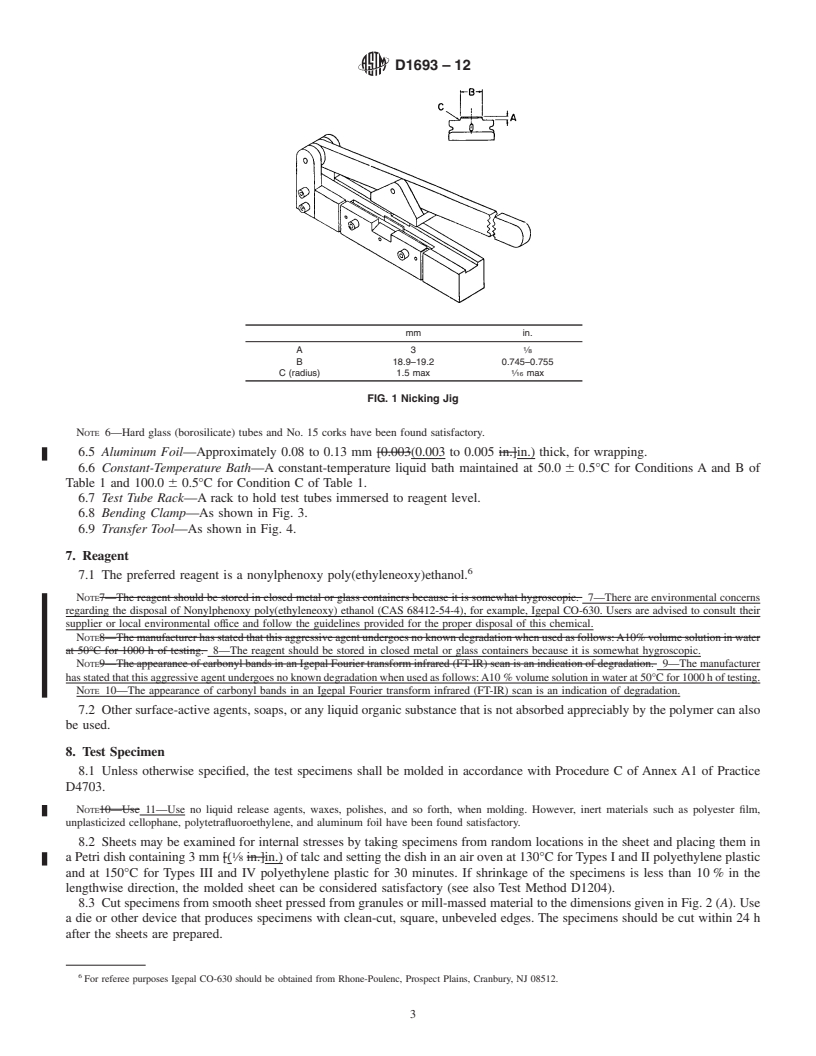
Note 3—Caution should be used in comparing and ranking various ethylene plastics into distinct and separate groups by this test method (see Section 13 and Note 12).
As thermal history is recognized as an important variable, test results by this test method employing laboratory molded samples cannot necessarily be expected to show agreement with test results from samples obtained by other means. The true performance potential of a given ethylene plastic may, however, best be determined with specimens obtained from commercially prepared items (5).
TABLE 1 Standard Test Conditions ConditionSpecimen ThicknessNotch DepthBath Temperature, °C mmAin.mmAin. ABmin3.000.1200.500.02050 max3.300.1300.650.025 BBmin1.840.07250.300.01250 max1.970.07750.400.015 CCmin1.840.07250...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the susceptibility of ethylene plastics, as defined in Terminology D883, to environmental stress-cracking when subjected to the conditions herein specified. Under certain conditions of stress and in the presence of environments such as soaps, wetting agents, oils, or detergents, ethylene plastics may exhibit mechanical failure by cracking.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—There is no known ISO equivalent for this standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1693 − 12
StandardTest Method for
1
Environmental Stress-Cracking of Ethylene Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1693; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the sus-
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
ceptibility of ethylene plastics, as defined in Terminology
3
Apparatus Drawings and Blueprints
D883, to environmental stress-cracking when subjected to the
conditions herein specified. Under certain conditions of stress
3. Terminology
and in the presence of environments such as soaps, wetting
agents, oils, or detergents, ethylene plastics may exhibit 3.1 Definitions:
mechanical failure by cracking.
3.1.1 stress-crack, n—an external or internal rupture in a
plastic caused by tensile stresses less than its short-time
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
mechanical strength.
standard.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—The development of such cracks is
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
frequently accelerated by the environment to which the plastic
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
is exposed. The stresses which cause cracking may be present
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
internally or externally, or may be a combination of these
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
stresses. The appearance of a network of fine cracks is called
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
crazing.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent for this standard.
3.1.2 stress-crack failure, n—for purposes of this test
method, any crack visible to an observer with normal eyesight
2. Referenced Documents
4
shall be interpreted as a failure of the entire specimen (1).
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Extension of the controlled imperfection shall not be construed
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
as a failure. The appearance of more than one crack in a single
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
specimen shall be construed as a single failure.
D1204 Test Method for Linear Dimensional Changes of
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Cracks generally develop at the con-
Nonrigid Thermoplastic Sheeting or Film at Elevated
trolled imperfection and run to the outer edge of the specimen
Temperature
approximately at right angles to it (2). The cracks need not
D1248 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Extrusion
extend completely through the specimen to constitute failure.
Materials for Wire and Cable
Cracks sometimes develop under the polymer surface, mani-
D3350 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Pipe and Fit-
festing themselves as depressions on the surface. The time
tings Materials
when this occurs should be noted, and if the depression later
D4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic
develops into a crack, the time of dimpling should be consid-
Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
ered as the failure time.
D4976 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Molding and
Extrusion Materials
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Bent specimens of the plastic, each having a controlled
1
imperfection on one surface, are exposed to the action of a
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materi-
surface-active agent. The proportion of the total number of
als.
specimens that crack in a given time is observed.
Current edition approved April 1, 2012. Published May 2012. Originally
approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D1693 - 08. DOI:
10.1520/D1693-12.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Detail drawings of the apparatus are available from ASTM Headquarters.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Request ADJD169301,ADJD169302,ADJD169303, and ADJD169304.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
the ASTM website. this test method.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1693 − 12
TABLE 1 Standard Test Conditions
Specimen
Notch Depth
Bath Temperatur
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D1693–08 Designation:D1693–12
Standard Test Method for
1
Environmental Stress-Cracking of Ethylene Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1693; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the susceptibility of ethylene plastics, as defined in Terminology D883, to
environmental stress-cracking when subjected to the conditions herein specified. Under certain conditions of stress and in the
presence of environments such as soaps, wetting agents, oils, or detergents, ethylene plastics may exhibit mechanical failure by
cracking.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard. 1—There is no known ISO equivalent for this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1204 Test Method for Linear Dimensional Changes of Nonrigid Thermoplastic Sheeting or Film at Elevated Temperature
D1248 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Extrusion Materials for Wire and Cable
D3350 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Pipe and Fittings Materials
D4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
D4976 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Molding and Extrusion Materials
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
3
Apparatus Drawings and Blueprints
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 stress-crack, n—an external or internal rupture in a plastic caused by tensile stresses less than its short-time mechanical
strength.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—The development of such cracks is frequently accelerated by the environment to which the plastic is
exposed.The stresses which cause cracking may be present internally or externally, or may be a combination of these stresses.The
appearance of a network of fine cracks is called crazing.
3.1.2 stress-crack failure, n—for purposes of this test method, any crack visible to an observer with normal eyesight shall be
4
interpreted as a failure of the entire specimen (1). Extension of the controlled imperfection shall not be construed as a failure.The
appearance of more than one crack in a single specimen shall be construed as a single failure.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Cracks generally develop at the controlled imperfection and run to the outer edge of the specimen
approximately at right angles to it (2). The cracks need not extend completely through the specimen to constitute failure. Cracks
sometimes develop under the polymer surface, manifesting themselves as depressions on the surface. The time when this occurs
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Materials.
Current edition approved MarchApril 1, 2008.2012. Published March 2008.May 2012. Originally approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 20072008 as
D1693-07a.D1693 - 08. DOI: 10.1520/D1693-08.10.1520/D1693-12.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Detail drawings of the apparatus are available from ASTM Headquarters. Request ADJD169301, ADJD169302, ADJD169303, and ADJD169304.
4
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of this test method.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1693–12
should be noted, and if the depression later develops into a crack, the time o
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.