ASTM E2029-11(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Volumetric and Mass Flow Rate Measurement in a Duct Using Tracer Gas Dilution
Standard Test Method for Volumetric and Mass Flow Rate Measurement in a Duct Using Tracer Gas Dilution
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The method presented here is a field method that may be used to determine mass and volume flow rates in ducts where flow conditions may be irregular and nonuniform. The gas flowing in the duct is considered to be an ideal gas. The method may be especially useful in those locations where conventional pitot tube or thermal anemometer velocity measurements are difficult or inappropriate due either to very low average flow velocity or the lack of a suitable run of duct upstream and downstream of the measurement location.
5.2 This test method can produce the volumetric flow rate at standard conditions without the need to determine gas stream composition, temperature, and water vapor content.
5.3 This test method is useful for determining mass or volumetric flow rates in HVAC ducts, fume hoods, vent stacks, and mine tunnels, as well as in performing model studies of pollution control devices.
5.4 This test method is based on first principles (conservation of mass) and does not require engineering assumptions.
5.5 This test method does not require the measurement of the area of the duct or stack.
5.6 The test method does not require flow straightening.
5.7 The test method is independent of flow conditions, such as angle, swirl, turbulence, reversals, and hence, does not require flow straightening.
5.8 The dry volumetric airflow can be determined by drying the air samples without measuring the water vapor concentration.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the measurement of the volumetric and mass flow rate of a gas stream within a duct, stack, pipe, mine tunnel, or flue using a tracer gas dilution technique. For editorial convenience all references in the text will be to a duct, but it should be understood that this could refer equally well to a stack, pipe, mine tunnel, or flue. This test method is limited to those applications where the gas stream and the tracer gas can be treated as ideal gases at the conditions of the measurement. In this test method, the gas stream will be referred as air, though it could be any another gas that exhibits ideal gas law behavior.
1.2 This test method is not restricted to any particular tracer gas although experimental experience has shown that certain gases are used more readily than others as suitable tracer gases. It is preferable that the tracer gas not be a natural component of the gas stream.
1.3 Use of this test method requires a knowledge of the principles of gas analysis and instrumentation. Correct use of the formulas presented here requires consistent use of units.
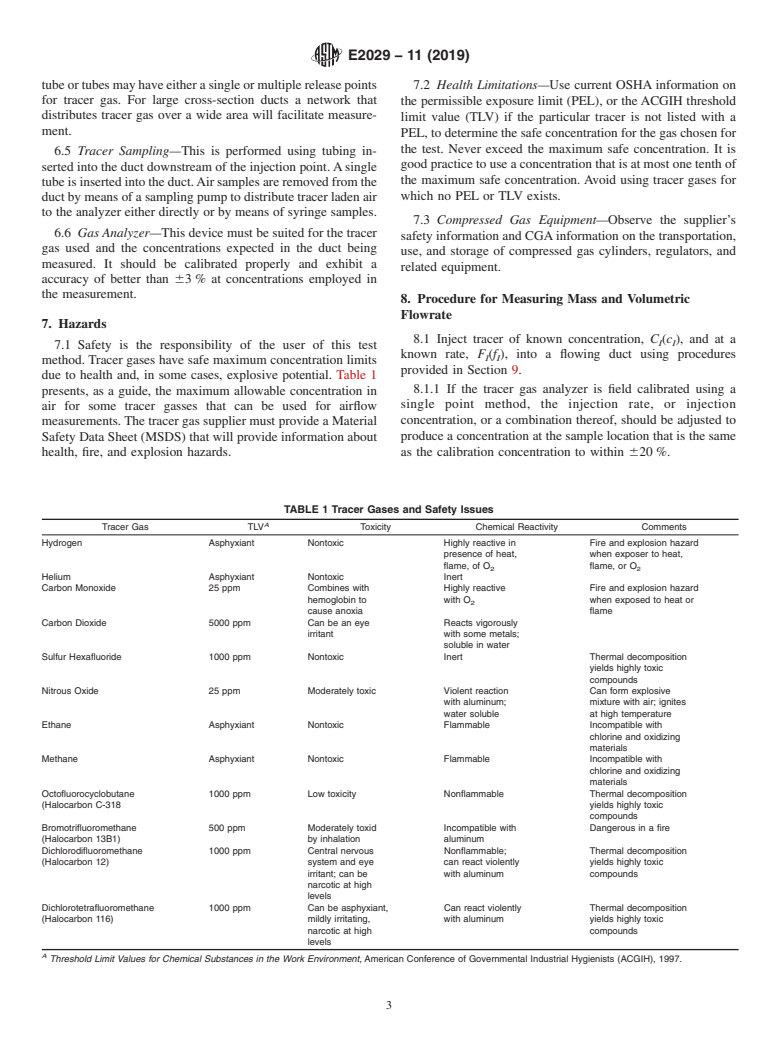
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see Section 7.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2029 − 11 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Volumetric and Mass Flow Rate Measurement in a Duct
1
Using Tracer Gas Dilution
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2029; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standard:
1.1 This test method describes the measurement of the
E631Terminology of Building Constructions
volumetric and mass flow rate of a gas stream within a duct,
3
2.2 ANSI/ASME Standard:
stack, pipe, mine tunnel, or flue using a tracer gas dilution
ANSI/ASMETC19.1–1985(1994) Measurement Uncer-
technique. For editorial convenience all references in the text
tainty: Instrument Apparatus
will be to a duct, but it should be understood that this could
referequallywelltoastack,pipe,minetunnel,orflue.Thistest
3. Terminology
method is limited to those applications where the gas stream
3.1 Definitions:
andthetracergascanbetreatedasidealgasesattheconditions
3.1.1 For definitions of general terms related to building
of the measurement. In this test method, the gas stream will be
construction used in this test method, refer to Terminology
referred as air, though it could be any another gas that exhibits
E631.
ideal gas law behavior.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 Thistestmethodisnotrestrictedtoanyparticulartracer 3.2.1 ideal gas, n—a gas or gas mixture for which the ratio
of the pressure divided by product of the density and tempera-
gas although experimental experience has shown that certain
ture is a constant.
gasesareusedmorereadilythanothersassuitabletracergases.
It is preferable that the tracer gas not be a natural component
3.2.2 mass flow, n—the total mass of air passing the sam-
of the gas stream.
pling point per unit time (kg/s, lb/min).
3.2.3 tracer gas, n—a gas that can be mixed with air and
1.3 Use of this test method requires a knowledge of the
measured in very low concentrations.
principles of gas analysis and instrumentation. Correct use of
3.2.4 tracer gas analyzer, n—a device that measures the
the formulas presented here requires consistent use of units.
concentration of tracer gas in an air sample.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.5 tracer gas mass concentration, n—the ratio of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mass of tracer gas in air to the total mass of the air-tracer
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
mixture. For an ideal gas, the mass concentration is indepen-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and to
dent of temperature and pressure.
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
3.2.6 tracer gas molar concentration, n—the ratio of the
use. For specific precautionary statements, see Section 7.
number of moles of tracer gas in air to the total number of
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
moles of the air-tracer mixture.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2.7 tracer gas volume concentration, n—the ratio of the
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
volume of tracer gas in air to the total volume of the air-tracer
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mixture. For an ideal gas, the volume concentration is inde-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
pendent of temperature and pressure and is equal to the molar
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
concentration.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.41 contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
on Air Leakage and Ventilation Performance. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved April 15, 2019. Published April 2019. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as E2029–11. DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/E2029–11R19. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2029 − 11 (2019)
3.2.8 volumetric flow,
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.