ASTM F3172-15(2021)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Design Verification Device Size and Sample Size Selection for Endovascular Devices
Standard Guide for Design Verification Device Size and Sample Size Selection for Endovascular Devices
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The purpose of this guide is to provide guidance for selecting appropriate device size(s) and determining appropriate sample size(s) for design verification of endovascular devices. The device size(s) and sample size(s) for each design input requirement should be determined before testing. The device size(s) selected for verification testing should establish that the entire device matrix is able to achieve the design input requirements. If testing is not performed on all device sizes, justification should be provided.
4.2 The sample size justification and statistical procedures used to analyze the data should be based on sound scientific principles and should be suitable for reaching a justifiable conclusion. Insufficient sample size may lead to erroneous conclusions more often than desired.
4.3 Guidance regarding methodologies for determining device size selection and appropriate sample size is provided in Sections 5 and 6.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides guidance for selecting an appropriate device size(s) and determining an appropriate sample size(s) (that is, number of samples) for design verification testing of endovascular devices. A methodology is presented to determine which device size(s) should be selected for testing to verify the device design adequately for each design input requirement (that is, test characteristic). Additionally, different statistical approaches are presented and discussed to help guide the developer to determine and justify sample size(s) for the design input requirement being verified. Alternate methodologies for determining device size selection and sample size selection may be acceptable for design verification.
1.2 This guide applies to physical design verification testing. This guide addresses in-vitro testing; in-vivo/animal studies are outside the scope of this guide. This guide does not directly address design validation; however, the methodologies presented may be applicable to in-vitro design validation testing. Guidance for sampling related to computational simulation (for example, sensitivity analysis and tolerance analysis) is not provided. Guidance for using models, such as design of experiments (DOE), for design verification testing is not provided. This guide does not address sampling across multiple manufacturing lots as this is typically done as process validation. Special considerations are to be given to certain tests such as fatigue (see Practice E739) and shelf-life testing (see Section 8).
1.3 Regulatory guidance may exist for endovascular devices that should be considered for design verification device size and sample size selection.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F3172 −15 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Guide for
Design Verification Device Size and Sample Size Selection
1
for Endovascular Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3172; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1 This guide provides guidance for selecting an appropri-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ate device size(s) and determining an appropriate sample
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
size(s) (that is, number of samples) for design verification
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
testing of endovascular devices.Amethodology is presented to
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
determinewhichdevicesize(s)shouldbeselectedfortestingto
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
verify the device design adequately for each design input
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
requirement (that is, test characteristic).Additionally, different
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
statisticalapproachesarepresentedanddiscussedtohelpguide
the developer to determine and justify sample size(s) for the
2. Referenced Documents
design input requirement being verified. Alternate methodolo-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
gies for determining device size selection and sample size
E739 PracticeforStatisticalAnalysisofLinearorLinearized
selection may be acceptable for design verification.
Stress-Life (S-N) and Strain-Life (ε-N) Fatigue Data
1.2 This guide applies to physical design verification test-
F2914 Guide for Identification of Shelf-life Test Attributes
ing. This guide addresses in-vitro testing; in-vivo/animal stud-
for Endovascular Devices
3
ies are outside the scope of this guide. This guide does not
2.2 ISO Standards:
directly address design validation; however, the methodologies
ISO 14971:2012 Medical devices—Application of risk man-
presented may be applicable to in-vitro design validation
agement to medical devices
testing. Guidance for sampling related to computational simu-
lation (for example, sensitivity analysis and tolerance analysis) 3. Terminology
is not provided. Guidance for using models, such as design of
3.1 Definitions:
experiments (DOE), for design verification testing is not
3.1.1 attribute data, n—data that identify the presence or
provided.Thisguidedoesnotaddresssamplingacrossmultiple
absenceofacharacteristic(forexample,good/badorpass/fail).
manufacturing lots as this is typically done as process valida-
3.1.2 design input requirements, n—physical and perfor-
tion.Specialconsiderationsaretobegiventocertaintestssuch
mance requirements of a device that are used as a basis for
asfatigue(seePracticeE739)andshelf-lifetesting(seeSection
device design (typically defined as test characteristics such as
8).
balloon burst pressure, shaft tensile strength, and so forth).
1.3 Regulatoryguidancemayexistforendovasculardevices
3.1.3 design output, n—features of the device (that is,
that should be considered for design verification device size
dimensions, materials, and so forth) that define the design and
and sample size selection.
make it capable of achieving design input requirements.
1.4 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
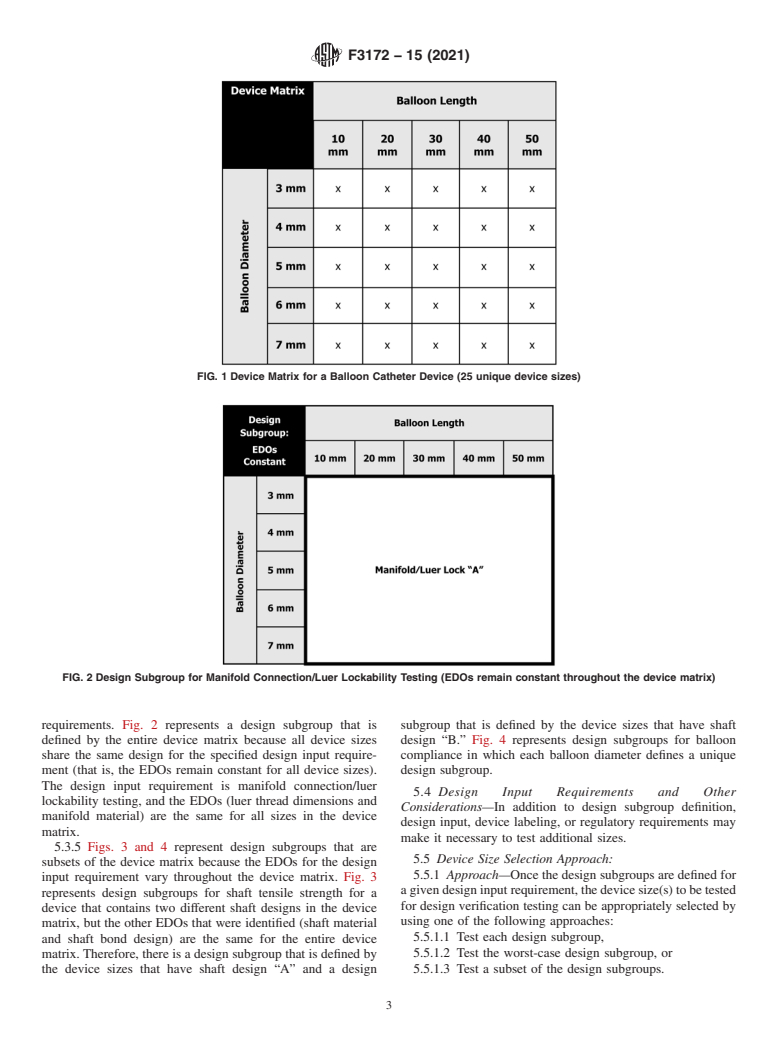
3.1.4 design subgroup, n—set defined by the device sizes
as the standard. No other units of measurement are included in
within the device matrix in which the essential design outputs
this standard.
do not vary for a specified design input requirement (that is,
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
device sizes that share the same design for a specified design
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
input requirement).
1 2
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
F04.30 on Cardiovascular Standards. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2021. Published August 2021. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2015. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as F3172
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.