ASTM B367-13
(Specification)Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Castings
Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Castings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the standard requirements for titanium and titanium alloy castings intended for general corrosion resistant and industrial applications. Materials for this specification shall be melted by conventional processes used for reactive metals such as consumable electrode and induction-slag, plasma arc, induction-skull, and electron beam melting processes. The materials shall undergo chemical, pour, and product analysis to determine the chemical composition which shall conform to the requirements for nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, iron, oxygen, aluminum, vanadium, tin, ruthenium, palladium, cobalt, molybdenum, chromium, nickel, niobium, zirconium, silicon, and titanium. All castings shall be supplied in the as-cast condition except when post-weld heat treatment is required wherein it shall consist of a stress relief performed at certain temperatures. The surface of the castings shall be free of adhering mold material, scale, cracks, and hot tears as determined by visual inspection.
SCOPE
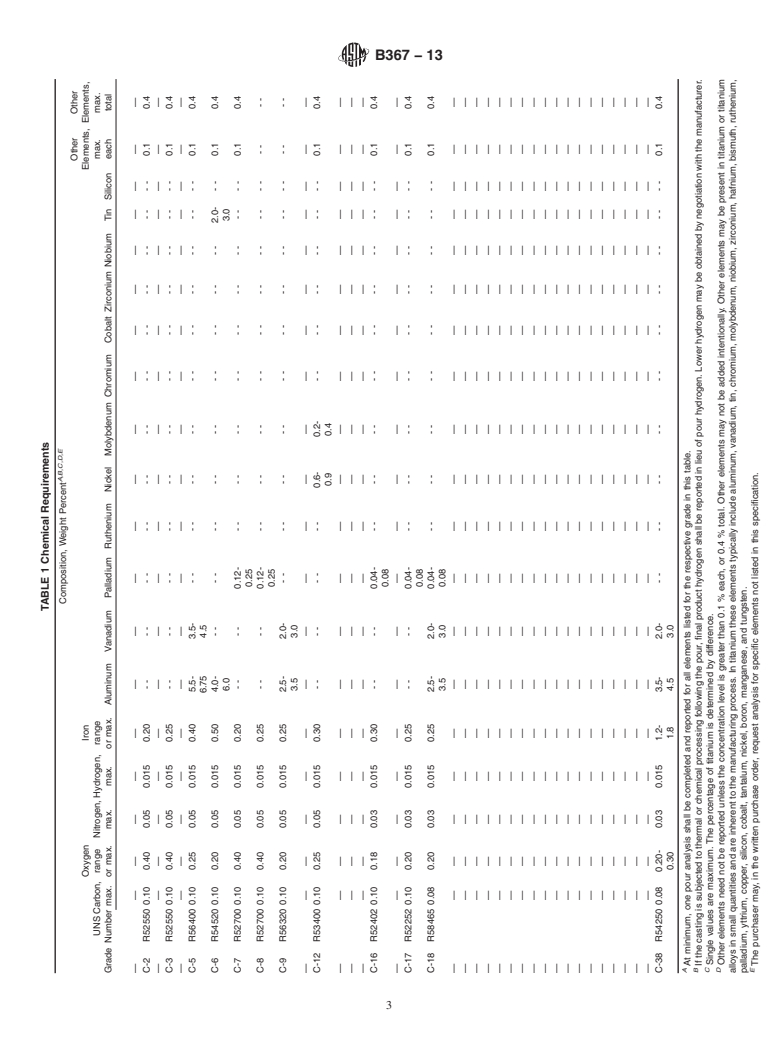
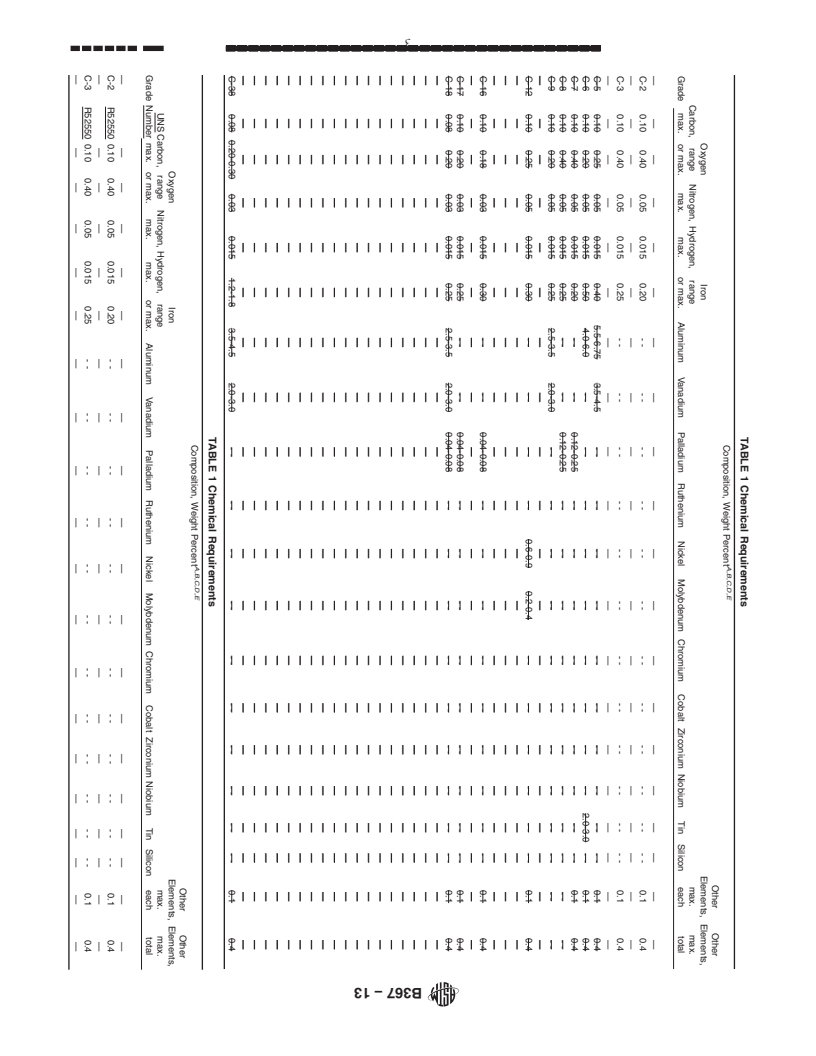
1.1 This specification covers titanium and titanium alloy castings intended for general corrosion resistant and industrial applications. as follows:
1.1.1 Grade C-2—UNS R52550. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.2 Grade C-3—UNS R52550. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.3 Grade C-5—UNS R56400. Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium),
1.1.4 Grade C-7—UNS R52700. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.5 Grade C-8—UNS R52700. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.6 Grade C-9—UNS R56320. Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium),
1.1.7 Grade C-12—UNS R53400. Titanium alloy (0.3 % molybdenum, 0.8 % nickel),
1.1.8 Grade C-16—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.9 Grade C-17—UNS R52252. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium, and
1.1.10 Grade C-38—UNS R54250. Titanium alloy (4 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium, 1.5 % iron).
1.2 This specification is intended for use of purchasers and/or producers of reactive metal castings for defining the requirements and assuring the properties of castings for unique corrosion-resistant applications, that is, not for commodity items which must meet all potential purchasers' requirements.
1.2.1 Users are advised to use the specification as a basis for obtaining castings which will meet minimum acceptance requirements established and revised by consensus of the members of the committee.
1.2.2 User requirements considered more stringent may be met by the addition to the purchase order of one or more supplementary requirements, which may include, but are not limited to, those listed in Sections S1 through S8.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B367 −13
Standard Specification for
1
Titanium and Titanium Alloy Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B367; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
1.1 This specification covers titanium and titanium alloy
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
castings intended for general corrosion resistant and industrial
and are not considered standard.
applications. as follows:
1.1.1 Grade C-2—UNS R52550. Unalloyed titanium,
2. Referenced Documents
1.1.2 Grade C-3—UNS R52550. Unalloyed titanium,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1.3 Grade C-5—UNS R56400. Titanium alloy (6 %
A802/A802M Practice for Steel Castings, Surface Accep-
aluminum, 4 % vanadium),
tance Standards, Visual Examination
1.1.4 Grade C-7—UNS R52700. Unalloyed titanium plus
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
1.1.5 Grade C-8—UNS R52700. Unalloyed titanium plus
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
terials
1.1.6 Grade C-9—UNS R56320. Titanium alloy (3 %
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium),
Determine Conformance with Specifications
1.1.7 Grade C-12—UNS R53400. Titanium alloy (0.3 %
E94 Guide for Radiographic Examination
molybdenum, 0.8 % nickel),
E142 Method for Controlling Quality of Radiographic Test-
1.1.8 Grade C-16—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium plus
3
ing (Withdrawn 2000)
0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
E165 Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General
1.1.9 Grade C-17—UNS R52252. Unalloyed titanium plus
Industry
0.04 to 0.08 % palladium, and
E446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in.
1.1.10 Grade C-38—UNS R54250. Titanium alloy (4 %
(50.8 mm) in Thickness
aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium, 1.5 % iron).
E539 TestMethodforAnalysisofTitaniumAlloysbyX-Ray
1.2 This specification is intended for use of purchasers
Fluorescence Spectrometry
and/or producers of reactive metal castings for defining the
E1409 Test Method for Determination of Oxygen and Nitro-
requirements and assuring the properties of castings for unique
gen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas
corrosion-resistant applications, that is, not for commodity
Fusion Technique
items which must meet all potential purchasers’ requirements.
E1447 Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen in Tita-
1.2.1 Usersareadvisedtousethespecificationasabasisfor
nium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion Thermal
obtaining castings which will meet minimum acceptance
Conductivity/Infrared Detection Method
requirements established and revised by consensus of the
E1941 Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refrac-
members of the committee.
tory and Reactive Metals andTheirAlloys by Combustion
1.2.2 User requirements considered more stringent may be
Analysis
met by the addition to the purchase order of one or more
E2371 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium and Titanium
supplementary requirements, which may include, but are not
Alloys by Direct Current Plasma and Inductively Coupled
limited to, those listed in Sections S1 through S8.
Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (Performance-
Based Test Methodology)
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee B10.01 on Titanium. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved July 1, 2013. Published August 2013. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 20098 as B367 – 09. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/B0367-13. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B367−13
E2626 Guide for Spectrometric Analysis of Reactive and 6.4 Sampling—Samples for chemical analysis may be made
Refractory Metals by the purchaser on a representative casting from any lot. Due
to the possibility
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B367 − 09 B367 − 13
Standard Specification for
1
Titanium and Titanium Alloy Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B367; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers titanium and titanium alloy castings intended for general corrosion resistant and industrial
applications. as follows:
1.1.1 Grade C-2—UNS R52550. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.2 Grade C-3—UNS R52550. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.3 Grade C-5—UNS R56400. Titanium alloy (6 % aluminum, 4 % vanadium),
1.1.4 Grade C-7—UNS R52700. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.5 Grade C-8—UNS R52700. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.6 Grade C-9—UNS R56320. Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium),
1.1.7 Grade C-12—UNS R53400. Titanium alloy (0.3 % molybdenum, 0.8 % nickel),
1.1.8 Grade C-16—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.9 Grade C-17—UNS R52252. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium, and
1.1.10 Grade C-38—UNS R54250. Titanium alloy (4 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium, 1.5 % iron).
1.2 This specification is intended for use of purchasers and/or producers of reactive metal castings for defining the requirements
and assuring the properties of castings for unique corrosion-resistant applications, that is, not for commodity items which must
meet all potential purchasers’ requirements.
1.2.1 Users are advised to use the specification as a basis for obtaining castings which will meet minimum acceptance
requirements established and revised by consensus of the members of the committee.
1.2.2 User requirements considered more stringent may be met by the addition to the purchase order of one or more
supplementary requirements, which may include, but are not limited to, those listed in Sections S1 through S8.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A802/A802M Practice for Steel Castings, Surface Acceptance Standards, Visual Examination
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E94 Guide for Radiographic Examination
3
E142 Method for Controlling Quality of Radiographic Testing (Withdrawn 2000)
E165 Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General Industry
E446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in. (50.8 mm) in Thickness
E539 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium Alloys by X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B10.01 on Titanium.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009July 1, 2013. Published June 2009August 2013. Originally approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 200820098 as
B367 – 08b.B367 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/B0367-09.10.1520/B0367-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B367 − 13
E1409 Test Method for Determination of Oxygen and Nitrogen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas Fusion
Technique
E1447 Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion Thermal
Conductivity/Infrared Detection Method
E1941 Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refractory and Reactive Metals and Their Alloys by Combustion Analysis
E2371 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.