ASTM D7011-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Trace Thiophene in Refined Benzene by Gas Chromatography and Sulfur Selective Detection
Standard Test Method for Determination of Trace Thiophene in Refined Benzene by Gas Chromatography and Sulfur Selective Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Accurate gas chromatographic determination of trace levels of thiophene in benzene involves special analytical problems because of the difficulties of trace level analysis. These problems arise from the low concentration levels that need to be measured, the type of column and detector needed for analysis, and the potential interference from the benzene matrix.
This test method was found applicable for determining thiophene in refined benzene conforming to the specifications described in Specifications D 2359, D 4734, and D 5871 and may be applicable toward other grades of benzene if the user has taken the necessary precautions as described in the text.
This test method was developed as an alternative technique to Test Methods D 1685 and D 4735.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of thiophene in refined benzene using gas chromatography and sulfur selective detection. The test method is applicable to the determination of thiophene at levels of 0.02 to 2 mg/kg thiophene in benzene.
1.2 In determining the conformance of the test results using this method to applicable specifications, results shall be rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D7011 – 04
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Trace Thiophene in Refined Benzene by
Gas Chromatography and Sulfur Selective Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7011; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Ma-
terials
1.1 This test method covers the determination of thiophene
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
in refined benzene using gas chromatography and sulfur
Determine Conformance with Specifications
selective detection. The test method is applicable to the
E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
determination of thiophene at levels of 0.02 to 2 mg/kg
Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
thiophene in benzene.
2.2 Other Document:
1.2 In determining the conformance of the test results using
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR, paragraphs 1910.1000 and
this method to applicable specifications, results shall be
1910.1200
rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of
Practice E29.
3. Summary of Test Methods
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1 The thiophene concentration in refined benzene is de-
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
termined at the sub-mg/kg to low mg/kg level using conven-
only.
tional gas chromatography with a sulfur selective detector. A
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
reproducible volume of sample is injected. Quantitative results
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
are obtained by the use of the external standard calibration
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
technique.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2 The method allows the use of a sulfur chemilumines-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
cence detector, atomic emission detector, pulsed flame photo-
statements, see Section 7.
metric detector, or any other sulfur selective detector provided
2. Referenced Documents that its performance meets requirements as set forth in 5.4.As
sulfur compounds elute from the gas chromatographic column,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
they are detected and quantified. While the benzene molecule
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
does not contain any sulfur atoms, the possibility of matrix
D1685 Test Method for Traces of Thiophene in Benzene by
quenching and interference is a concern, especially for
Spectrophotometry
thiophene determination at levels less than about 0.5 mg/kg.
D2359 Specification for Refined Benzene-535
The column and conditions specified in Table 1 yield accept-
D3437 Practice for Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic
able results with minimal matrix quenching and interference.
Products
Employing the column and conditions listed in Table 1 is not a
D4734 Specification for Refined Benzene-545
requirement to meet the needs of all users. For example, there
D4735 Test Method for Determination of Trace Thiophene
is less concern of quenching and interference encountered with
in Refined Benzene by Gas Chromatography
thiopheneconcentrationlevelsgreaterthan0.5mg/kg.Usersof
D5871 Specification for Benzene for Cyclohexane Feed-
flame photometric detectors should refer to Test Method
stock
D4735.
D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Accurate gas chromatographic determination of trace
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
levels of thiophene in benzene involves special analytical
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D16.04 on Instrumental Analysis. problems because of the difficulties of trace level analysis.
Current edition approved July 1, 2004. Published July 2004. DOI: 10.1520/
These problems arise from the low concentration levels that
D7011-04.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
the ASTM website. 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D7011 – 04
TABLE 1 Typical Chromatographic Conditions
water, oxygen, hydrocarbons, and sulfur contaminants. Gases
Column 30 m length, 0.32 mm internal diameter, 1 µm thick film, shall be regulated to ensure a constant carrier gas flow rate.
cross-linked polyethylene glycol (wax-type)
5.6.2 Detector Gases—Hydrogen and air are required as
Oven Temperature 40°C for 2 min; ramp to 100°C at 10°C/min, hold at
detector gases (99.995+ % purity). Additionally, oxygen
100°C for 1 min
Flow Rate 2 mL/min (99.8+ %) may be substituted for air. These gases shall be free
Split Ratio 1:4 to 1:10
of interfering contaminants, especially sulfur compounds.
Injection Temperature 125°C
5.6.3 Carrier and Detector Gas Control— Constant flow
Injection Volume 1-2 µL
control of carrier and detector gases is critical to optimum and
consistent analytical performance. Control is best provided by
the use of pressure regulators and fixed flow restrictions or
need to be measured, the type of column and detector needed
mass flow controllers capable of maintaining gas flow constant
for analysis, and the potential interference from the benzene
to 61 % at the required flow rates. The gas flow rate is
matrix.
measuredbyanyappropriatemeans.Thesupplypressureofthe
4.2 This test method was found applicable for determining
gas delivered to the gas chromatograph shall be at least 70 kPa
thiophene in refined benzene conforming to the specifications
(10 psig) greater than the regulated gas at the instrument to
described in Specifications D2359, D4734, and D5871 and
compensate for the system back pressure of the flow control-
may be applicable toward other grades of benzene if the user
lers. In general, a supply pressure of 550 kPa (80 psig) is
has taken the necessary precautions as described in the text.
satisfactory.
4.3 This test method was developed as an alternative tech-
5.7 Microsyringes—10, 50, 100, and 250 µL capacity
nique to Test Methods D1685 and D4735.
(61 % accuracy).
5.8 Volumetric Pipettes—0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mL capacity
5. Apparatus
(Class A).
5.1 Gas Chromatograph—The gas chromatograph shall be
5.9 Volumetric Flasks—10, 50, 100, and 500 mL capacity
capable of producing retention times for thiophene repeatable
(class A).
to within 0.05 min. The gas chromatograph shall be equipped
5.10 Separatory Funnel—1 L capacity.
with an appropriate sulfur selective detector, column for
separation, and sample inlet system for repeatable injection of
6. Reagents and Materials
sample volume.
6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
5.2 Column—Specifications and conditions described in
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
Table 1 have been judged satisfactory for this analysis.The use
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
of any column that permits separation and determination of
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
thiophene in benzene at levels consistent with the scope of this
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
method is allowed. Specific chromatographic results and con-
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
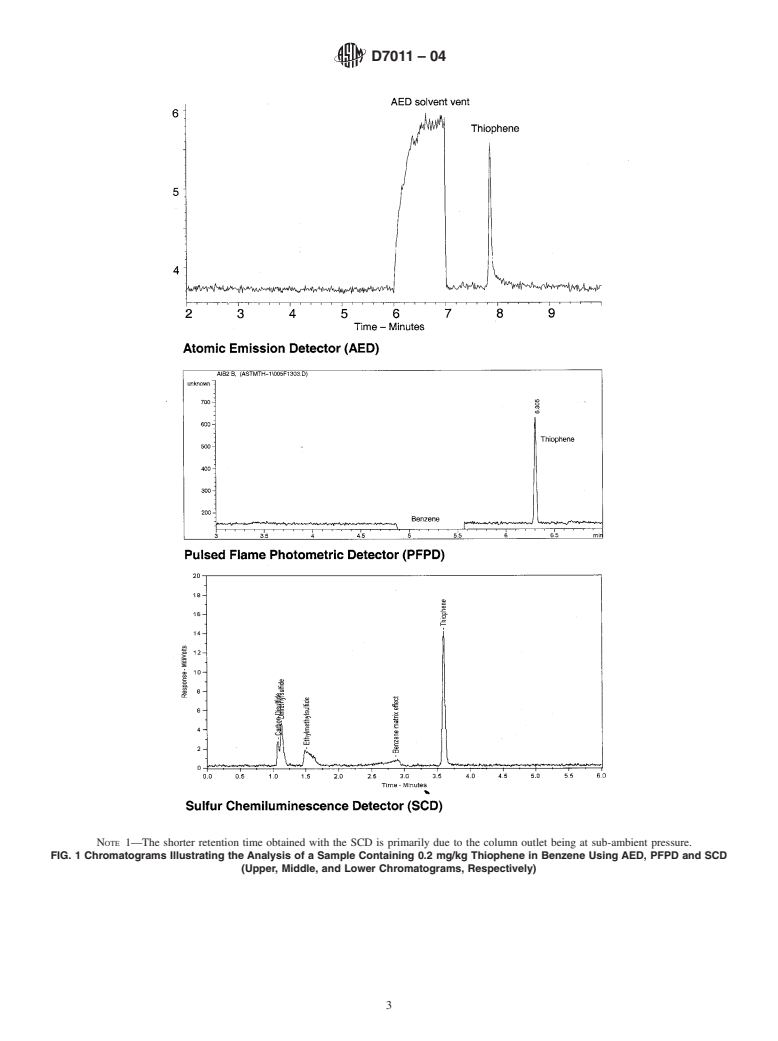
ditions are illustrated in Fig. 1. The user is referred to Practice
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
E1510 for information on installation of fused silica capillary
accuracy of the determination.
columns.
6.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, reference
5.3 Sample Inlet System—The sample inlet system shall be
towatershallbeunderstoodtomeanreagentwaterconforming
able to quantitatively transfer the sample to the analytical
to Type IV of Specification D1193.
column. It shall be capable of introducing constant and
6.3 Benzene, Thiophene-free:
repeatablevolumesofsampleandcalibrationstandards.Useof
6.3.1 In a fume hood, wash 700 mL of benzene in a 1000
a liquid autosampler or liquid sampling valve is permitted for
mL separatory funnel to which has been added 5 mL of isatin
the analysis of thiophene in benzene.
solution, with successive 100 mL portions of concentrated
5.4 Detector—A sulfur selective detector is used and shall
sulfuric acid until the acid layer is light yellow to colorless.
meet or exceed the following specifications: (1) linearity or
Wash the benzene with 100 mL of water, then twice with 100
compensated linearity of at least 10 , (2) minimum detectable
mL of cadmium chloride solution (CdCl ). Finally wash with
level of less than 0.02 mg/kg thiophene in benzene, (3)
another 100 mLportion of water and filter the benzene through
selectivity of sulfur to carbon greater than 10 , and (4) absence
medium filter paper into a storage bottle, stopper the bottle
of quenching that affect results under the conditions used for
tightly and save for future use.
the analysis.
6.3.2 Alternatively, thiophene-free benzene can be pur-
5.5 DataHandlingSystem—Useofanelectronicintegrating
chased commercially and used within this method, if its
device or computer is necessary. The device shall have the
thiophene level meets the criteria within 10.4.
following capabilities: (1) graphic presentation of the chro-
matogram, (2) digital display of chromatographic peak areas,
(3)identificationofpeaksbyretentiontime,and (4)calculation
and use of response factors.
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
5.6 Gases:
listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
5.6.1 Carrier Gases—Helium or nitrogen of high purity
Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
(99.995+ %). Additional purification is recommended by the
and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
use of molecular sieves or other suitable agents to remove MD.
D7011 – 04
NOTE 1—The shorter retention time obtained with the SCD is primarily due to the column outlet being at sub-ambient pressure.
FIG. 1 Chromatograms Illustrating the Analysis of a Sample Containing 0.2 mg/kg Thiophene in Benzene Using AED, PFPD and SCD
(Upper, Middle, and Lower Chromatograms, Respectively)
D7011 – 04
6.4 Cadmium Chloride Solution (20 g/L)—Dissolve 20 g of sulfur compounds. The most likely cause of error in this
anhydrous cadmium chloride (CdCl ) into 200 mL of water method is presence of thiophene in matrix blanks (see 10.4).
and dilute to 1 L.
9.2 Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mounting the
6.5 Chloroform—Reagent grade or better.
column into the gas chromatograph and adjusting the instru-
6.6 Isatin Solution—Add 0.5 g of isatin to 200 mL of
ment to typical conditions as described in Table 1. General
chloroform. Heat under a fume hood to a temperature just
guidelines for the installation of capillary columns can be
below the boiling point of chloroform (61°C) and maintain for
found in Practice E1510.
5 min with stirring. Filter the hot solution through hardened
9.3 The gas chromatograph and detector should be placed
rapid-filter paper into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilute to
intoserviceinaccordancewiththemanufacturer’sinstructions.
volume with chloroform.
6.7 Stock Solutions—Commercially prepared stock solution
10. Calibration
of thiophene in benzene are available for use as calibration
10.1 A manual or electronic calibration curve shall be
standards or for preparation of calibration standards.
prepared for the method of analysis. In some instances, for
6.8 Sulfuric Acid—Concentrated H SO .
2 4
example when compliance with a certain specification is
6.9 Thiophene—Available from commercial sources for
determined, it is sufficient to use a single point calibration
preparation of calibration standards, minimum 99 % purity.
according to user needs.
10.2 Prepare a stock solution of thiophene in benzene at the
7. Hazards
100 mg/kg level by adding 0.1000 g of thiophene to 1000 g of
7.1 Benzene is listed as a known carcinogen and is consid-
thiophene-free benzene. Record actual measurements to 4
ered a hazardous material. Consult current OSHA regulations
significant figures.
and suppliers’ Material Safety Data Sheets for all materials
10.3 Prepare calibration blends covering the range of deter-
used in this method.
mination of thiophene in benzene. For example, use a microsy-
7.2 Helium and nitrogen are compressed gases under high
ringe or volumetric pipette to dispense appropriate amounts of
pressure and can cause asphyxiation.
the stock solution into a volumetric flask containing thiophene-
7.3 Hydrogen is an extremely flammable gas under high
free benzene to prepare calibration blends containing nomi-
pressure.
nally 0.02, 0.2, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg thiophene in benzene.
7.4 Compressed air and oxygen are gases under high pres-
sure and they support combustion. 10.4 Inject 1-2 µL of each solution and benzene blank into
7.5 Sulfur compounds are generally flammable, toxic, and the chromatograph. Integrate the area under the thiophene
produce noxious odors, and therefore shall be handled with peak. Each standard solution and the blank should be analyzed
appropriate precautions for safety. in duplicate. The data collected will be used for generation of
7.6 Isatin is a toxic, cancer causing agent. the calibration curve (see 10.1). The benzene blank should
7.7 Chloroform is flammable, toxic and is a carcinogen. contain less than 0.02 mg/kg thiophene. Higher levels warrant
7.8 Cadmium chloride is a highly toxic cancer causing thiophene removal by 6.3.
agent.
10.5 Quality Check—A quality assurance check should be
used to determine if the analysis is in control. If out of control,
8. Sample Handling
the cause shall be determined and corrective action taken to
bring the analysis into control. The volume of the calibration
8.1 Collect the samples in accordance with Practice D3437.
blends injected for calibration shall be exactly the same as the
8.2 To preserve sample integrity and prevent the loss of
sample volume injected for analysis.
volatile compounds that may be in some samples, collect
samples wi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.